True identity of mysterious gamma-ray source revealed
2021-02-03
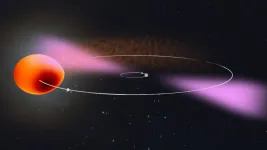
(Press-News.org) An international research team including members from The University of Manchester has shown that a rapidly rotating neutron star is at the core of a celestial object now known as PSR J2039?5617
The international collaboration used novel data analysis methods and the enormous computing power of the citizen science project Einstein@Home to track down the neutron star's faint gamma-ray pulsations in data from NASA's Fermi Space Telescope. Their results show that the pulsar is in orbit with a stellar companion about a sixth of the mass of our Sun. The pulsar is slowly but surely evaporating this star. The team also found that the companion's orbit varies slightly and unpredictably over time. Using their search method, they expect to find more such systems with Einstein@Home in the future.
Searching for the so-called 'Spider' pulsar systems - rapidly spinning neutron stars whose high-energy outflows are destroying their binary companion star, required 10 years of precise data. The pulsars have been given arachnid names of 'Black widows' or 'Redbacks', after species of spider where the females have been seen to kill the smaller males after mating.
New research published in, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, details how researchers found a neutron star rotating 377 times a second in an exotic binary system using data from NASA's Fermi Space Telescope.
The astronomer's findings were uniquely boosted by the Einstein@Home project, a network of thousands of civilian volunteers lending their home computing power to the efforts of the Fermi Telescope's work.
The group's search required combing very finely through the data in order not to miss any possible signals. The computing power required is enormous. The search would have taken 500 years to complete on a single computer core. By using a part of the Einstein@Home resources it was done in 2 months.
With the computing power donated by the Einstein@Home volunteers, the team discovered gamma-ray pulsations from the rapidly rotating neutron star. This gamma-ray pulsar, now known as J2039?5617, rotates about 377 times each second.
"It had been suspected for years that there is a pulsar, a rapidly rotating neutron star, at the heart of the source we now know as PSR J2039?5617," says Lars Nieder, a PhD student at the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute; AEI) in Hannover. "But it was only possible to lift the veil and discover the gamma-ray pulsations with the computing power donated by tens of thousands of volunteers to Einstein@Home," he adds.
The celestial object has been known since 2014 as a source of X-rays, gamma rays, and light. All evidence obtained so far pointed at a rapidly rotating neutron star in orbit with a light-weight star being at the heart of the source. But clear proof was missing.
The first step to solving this riddle were new observations of the stellar companion with optical telescopes. They provided precise knowledge about the binary system without which a gamma-ray pulsar search (even with Einstein@Home's huge computing power) would be unfeasible.
The system's brightness varies during an orbital period depending on which side of the neutron star's companion is facing the Earth. "For J2039-5617, there are two main processes at work," explains Dr. Colin Clark from Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics, lead author of the study. "The pulsar heats up one side of the light-weight companion, which appears brighter and more bluish. Additionally, the companion is distorted by the pulsar's gravitational pull causing the apparent size of the star to vary over the orbit. These observations allowed the team to get the most precise measurement possible of the binary star's 5.5-hour orbital period, as well as other properties of the system."
With this information and the precise sky position from Gaia data, the team used the aggregated computing power of the distributed volunteer computing project Einstein@Home for a new search of about 10 years of archival observations of NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. Improving on earlier methods they had developed for this purpose, they enlisted the help of tens of thousands of volunteers to search Fermi data for periodic pulsations in the gamma-ray photons registered by the Large Area Telescope onboard the space telescope. The volunteers donated idle compute cycles on their computers' CPUs and GPUs to Einstein@Home.
The new knowledge of the frequency of the gamma-ray pulsations also allowed collaborators to detect radio pulsations in archival data from the Parkes radio telescope. Their results, also published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, show that the pulsar's radio emission is often eclipsed by material that has been blown off the companion star by its nearby Redback pulsar.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-03
Consider for a moment a tree swaying in the wind. How long does it take for the movement of a twig to reach the trunk of the tree? How is this motion actually transmitted through the tree? Researchers at the University of Freiburg are transferring this kind of question to the analysis of proteins - which are the molecular machinery of cells. A team of researchers lead by Prof. Dr. Thorsten Hugel of the Institute of Physical Chemistry, and Dr. Steffen Wolf and Prof. Dr. Gerhard Stock of the Institute of Physics are investigating how the signals that cause structural changes in proteins travel from one site to another. They are also trying to ...
2021-02-03
Washington, DC / New Delhi, India - Researchers at CDDEP have released, The State of the World's Antibiotics in 2021, which presents extensive data on global antimicrobial use and resistance as well as drivers and correlates of antimicrobial resistance, based on CDDEP's extensive research and data collection through ResistanceMap, a global repository that has been widely used by researchers, policymakers, and the media.
Since the first State of the World's Antibiotics report in 2015, antimicrobial resistance has leveled off in some high-income countries but continues to rise in many low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where access to antibiotics has risen with increases in gross ...
2021-02-03
Researchers have found new evidence that global warming is affecting the size of commercial fish species, documenting for the first time that juvenile fish are getting bigger, as well as confirming that adult fish are getting smaller as sea temperatures rise. The findings are published in the British Ecological Society's Journal of Applied Ecology.
The researchers from the University of Aberdeen looked at four of the most important commercial fish species in the North Sea and the West of Scotland: cod, haddock, whiting and saithe. They found that juvenile fish in the North Sea and on the West of Scotland have been getting bigger while adult fish have been getting smaller. These changes ...
2021-02-03
The world's largest bird, the ostrich, has problems reproducing when the temperature deviates by 5 degrees or more from the ideal temperature of 20 °C. The research, from Lund University in Sweden, is published in Nature Communications.
The results show that the females lay up to 40 percent fewer eggs if the temperature has fluctuated in the days before laying eggs. Both male and female production of gametes is also negatively affected.
"Many believe that ostriches can reproduce anywhere, but they are actually very sensitive to changes in temperature. Climate change means that temperatures will fluctuate even more, and that could be a challenge for the ostrich", says Mads Schou, researcher at Lund ...
2021-02-03
Mothers are at increased risk of mental health problems as they struggle to balance the demands of childcare and remote working in COVID-19 lockdowns, according to new research from an international team of researchers.
The findings, published in the journal Psychological Medicine, were drawn from a comprehensive, online survey of mothers in China, Italy and the Netherlands.
Changes to their working lives, family strife and loss of social networks emerged as common factors affecting the mental health of mothers in all three countries.
The study was carried out by a team from Radboud University, ...
2021-02-03
Scientists from MIPT, Moscow Pedagogical State University and the University of Manchester have created a highly sensitive terahertz detector based on the effect of quantum-mechanical tunneling in graphene. The sensitivity of the device is already superior to commercially available analogs based on semiconductors and superconductors, which opens up prospects for applications of the graphene detector in wireless communications, security systems, radio astronomy, and medical diagnostics. The research results are published in a high-rank journal Nature Communications.
Information transfer in wireless networks is based on transformation of a high-frequency continuous electromagnetic wave into a discrete sequence of bits. This technique is known as signal modulation. ...
2021-02-03
People receiving treatment for cancer are known to feel better with physical training. But does it make any difference how vigorously they exercise? A new study by researchers at Uppsala University shows that whether the training is intensive or rather less strenuous, its effect is roughly the same. The results are published in the journal Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports.
Physical activity and training during cancer therapy improve physical and mental health, and may also reduce the most common side effects of the treatment. This has been confirmed in several international studies. Many patients suffer from cancer-related fatigue, and both resistance and endurance training are known to lessen fatigue. ...
2021-02-03
The IBeA research group from the University of the Basque Country's Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Technology, is participating in NASA's Mars2020 space mission, which is scheduled to touch down on Mars in February this year. Specifically, the group has participated in constructing and verifying the chemical homogeneity of the templates included on the calibration card of the SuperCam instrument mounted on the Perseverance. 'We made a set of pads perfectly characterised in accordance the instruments we have here, in order to enable us to verify that the LIBS and Raman spectroscopy measurements taken by the SuperCam are correct,' explains Doctor Cristina García-Florentino. 'Raman spectroscopy is a technique ...
2021-02-03
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound effect on higher education -- shifting classes online, canceling events, and putting financial strain on institutions.
One area of academia that has actually shown positive increases, however, is the submission of research papers. A study conducted by Michelle Bell, Mary E. Pinchot Professor of Environmental Health at the Yale School of the Environment (YSE), and postdoctoral associate Kelvin C. Fong found the rate of manuscript submission to a major peer-reviewed journal (American Journal of Public Health) were higher during the pandemic -- but also revealed ...
2021-02-03
In the wake of repeated school shootings across the United States, today's youth have been called the mass shooting generation. A new study examined public support for arming school employees. The study found consensus for arming school resource officers, but division over whether to arm teachers and nonteaching staff. The research has clear implications for policy, including the possibility that support for arming school staff may diminish over time as young people (who are less supportive) make up a larger share of voters.
The study was conducted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] True identity of mysterious gamma-ray source revealed