Nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst is the full package
Osaka University researchers report an air-stable, reusable, non-noble metal catalyst for the environmentally friendly hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol with high activity
2021-02-04
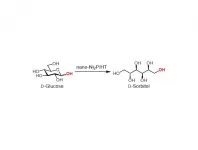
(Press-News.org) Osaka - Many different catalysts that promote the conversion of glucose to sorbitol have been studied; however, most offer certain properties while requiring compromises on others. Now, researchers from Osaka University have reported a hydrotalcite-supported nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst (nano-Ni2P/HT) that ticks all the boxes. Their findings are published in Green Chemistry.
Sorbitol is a versatile molecule that is widely used in the food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals industries. There is therefore a pressing need to produce sorbitol in a sustainable, low-cost, and green manner.
The nickel catalysts that are commonly used in the industrial hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol are unstable in air and require hash reaction conditions. Rare metal alternatives--despite being more efficient--can be expensive and are susceptible to poisoning.
nano-Ni2P/HT is stable in air and has a high activity for the hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol. In addition, nano-Ni2P/HT produces a particular sorbitol structure, known as D-sorbitol, at more than 99% yield. This high selectivity means that a high-purity product can be obtained.
The nano-Ni2P/HT-catalyzed hydrogenation can be carried out in water. Moreover, the catalyst shows good conversion and selectivity when the temperature is just 25°C--compared with 100-180°C for conventional processes--or when the hydrogen gas pressure is only 1 bar--compared with 50-150 bar. The energy saved by using these mild conditions would lead to greener and more sustainable procedures, as well as reduce operating costs.
"Our nano-Ni2P/HT catalyst outperformed conventional nickel alternatives in terms of both the catalytic activity and the amount of D-sorbitol that was produced, which is very encouraging," study first author Sho Yamaguchi explains. "nano-Ni2P/HT also gave a better yield of D-sorbitol than a commercially available noble metal catalyst."
Repeated use of the catalyst showed that nano-Ni2P/HT could be recycled with no significant loss of performance. The reaction could also be carried out at high glucose concentration (50 wt%), which demonstrates the viability of the catalyst for large scale use.
"The continual improvement of industrial catalyst is necessary to achieve sustainable, low-cost production with an environmental conscience," says study corresponding author Takato Mitsudome. "We believe our catalyst will make an important contribution, not only to D-sorbitol production, but to the development of other processes that support the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics industries."
INFORMATION:
The article, "Air-stable and reusable nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst for the highly selective hydrogenation of D-glucose to D-sorbitol," was published in Green Chemistry at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0GC03301D
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-04
Remember the first rule of fight club? That's right: You don't talk about fight club. Luckily, the rules of Hollywood don't apply to science. In new published research, University of Arizona researchers report what they learned when they started their own "fight club" - an exclusive version where only insects qualify as members, with a mission to shed light on the evolution of weapons in the animal kingdom.
In many animal species, fighting is a common occurrence. Individuals may fight over food, shelter or territory, but especially common are fights between males over access to females for mating. Many of the most striking and unusual features of animals are associated with these mating-related fights, including the horns of beetles and the antlers of deer. What is less clear ...
2021-02-04
PHILADELPHA--Inflammation in the blood could serve as a new biomarker to help identify patients with advanced pancreatic cancer who won't respond to the immune-stimulating drugs known as CD40 agonists, suggests a new study from researchers in the Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania published in JCI Insight
It is known that pancreatic cancer can cause systemic inflammation, which is readily detectable in the blood. The team found that patients with systemic inflammation had worse overall survival rates than patients without inflammation when treated with both a CD40 agonist and the chemotherapy gemcitabine.
The ...
2021-02-04
This study is the first randomised control trial to rigorously test a sequential approach to treating comorbid PTSD and major depressive disorder.
Findings from a trial of 52 patients undergoing three types of treatment regime - using only Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), using Behavioural Activation Therapy (BA) with some CPT, or CPT with some BA - found that a combined treatment protocol resulted in meaningful reductions in PTSD and depression severity, with improvements maintained at six-month follow-up investigations.
"We sought to examine whether a protocol that specifically targeted both PTSD and comorbid ...
2021-02-04
TOKYO --Toshiba Corporation (TOKYO: 6502) and Toshiba Digital Solutions Corporation (collectively Toshiba), industry leaders in solutions for large-scale optimization problems, today announced the Ballistic Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (bSB) and the Discrete Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (dSB), new algorithms that far surpass the performance of Toshiba's previous Simulated Bifurcation Algorithm (SB). The new algorithms will be applied to finding solutions to highly complex problems in areas as diverse as portfolio management, drug development and logistics management. ...
2021-02-04
Borderline Personality Disorder, or BPD, is the most common personality disorder in Australia, affecting up to 5% of the population at some stage, and Flinders University researchers warn more needs to be done to meet this high consumer needs.
A new study in the Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing (Wiley) describes how people with BPD are becoming more knowledgeable about the disorder and available treatments, but may find it difficult to find evidence-based help for their symptoms.
The South Australian psychiatric researchers warn these services are constrained by stigma ...
2021-02-04
Researchers at Flinders University are working to remedy this situation by identifying what triggers this chronic pain in the female reproductive tract.
Dr Joel Castro Kraftchenko - Head of Endometriosis Research for the Visceral Pain Group (VIPER), with the College of Medicine and Public Health at Flinders University - is leading research into the pain attached to Dyspareunia, also known as vaginal hyperalgesia or painful intercourse, which is one of the most debilitating symptoms experienced by women with endometriosis and vulvodynia.
Pain is detected by specialised proteins (called ion channels) that are present in sensory nerves and project from peripheral organs to the central ...
2021-02-04
Researchers from the international BASE collaboration at CERN, Switzerland, which is led by the RIKEN Fundamental Symmetries Laboratory, have discovered a new avenue to search for axions--a hypothetical particle that is one of the candidates of dark matter particles. The group, which usually performs ultra-high precision measurements of the fundamental properties of trapped antimatter, has for the first time used the ultra-sensitive superconducting single antiproton detection system of their advanced Penning trap experiment as a sensitive dark matter antenna.
If our current understanding of cosmology is correct, ordinary "visible" matter only ...
2021-02-04
When health researchers ask pregnant women about their alcohol use, expectant women may underreport their drinking, hampering efforts to minimize alcohol use in pregnancy and prevent development of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) in children.
In a recently published study in Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research, University of New Mexico scientists found that pregnant women's reporting of their own risky drinking varies greatly depending on how key questions are worded.
Most women know that alcohol use during pregnancy may harm their unborn child - and that leads to fear of being ...
2021-02-04
Genetics contributes to the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, and the APOE gene is the strongest genetic risk factor, specifically the APOE4 allele. However, it has been known for a while that the risk due to the APOE4 allele differs considerably across populations, with Europeans having a greater risk from the APOE4 allele than Africans and African Americans.
"If you inherited your APOE4 allele from your African ancestor, you have a lower risk for Alzheimer disease than if you inherited your APOE4 allele from your European ancestor," said Jeffery M. Vance, M.D., Ph.D., professor and founding chair of ...
2021-02-04
ATLANTA - FEBRUARY 4, 2021 - Cancer ranks as a leading cause of death in every country in the world, and, for the first time, female breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer, overtaking lung cancer, according to a collaborative report, Global Cancer Statistics 2020, from the American Cancer Society (ACS) and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Data show that 1 in 5 men and women worldwide develop cancer during their lifetime, and 1 in 8 men and 1 in 11 women die from the disease.
The article describes cancer incidence and mortality at the global level and according to sex, geography, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nickel phosphide nanoparticle catalyst is the full package
Osaka University researchers report an air-stable, reusable, non-noble metal catalyst for the environmentally friendly hydrogenation of glucose to sorbitol with high activity