(Press-News.org) Global greenhouse gas emissions over the last century have made southern China a hotspot for bat-borne coronaviruses, by driving growth of forest habitat favoured by bats.
A new study published today in the journal Science of the Total Environment provides the first evidence of a mechanism by which climate change could have played a direct role in the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that caused the COVID-19 pandemic.
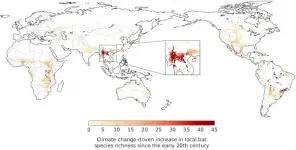
The study has revealed large-scale changes in the type of vegetation in the southern Chinese Yunnan province, and adjacent regions in Myanmar and Laos, over the last century. Climatic changes including increases in temperature, sunlight, and atmospheric carbon dioxide - which affect the growth of plants and trees - have changed natural habitats from tropical shrubland to tropical savannah and deciduous woodland. This created a suitable environment for many bat species that predominantly live in forests.
The number of coronaviruses in an area is closely linked to the number of different bat species present. The study found that an additional 40 bat species have moved into the southern Chinese Yunnan province in the past century, harbouring around 100 more types of bat-borne coronavirus. This 'global hotspot' is the region where genetic data suggests SARS-CoV-2 may have arisen.
"Climate change over the last century has made the habitat in the southern Chinese Yunnan province suitable for more bat species," said Dr Robert Beyer, a researcher in the University of Cambridge's Department of Zoology and first author of the study, who has recently taken up a European research fellowship at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Germany.
He added: "Understanding how the global distribution of bat species has shifted as a result of climate change may be an important step in reconstructing the origin of the COVID-19 outbreak."
To get their results, the researchers created a map of the world's vegetation as it was a century ago, using records of temperature, precipitation, and cloud cover. Then they used information on the vegetation requirements of the world's bat species to work out the global distribution of each species in the early 1900s. Comparing this to current distributions allowed them to see how bat 'species richness', the number of different species, has changed across the globe over the last century due to climate change.
"As climate change altered habitats, species left some areas and moved into others - taking their viruses with them. This not only altered the regions where viruses are present, but most likely allowed for new interactions between animals and viruses, causing more harmful viruses to be transmitted or evolve," said Beyer.
The world's bat population carries around 3,000 different types of coronavirus, with each bat species harbouring an average of 2.7 coronaviruses - most without showing symptoms. An increase in the number of bat species in a particular region, driven by climate change, may increase the likelihood that a coronavirus harmful to humans is present, transmitted, or evolves there.
Most coronaviruses carried by bats cannot jump into humans. But several coronaviruses known to infect humans are very likely to have originated in bats, including three that can cause human fatalities: Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) CoV, and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) CoV-1 and CoV-2.
The region identified by the study as a hotspot for a climate-driven increase in bat species richness is also home to pangolins, which are suggested to have acted as intermediate hosts to SARS-CoV-2. The virus is likely to have jumped from bats to these animals, which were then sold at a wildlife market in Wuhan - where the initial human outbreak occurred.
The researchers echo calls from previous studies that urge policy-makers to acknowledge the role of climate change in outbreaks of viral diseases, and to address climate change as part of COVID-19 economic recovery programmes.
"The COVID-19 pandemic has caused tremendous social and economic damage. Governments must seize the opportunity to reduce health risks from infectious diseases by taking decisive action to mitigate climate change," said Professor Andrea Manica in the University of Cambridge's Department of Zoology, who was involved in the study.
"The fact that climate change can accelerate the transmission of wildlife pathogens to humans should be an urgent wake-up call to reduce global emissions," added Professor Camilo Mora at the University of Hawai'i at Manoa, who initiated the project.
The researchers emphasised the need to limit the expansion of urban areas, farmland, and hunting grounds into natural habitat to reduce contact between humans and disease-carrying animals.
The study showed that over the last century, climate change has also driven increases in the number of bat species in regions around Central Africa, and scattered patches in Central and South America.
INFORMATION:
Neanderthals' gut microbiota already included some beneficial micro-organisms that are also found in our own intestine. An international research group led by the University of Bologna achieved this result by extracting and analysing ancient DNA from 50,000-year-old faecal sediments sampled at the archaeological site of El Salt, near Alicante (Spain).
Published in Communication Biology, their paper puts forward the hypothesis of the existence of ancestral components of human microbiota that have been living in the human gastrointestinal tract since before the separation between the Homo Sapiens and Neanderthals that occurred more than 700,000 years ago.
"These results allow us to understand which components of the human gut microbiota ...
New research has identified a nanostructure that improves the anode in lithium-ion batteries
Instead of using graphite for the anode, the researchers turned to silicon: a material that stores more charge but is susceptible to fracturing
The team made the silicon anode by depositing silicon atoms on top of metallic nanoparticles
The resulting nanostructure formed arches, increasing the strength and structural integrity of the anode
Electrochemical tests showed the lithium-ion batteries with the improved silicon anodes had a higher charge capacity and longer lifespan
New research conducted by the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology ...
USC researchers have developed a new method to counter emergent mutations of the coronavirus and hasten vaccine development to stop the pathogen responsible for killing thousands of people and ruining the economy.
Using artificial intelligence (AI), the research team at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering developed a method to speed the analysis of vaccines and zero in on the best potential preventive medical therapy.
The method is easily adaptable to analyze potential mutations of the virus, ensuring the best possible vaccines are quickly identified -- solutions that give ...
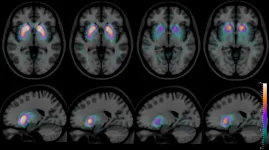
The early prognosis of high-risk older adults for amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), using noninvasive and sensitive neuromarkers, is key for early prevention of Alzheimer's disease. A recent study, published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, by researchers at the University of Kentucky establishes what they believe is a new way to predict the risk years before a clinical diagnosis. Their work shows that direct measures of brain signatures during mental activity are more sensitive and accurate predictors of memory decline than current standard behavioral testing.
"Many studies have measured electrophysiological rhythms during resting and sleep ...
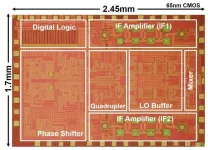
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) and NTT Corporation (NTT) develop a novel CMOS-based transceiver for wireless communications at the 300 GHz band, enabling future beyond-5G applications. Their design addresses the challenges of operating CMOS technology at its practical limit and represents the first wideband CMOS phased-array system to operate at such elevated frequencies.
Communication at higher frequencies is a perpetually sought-after goal in electronics because of the greater data rates that would be possible and to take advantage of underutilized ...
A new study in Frontiers in Marine Science provides a first-of-its-kind evaluation of which regions of southern European seas are in the most need of fishing restrictions. These areas have persistently shown high numbers of undersized fish and crustaceans, which are typically discarded because they are below the allowable size limit for collection. These findings may offer a strategy for prioritizing conservation efforts and ensuring more sustainable fishery management in the future.
"Natural fish populations need time to reproduce and recover from fishing impacts -- this is the only way to achieve a balance between natural resources and human exploitation," says lead author Dr Giacomo Milisenda, of the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn di Napoli in ...
Multidisciplinary team of international experts suggests participants should receive a "substantial" amount, be paid ethically
Healthy people volunteering to be infected with SARS-CoV-2, in order to help scientists better understand how to tackle the virus, should receive payment - if it is determined that these studies are otherwise ethical to proceed.
Those are the findings of a new peer-reviewed study published in the American Journal of Bioethics, which has assessed the ethics of paying participants to take part in so-called 'Human Infection Challenge Studies' (HICS).
Over ...
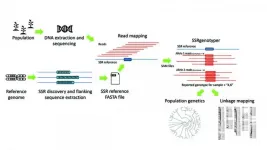
SSRgenotyper is a newly developed, free bioinformatic tool that allows researchers to digitally genotype sequenced populations using simple sequence repeats (SSRs), a task that previously required time-consuming lab-based methods.
Reporting in a recent issue of Applications in Plant Sciences, the tool's developers designed the program to seamlessly integrate with other applications currently used for the detection and analysis of SSRs.
Simple sequence repeats are short chains of repeating nucleotides that are prone to mutation. The variability of these DNA sequences makes them ideal for genetic analyses to distinguish between individuals and are often the marker of choice for paternity and forensic testing.
In research fields, SSRS have ...
American actor Robin Williams had a neurodegenerative brain disease called dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): a distressing disease, with symptoms in common with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). But unlike these two conditions, DLB also entails prominent mood and cognitive swings, sleep disorders, and vivid, sometimes terrifying, visual hallucinations. It is now thought that Robin Williams, whose diagnosis was only ascertained post-mortem, was likely driven to suicide, in 2014, by the terrifying hallucinatory experiences he suffered for years - and about which he never told anyone, not even his wife. Susan Schneider Williams recounted the tragic story in an editorial published in the journal ...
As a new presidential administration takes steps to examine options to control the spread of COVID-19 through increased testing, epidemiologists at The University of Texas at Austin and other institutions have a new analysis that shows the value of having all people in the U.S. tested on a regular, rotating basis to slow the spread of the novel coronavirus and the loss of life from COVID-19. The team's model is outlined in a paper published online today in The Lancet Public Health.
With the introduction of accurate and inexpensive rapid tests, researchers say there is an optimal testing schedule that minimizes costs as well ...