(Press-News.org) A pilot program to offer mental health services offered resident physicians at the University of Colorado School of Medicine provides a model for confidential and affordable help, according to an article published today by the journal Academic Medicine.
For the 2017-2018 class, 80 resident physicians in the internal medicine and in internal medicine-pediatrics programs were enrolled in a mental health program that provided scheduled appointments at the campus mental health center. Residents were allowed to opt-out of the appointments. The cost of the appointments was covered by the residency programs, not charged to residents. Programs received de-identified invoices so that residents who participated could receive care confidentially.
"Developing mental health programs for residents can be challenging, as previous research has revealed that lack of time, concerns about confidentiality, concerns about stigma, and cost are significant barriers to residents seeking mental health care," the authors write.
Concerns about mental health for health care workers, and resident physicians in particular, have been elevated in in recent years as studies have identified the prevalence of burnout and depression. The authors explain that unaddressed mental health concerns among resident physicians can have a direct impact on patient care.
Of the 80 resident physicians who were automatically enrolled for mental health services in the pilot program, 23 attended the scheduled appointments, 12 were no-shows, and 45 opted out. Forty-one of the 80 resident physicians responded to an anonymous post-appointment survey. Among the survey respondents were 16 who attended their mental health appointments. Survey respondents, even those who opted out, were mostly appreciative of the program.
While the number of residents participating in the study is relatively small, the authors write that the "mental health program positively influenced the well-being of residents by demonstrating that the residency program was 'walking the walk' and not simply 'talking the talk' with regard to wellness."
INFORMATION:
The CU-affiliated authors of the article are Ajay Major, MD, MBA, a former resident who is now a hematology/oncology fellow at the University of Chicago; John G. Williams, MD, a former resident who is now a pulmonary/critical care fellow at University of Maryland; W. Cameron McGuire, a former resident who is now a pulmonary/critical care fellow at University of California San Diego; Eleanor Floyd, MD, instructor of medicine; and Karen Chacko, MD, professor of medicine.
About the University of Colorado School of Medicine
Faculty at the University of Colorado School of Medicine work to advance science and improve care. These faculty members include physicians, educators and scientists at UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital, Children's Hospital Colorado, Denver Health, National Jewish Health, and the Veterans Affairs Eastern Colorado Health Care System. The school is located on the Anschutz Medical Campus, one of four campuses in the University of Colorado system.
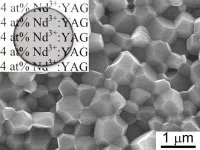
Scientists of Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU) have advanced the technology of high-speed sintering for optical ceramics (Nd3+:YAG), i.e. active elements generating laser emission in the near-infrared wavelength range (1.06 μm) for cutting the edge microelectronics and medicine. The researchers have managed to reduce significantly the initial nanopowders consolidation period (10 - 100 times) forming a nanostructure with ensured high optical transparency of the ceramic material. A related article appears in Optical Materials.
Diode-pumped ...
Inflammation is supposed to help protect us--it's part of an immune response to fight off pathogens and clear infections. But patients with cardiac disease often have chronic inflammation that damages their hearts, even with no infection present.
In a recent study published in Circulation, immunologists at Tufts University School of Medicine in collaboration with investigators at Vanderbilt University and Tufts Medical Center revealed a mechanism that is activating T cells, a type of immune cell, and causing inflammation in the heart.
"Not all inflammation is the same," says Pilar Alcaide, a Kenneth and JoAnn G. Wellner Professor at Tufts School of Medicine and corresponding ...
The 2019-2020 flu season in the U.S. was unusual in a number of ways. Cases picked up in August rather than the more typical fall and early winter months, and it hit children particularly hard. It was also dominated early on by a Type B influenza virus instead of one of the much more common Type A viruses like H1N1 or H3N2.
A new study by researchers at the University of Georgia suggests that these dynamics were driven largely by a new, more transmissible strain encountering a population with very little existing immunity to it.
Their findings, just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, have implications for future vaccination ...
A new white paper from The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) highlights the variety of challenges that persons with dementia-related psychosis and their caregivers have encountered during moves through different health care settings -- and proposes strategies to address these challenges.
It is estimated that over 2 million Americans with dementia experience delusions (false beliefs) and hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that others do not see or hear). This group of symptoms, known as dementia-related psychosis, frequently goes undetected in people who may ...
NEWPORT, Ore. - Researchers can now determine the age and sex of living beluga whales in Alaska's Cook Inlet thanks to a new DNA-based technique that uses information from small samples of skin tissue.
Accurate age estimates are vital to conservation efforts for Cook Inlet belugas, which were listed as endangered following a significant population decline in the 1990s. Previously, researchers could only determine the age of beluga whales by studying the teeth of dead animals.
The new aging method uses DNA methylation data and machine learning to develop a model that captures ...
If you have a second, try typing "time management" into your favourite search engine.
You will get literally millions of results: books, tips, lessons, do's and don'ts.
It's a big industry. But as END ...
A new analysis of a horse previously believed to be from the Ice Age shows that the animal actually died just a few hundred years ago--and was raised, ridden and cared for by Native peoples. The study sheds light on the early relationships between horses and their guardians in the Americas.
The findings, published today in the journal American Antiquity, are the latest in the saga of the "Lehi horse."
In 2018, a Utah couple was doing landscaping in their backyard near the city of Provo when they unearthed something surprising: an almost complete skeleton of a horse about the size of a Shetland pony. Scientists and the media took note. Preliminary data suggested ...
For a girl in Ethiopia, her mother's wealth can protect her from becoming a child bride - but if a father prefers child marriage, his own wealth may increase the likelihood that she will be married before 18, according to a Rutgers University-New Brunswick study.
Published in the journal World Development, the study found that girls whose mothers have more asset holdings - a cellphone, bicycle, sewing machine, jewelry or other valuables - have a reduced rate of entering into a child marriage, while the rate is higher for girls whose fathers have more asset holdings.
"Child marriage is concerning from a human rights, health and economic perspective," said the study's author Felix Muchomba, assistant professor at the Rutgers School of Social Work. "Girls married before ...
Getting children to eat their vegetables can seem like an insurmountable task, but nutrition researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have found one way: school gardens and lessons on using what's grown in them.
Researchers worked with 16 elementary schools across Central Texas to install vegetable gardens and teach classes to students and parents about nutrition and cooking. In a study recently published in the END ...
Humans, wildlife, and the environment are all interconnected and play a role in one another's health and well-being. Sentinel species, such as birds, are good indicators of environmental health, and they can send subtle warning signs that humans may be in danger next.
In an experimental exposure study, Kendra Sewall, an associate professor of biological sciences in the College of Science, and a diverse team of scientists and students have found that lead levels like those reported in Flint, Michigan, can interfere with the neural mechanisms of vocal development of songbirds and affect mate attraction.
By examining the effects of lead exposure ...