(Press-News.org) In the first longitudinal study to follow Georgia pre-K students through middle school, Stacey Neuharth-Pritchett, associate dean for academic programs and professor in UGA's Mary Frances Early College of Education, found that participating in pre-K programs positively predicted mathematical achievement in students through seventh grade.
"Students who participated in the study were twice as likely to meet the state standards in their mathematics achievement," said Neuharth-Pritchett. "School becomes more challenging as one progresses through the grades, and so if in middle school, students are still twice as likely to meet the state standards, it's clear that something that happened early on was influencing their trajectory."
The study found that, in fourth through seventh grades, the odds of a pre-K participant in the study meeting Georgia's state academic standards on the statewide standardized test were 1.67-2.10 times greater than the odds for a nonparticipant, providing evidence of sustained benefits of state-funded pre-K programs.
"Pre-K is a critical space where children experience success, and it sets them on a trajectory for being successful as they make the transition to kindergarten," she said. "The hope is that when children are successful early in school, they are more likely to be engaged as they progress and more likely to complete high school."
Although quality learning experiences during the early years of development have been shown to provide the skills and knowledge for later mathematics achievement, access and entry to high-quality preschool programs remain unequal across the nation.
"Our study looked at a high-needs school district that enrolled children from vulnerable situations in terms of economics and access to early learning experiences," said Neuharth-Pritchett. "A number of the children in the study had not had any other formative experiences before they went to kindergarten."
Educational experiences are seen as foundational to later school success with some studies documenting other beneficial outcomes for students who attend pre-K, including a higher chance to complete high school, less mental health concerns, less reliance on the welfare system and more. However, students from low-income families often have more limited opportunities to learn at home as well as in pre-K programs.
While some families are knowledgeable about providing their children with basic mathematical concepts and other foundational skills for a smooth home to school entry, other families might not be aware of the expectations for having mastered a number of these foundational skills before entering kindergarten.
"Equal access to pre-K education has a long history that goes all the way back to the war on poverty. Part of the thinking during the 1960s was that such early learning opportunities would provide the high-quality preschool education that could level the educational playing field between those with economic resources and those without," she said. "Our study indicated sustained benefits for children's early learning experiences that persist into the elementary and middle school years."
Some implications of the study for policymakers to consider include ensuring more equitable access to pre-K programs and hiring highly skilled teachers to promote children's learning and development. More than half of the pre-K teachers involved in the study held either a master's or specialist degree, indicating the importance and influence of high-quality, experienced instructors on children's academic success.
Because of a change in program support for the Georgia Prekindergarten Program during Gov. Nathan Deal's term, a high proportion of pre-K teachers are now very early in their teaching careers.
Along with Jisu Han, an assistant professor at Kyung Hee University and co-author of the study, Neuharth-Pritchett plans to continue following the study's participants as they progress through high school.
"The state of Georgia invests substantial resources into this program, so it's good that these outcomes can be cited for its efficacy," said Neuharth-Pritchett. "The data from this study gives a much more longitudinal view of success and suggests these programs contribute to children's education and success. Our results ultimately contribute to evidence supporting early learning and factors influencing long-term academic success for Georgia's children."
INFORMATION:
The full study is available online at https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10566-020-09595-w
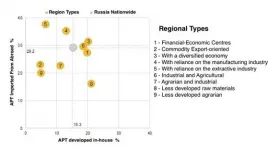
Russian enterprises have limited opportunities to carry out technological modernisation on their own. Their technological portfolios reveal a high dependence on imported solutions and a limited deployment of their own developments, HSE University researchers discovered.
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for the use of advanced manufacturing technologies (AMT) in Russia. Between 2011 and 2018, the number of AMT used increased by 33%, and in 2018 they amounted to almost 255,000 units in absolute terms. Meanwhile, innovation strategies focused on independent development of novel manufacturing solutions are not widespread in Russia. Fewer than ...
GROUND-BREAKING research from the University of Huddersfield, announced ahead of World Cancer Day 2021, proves that scalp cooling physically protects hair follicles from chemotherapy drugs. It is the world's first piece of biological evidence that explains how scalp cooling actually works and the mechanism behind its protection of the hair follicle.
The study, entitled 'Cooling-mediated protection from chemotherapy drug-induced cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes by inhibition of cellular drug uptake', has been published in the peer-reviewed journal PLOS ONE .
The data was part of an innovative hair follicle research project carried out by the dedicated Scalp Cooling ...
Antimicrobial packaging is being developed to extend the shelf life and safety of foods and beverages. However, there is concern about the transfer of potentially harmful materials, such as silver nanoparticles, from these types of containers to consumables. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces illustrate that silver embedded in an antimicrobial plastic can leave the material and form nanoparticles in foods and beverages, particularly in sweet and sugary ones.
Some polymers containing nanoparticles or nanocomposites can slow ...
In the Namib Desert in southwestern Africa, the Kuiseb River, an ephemeral river which is dry most of the year, plays a vital role to the region. It provides most of the vegetation to the area and serves as a home for the local indigenous people, and migration corridor for many animals. The overall vegetation cover increased by 33% between 1984 and 2019, according to a Dartmouth study published in Remote Sensing .
The study leveraged recent drone imagery and past satellite imagery to estimate past vegetation cover in this linear oasis of the Kuiseb River, a fertile area in the middle of one of the driest deserts ...
Some of the most commonly used drugs for treating hereditary breast and ovarian cancers may not work the way we thought they did, according to new University of Colorado Boulder research.
The paper, published February 2 in the journal Nature Communications, sheds new light on how they do work and could open the door to new next-generation medications that work better, the authors said.
"Despite the success of these drugs which sell in the billions of dollars per year and treat many thousands of patients, there are many unknowns about their potency and efficacy that if better understood ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - A popular streaming service boasts a film inventory approaching 4,000 titles. When it's time to pick a movie, are you more likely to quickly make a decision or meticulously sift through the possibilities?
Psychologists refer to those who search minimally for something to arrive at an adequate choice as "satisficers." It's the "maximizers," meantime, who search exhaustively for what might be considered as the perfect option.
Previous studies exploring both strategies after making a choice often present satisficing as a more psychologically ...
An important bacterial disease that affects citrus trees and causes lesions, citrus canker has been effectively controlled by spraying copper. However standard management techniques involve spraying excessive amounts of copper and water without consideration for the size of the trees.
"This technique resulted in a waste of resources as well as higher costs, detrimental environmental impact, and risk for development of copper resistant strains," explained plant pathologist Franklin Behlau, who recently published an article discussing a more sustainable approach to managing citrus canker.
Behlau and his colleagues showed that it is possible to control citrus canker by spraying ...
The instrumental climate record is the cultural heritage of humankind, the result of the diligent work of many generations of people all over the world. However, the changes in the way in which temperature is measured, as well as the environment in which weather stations are located can produce spurious trends. An international study carried out by researchers from the Universitat Rovira i Virgili (URV), the State Meteorology Agency and the University of Bonn (Germany) have succeeded in identifying the most reliable methods that help correct these trends. These "homogenization methods" are a key step in converting the enormous effort made by observers into reliable data about climate change. The results of this research, funded by ...
The inauguration of Joe Biden and Kamala Harris marks a new era for science policy in the U.S. and beyond. The new administration has inherited a global pandemic and worsening climate change, among other science-related issues. A cover story in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, delves into what this means for chemists and chemistry as a whole.
One of the most pressing issues facing the Biden administration is the fight against climate change. Biden campaigned on net-zero emissions of greenhouse gases by 2050 and has laid out a sweeping plan to switch the U.S. to cleaner energy sources, which experts say ...
For decades, scientists have wrestled with rival theories to explain how interactions between species, like competition, influence biodiversity. Tracking microbial life across the planet, researchers from McGill University show that biodiversity does in fact foster further diversity in microbiomes that are initially less diverse. However, diversity rates plateau with increased competition for survival and space in more diverse microbiomes.
Published in eLife, the findings could help scientists better understand how microbiomes - communities of micro-organisms living together in particular habitats like humans, animals and plants or even soils and oceans ...