A deadly fungus is killing frogs, but the bacteria on their skin could protect them
2021-02-03
(Press-News.org) Researchers in Costa Rica have found that some bacteria on the skin of amphibians prevent growth of the fungus responsible for what has been dubbed 'the amphibian apocalypse'.
Published in the journal Microbiology, the research identified a number of bacteria which could growth of the fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis (Bd). One particularly dangerous strain of the fungus, called BdGPL-2, is responsible for mass amphibian die-offs around the world.
The fungus infects the skin of amphibians, breaking down the cells. As amphibians breathe and regulate water through their skin, infection is often deadly. It is believed that almost 700 species of amphibian are vulnerable to the fungus, and Bd has led to the extinction of 90 amphibian species.
In order to investigate why some amphibian populations in Costa Rica were more resilient to Bd that others, a research group led by Dr Adrian Pinto, Professor at the University of Costa Rica sampled the circulating strains of Bd and the skin microbiome of amphibians at different sites.
To do this, the research group collected wild amphibians from areas of Costa Rica which had a history of Bd outbreaks. "Bd has previously been widely detected in Costa Rica, but this is the first study to isolate and compare the characteristics of different isolates," said Dr Pinto, "our work showed that the circulating strains of the pathogenic fungus belong to a highly virulent global strain known as BdGPL-2."
They found that the bacteria on the skin of some surviving amphibians prevented growth of the fungus in the lab. "Amphibian species that survived decline harbor bacteria on their skin capable of inhibiting the growth of the pathogen. However, this inhibitory capacity varies according to which strain of the fungus is being tested," said Dr Pinto. "These findings suggest that locally adapted skin bacteria may offer protection from the disease."
Although the researchers expected to see the highly virulent strain BdGPL-2 in Costa Rica, they did not expect to see so much variation in circulating strains. "We were surprised of the phenotypic variations among the pathogen isolates, including their different responses to the antagonistic bacteria," said Dr Pinto. "Local pathogen adaptations must be considered when designing mitigation strategies for this disease."
Dr Pinto hopes to combine their findings with other disease control strategies to protect amphibian populations from decimation by Bd: "We will further study the ability of skin bacteria to protect amphibians against disease, as another tool to combat this plague alongside the creation of climate shelters and fostering the amphibians' own immune system," he said.
Costa Rica is one of the countries that suffered a dramatic loss of amphibian species between the 1980 and 1990. In Costa Rica, there are currently 64 species of amphibians in some risk category according to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature. Species classified as critically endangered include the Holdridge's Toad (Incilius holdridgei), a native species found only in the mountain ranges of the central region; The Variable Harlequin Frog (Atelopus varius), a river species very sensitive to Bd, and several species of river tree frogs of the genus Isthmohyla that live in cold currents in high areas, a habitat where Bd proliferates successfully.
Amphibians are one of the most diverse groups in the tropics and represent crucial links in food webs. Protecting them keeps ecosystems healthy since biological diversity is the basis for resilient forests, thus helping control pests and zoonotic infections.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-03
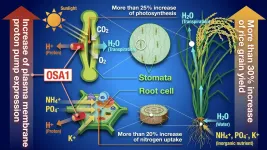
A group of scientists led by Drs Toshinori Kinoshita and Maoxing Zhang (Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules,Nagoya University, Japan) and Dr Yiyong Zhu (Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Solid Organic Waste Utilization, Nanjing Agricultural University, China) have developed a method which, by increasing the number of a plasma membrane proton pump gene in rice, simultaneously increases nutrient uptake through the roots and stomatal opening, thus increasing the yield of paddy field grown rice by over 30%.
In their previous research, the group had found that the plasma membrane proton pump played an important role in influencing stomatal opening. When they created a variant of rice with an overexpression of a particular plasma membrane proton pump gene, they found ...
2021-02-03
Modern-day robots are often required to interact with humans intelligently and efficiently, which can be enabled by providing them the ability to perceive touch. However, previous attempts at mimicking human skin have involved bulky and complex electronics, wiring, and a risk of damage. In a recent study, researchers from Japan sidestep these difficulties by constructing a 3D vision-guided artificial skin that enables tactile sensing with high performance, opening doors to innumerable applications in medicine, healthcare, and industry.
Robots have come a long way since their original inception for high-speed automation. Today, robots can be found in a wide variety of roles in medicine, rehabilitation, agriculture, and marine navigation. Since a ...
2021-02-03
Modern immunotherapeutic anti-cancer drugs support a natural mechanism of the immune system to inhibit the growth of cancer cells. They dock onto a specific receptor of the killer cell and prevent it from being switched off by the cancer cells. This is a complex molecular process, which is known but has not yet been fully understood. In a molecular dynamics study conducted by the group led by medical information scientist Wolfgang Schreiner and gynaecologists Heinz Kölbl and Georg Pfeiler from MedUni Vienna, working with biosimulation expert Chris Oostenbrink ...
2021-02-03
What are the reasons for such a contrast in outcomes? A scientist team led by the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) has now analysed the humoral innate immune defence of European greater mouse-eared bats to the fungus. In contrast to North American bats, European bats have sufficient baseline levels of key immune parameters and thus tolerate a certain level of infection throughout hibernation. The results are published in the journal "Developmental and Comparative Immunology".
During infections caused by Pseudogymnoascus destructans (Pd), North American bats arouse frequently from ...
2021-02-03
To date, research in the field of combinatorial catalysts has relied on serendipitous discoveries of catalyst combinations. Now, scientists from Japan have streamlined a protocol that combines random sampling, high-throughput experimentation, and data science to identify synergistic combinations of catalysts. With this breakthrough, the researchers hope to remove the limits placed on research by relying on chance discoveries and have their new protocol used more often in catalyst informatics.
Catalysts, or their combinations, are compounds that significantly lower the energy required to drive chemical reactions to completion. In the field of "combinatorial catalyst design," the requirement of synergy--where one component ...
2021-02-03
Life changes influence the amount of physical activity in a person, according to a recent study by the University of Jyväskylä. The birth of children and a change of residence, marital status and place of work all influence the number of steps of men and women in different ways. For women, having children, getting a job and moving from town to the countryside reduce everyday exercise.
A study conducted by the Faculty of Sports & Health Sciences found that the birth of the first child significantly reduces the number of everyday steps in women. As children grow, women's aerobic steps, in turn, increase. Although the birth of children did not have a statistically significant effect on the number of steps in men, changes were also observed ...
2021-02-03
Use of waste heat contributes largely to sustainable energy supply. Scientists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and T?hoku University in Japan have now come much closer to their goal of converting waste heat into electrical power at small temperature differences. As reported in Joule, electrical power per footprint of thermomagnetic generators based on Heusler alloy films has been increased by a factor of 3.4. (DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.10.019)
Many technical processes only use part of the energy consumed. The remaining fraction leaves the system ...
2021-02-03
In the race to stop the spread of COVID-19, a three-layer cloth mask that fits well can effectively filter COVID particles, says a group of UBC researchers.
After testing several different mask styles and 41 types of fabrics, they found that a mask consisting of two layers of low-thread-count quilting cotton plus a three-ply dried baby wipe filter was as effective as a commercial non-surgical mask at stopping particles--and almost as breathable.
The cloth masks filtered out up to 80 per cent of 3-micron particles, and more than 90 per cent of 10-micron particles.
"We focused on particles larger than one micron because these are likely most important to COVID-19 transmission," explains researcher Dr. Steven Rogak, a professor of mechanical engineering who ...
2021-02-03
The genus Ficus (figs) and their agaonid pollinating fig wasps are a classic example of coevolution. It represents perhaps the most extreme and ancient (about 75 million years) obligate pollination mutualism known.
Previous studies have suggested that pollinator host-switching and hybridization existed in some fig taxa with genetic evidence based on relatively few genes. However, those cases were mainly treated as rare exceptions, and strict-sense coevolution was still treated as the dominate coevolution model for the codiversification of this "extreme" obligate pollination system with high species richness.
Together with colleagues from 11 institutions from home and abroad, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical ...
2021-02-03
Scientists at Scripps Research have clarified the workings of a mysterious protein called Gαo, which is one of the most abundant proteins in the brain and, when mutated, causes severe movement disorders.
The findings, which appear in Cell Reports, are an advance in the basic understanding of how the brain controls muscles and could lead to treatments for children born with Gαo-mutation movement disorders. Such conditions--known as GNAO1-related neurodevelopmental disorders--were discovered only in the past decade, and are thought to affect at least hundreds of children around the world. Children with the disease suffer from severe developmental ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A deadly fungus is killing frogs, but the bacteria on their skin could protect them