(Press-News.org) GROUND-BREAKING research from the University of Huddersfield, announced ahead of World Cancer Day 2021, proves that scalp cooling physically protects hair follicles from chemotherapy drugs. It is the world's first piece of biological evidence that explains how scalp cooling actually works and the mechanism behind its protection of the hair follicle.
The study, entitled 'Cooling-mediated protection from chemotherapy drug-induced cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes by inhibition of cellular drug uptake', has been published in the peer-reviewed journal PLOS ONE .
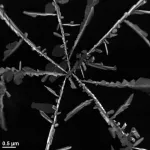
The data was part of an innovative hair follicle research project carried out by the dedicated Scalp Cooling Research Centre based at the University of Huddersfield. It involved the cultivation of cells isolated from human hair follicles in the lab.
The £1 million Scalp Cooling Research Centre was established at the University in 2019 with the backing of Huddersfield firm Paxman - global leaders in scalp cooling technology.
The team of experts in biology and design technology have been working together with the aim of Paxman becoming the only hair loss-preventing scalp cooling provider firmly based on biological research. It also brings the family-run business one step closer to achieving in its vision of 'zero hair loss' for cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment.
Chemotherapy works by targeting all rapidly dividing cells in the body. Hair is the second fastest dividing cell, and this is the reason why many chemotherapy drugs cause alopecia. The hair follicles in the growth phase are attacked, resulting in hair loss approximately two weeks after the commencement of chemotherapy treatment.
Co-director of the centre and lead author of the journal article is Dr Nik Georgopoulos, a cancer expert at the University's Department of Biological Sciences who has collaborated with Paxman since 2011.
"Scalp cooling is currently the only treatment to combat 'chemotherapy-induced alopecia', yet little is known about its cytoprotective effect on human hair follicles," said Dr Georgopoulos.
Before now, he explained, the most common and obvious presumption to describe how scalp cooling worked was that as the scalp is cooled, the veins become constricted thereby reducing the amount of blood flow, meaning less of the chemotherapy drug enters the hair follicle.
"However, this is a really exciting discovery because our research now shows it is not as simple as that. We were able to measure how much chemotherapy drug goes into the cultured cells from hair follicles and what we have found is that cooling actually dramatically reduces the amount of chemotherapy drug being absorbed by the rapidly-diving cells of the hair follicle," he added.
This means there is now evidence for the first time, which demonstrates cooling has a direct effect on reducing the amount of drug that goes in and is not an indirect effect as thought before with the restricted blood flow.
"Our results provide evidence that attenuation of cellular drug uptake represents at least one of the mechanisms underpinning the ability of cooling to rescue human keratinocytes from chemotherapy drug-cytotoxicity, thus supporting the clinical efficacy of scalp cooling," he added.
In addition to providing evidence of how the treatment works, the Centre has also been working on developing innovative scalp cooling-related treatments and individual 3D-printed cooling caps. This has involved a collaboration of researchers from across two of the University's schools of study, the School of Applied Sciences and the School of Art, Design and Architecture.
"This latest project builds upon our previous research," continued Dr Georgopoulos.
"We had already demonstrated that if you cool at just 3 or 4 degrees lower, this can be the difference between the cells surviving or dying. We have now shown that a few degrees in temperature can also mean a more dramatic reduction in chemotherapy drug uptake by cells.
"The more evidence we can provide, the more data the designers have to facilitate the design of a better a cap. A better fit could mean more of a reduction in temperature, so more effective cooling means more survival of the follicles, leading to a better outcome."
The percentage of hair loss can be further reduced when scalp cooling is combined with the application of a topical agent. One of the Centre's tasks has been to develop the best way to deliver this agent to hair follicles on the scalp.
Richard Paxman, CEO of Paxman, added: "This latest research brings us one step closer to achieving our vision of 'zero hair loss' for cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment. This is fabulous news and is a ground-breaking step in the field of scalp cooling research."
INFORMATION:
Antimicrobial packaging is being developed to extend the shelf life and safety of foods and beverages. However, there is concern about the transfer of potentially harmful materials, such as silver nanoparticles, from these types of containers to consumables. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces illustrate that silver embedded in an antimicrobial plastic can leave the material and form nanoparticles in foods and beverages, particularly in sweet and sugary ones.
Some polymers containing nanoparticles or nanocomposites can slow ...
In the Namib Desert in southwestern Africa, the Kuiseb River, an ephemeral river which is dry most of the year, plays a vital role to the region. It provides most of the vegetation to the area and serves as a home for the local indigenous people, and migration corridor for many animals. The overall vegetation cover increased by 33% between 1984 and 2019, according to a Dartmouth study published in Remote Sensing .
The study leveraged recent drone imagery and past satellite imagery to estimate past vegetation cover in this linear oasis of the Kuiseb River, a fertile area in the middle of one of the driest deserts ...
Some of the most commonly used drugs for treating hereditary breast and ovarian cancers may not work the way we thought they did, according to new University of Colorado Boulder research.
The paper, published February 2 in the journal Nature Communications, sheds new light on how they do work and could open the door to new next-generation medications that work better, the authors said.
"Despite the success of these drugs which sell in the billions of dollars per year and treat many thousands of patients, there are many unknowns about their potency and efficacy that if better understood ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - A popular streaming service boasts a film inventory approaching 4,000 titles. When it's time to pick a movie, are you more likely to quickly make a decision or meticulously sift through the possibilities?
Psychologists refer to those who search minimally for something to arrive at an adequate choice as "satisficers." It's the "maximizers," meantime, who search exhaustively for what might be considered as the perfect option.
Previous studies exploring both strategies after making a choice often present satisficing as a more psychologically ...
An important bacterial disease that affects citrus trees and causes lesions, citrus canker has been effectively controlled by spraying copper. However standard management techniques involve spraying excessive amounts of copper and water without consideration for the size of the trees.
"This technique resulted in a waste of resources as well as higher costs, detrimental environmental impact, and risk for development of copper resistant strains," explained plant pathologist Franklin Behlau, who recently published an article discussing a more sustainable approach to managing citrus canker.
Behlau and his colleagues showed that it is possible to control citrus canker by spraying ...
The instrumental climate record is the cultural heritage of humankind, the result of the diligent work of many generations of people all over the world. However, the changes in the way in which temperature is measured, as well as the environment in which weather stations are located can produce spurious trends. An international study carried out by researchers from the Universitat Rovira i Virgili (URV), the State Meteorology Agency and the University of Bonn (Germany) have succeeded in identifying the most reliable methods that help correct these trends. These "homogenization methods" are a key step in converting the enormous effort made by observers into reliable data about climate change. The results of this research, funded by ...
The inauguration of Joe Biden and Kamala Harris marks a new era for science policy in the U.S. and beyond. The new administration has inherited a global pandemic and worsening climate change, among other science-related issues. A cover story in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, delves into what this means for chemists and chemistry as a whole.
One of the most pressing issues facing the Biden administration is the fight against climate change. Biden campaigned on net-zero emissions of greenhouse gases by 2050 and has laid out a sweeping plan to switch the U.S. to cleaner energy sources, which experts say ...
For decades, scientists have wrestled with rival theories to explain how interactions between species, like competition, influence biodiversity. Tracking microbial life across the planet, researchers from McGill University show that biodiversity does in fact foster further diversity in microbiomes that are initially less diverse. However, diversity rates plateau with increased competition for survival and space in more diverse microbiomes.
Published in eLife, the findings could help scientists better understand how microbiomes - communities of micro-organisms living together in particular habitats like humans, animals and plants or even soils and oceans ...
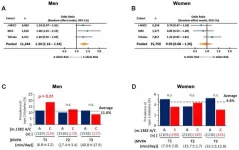
C polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to T2D in men, possibly interacting with exercise, and contributing to the risk of T2D in sedentary males by reducing the activity of MOTS-c.
Dr. Noriyuki Fuku from The Juntendo University and Dr. Pinchas Cohen from The University of Southern California said, "The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) is growing dramatically."
While diabetes syndromes directly caused by mutations in mtDNA are extremely rare, several genetic analyses reveal that mtDNA polymorphisms contribute to T2D risk in both European ...
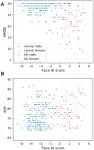
Aging-US published "Screening of Alzheimer's disease by facial complexion using artificial intelligence" which reported that despite the increasing incidence and high morbidity associated with dementia, a simple, non-invasive, and inexpensive method of screening for dementia is yet to be discovered.
This study aimed to examine whether artificial intelligence could distinguish between the faces of people with cognitive impairment and those without dementia.
121 patients with cognitive impairment and 117 cognitively sound participants were recruited for the study.
The binary differentiation of dementia / non-dementia facial image was expressed as a "Face AI score".
However, MMSE score showed significantly stronger ...