(Press-News.org) Multidisciplinary team of international experts suggests participants should receive a "substantial" amount, be paid ethically
Healthy people volunteering to be infected with SARS-CoV-2, in order to help scientists better understand how to tackle the virus, should receive payment - if it is determined that these studies are otherwise ethical to proceed.
Those are the findings of a new peer-reviewed study published in the American Journal of Bioethics, which has assessed the ethics of paying participants to take part in so-called 'Human Infection Challenge Studies' (HICS).
Over the past few months there has been vast media coverage and discussion about the first COVID-19 HICS in the world, planned to begin in the UK later this year. This type of study can be particularly valuable for testing vaccines and can speed up the development of new vaccines.
Using HICS for a disease that can be fatal and currently lacks a cure is ethically controversial. Part of that controversy has to do with whether participants should be paid for such a risky endeavor and how payment might affect their consent.
Among the advocates of pursuing COVID-19 challenge trials is the organization, 1Day Sooner.
1Day Sooner sponsored the report on which the new study is based, seeking an independent assessment of whether and how much people should get paid to take part in challenge trials.
The international research team from the UK, US, and Canada does not necessarily endorse the use of HICS for COVID-19. But if HICS proceed, their findings reflect that not only should participants be paid, but their payment should be "substantial".
The research team - including experts in bioethics, economics, science, medicine, and law, as well as two individuals expressing interest in participating in SARS-CoV-2 HICS - created a framework for scientists to follow in order to ethically assess payments for people taking part in HICS. They also looked at payment in similar studies, but noted the difficulty of finding out this information.
"Our work was spurred by concerns that payment for SARS-CoV-2 HICS might require a novel ethical framework, which we ultimately determined to be unfounded," states lead author Holly Fernandez Lynch, John Russell Dickson, MD Presidential Assistant Professor of Medical Ethics at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.
"Payment for HICS participation should be treated like payment in other clinical studies involving healthy participants," she says.
"High offers of payment are sometimes met with scrutiny and concern, but it can be ethically appropriate to offer substantial payment for research participation and we have to consider that low payment also raises significant ethical concerns."
Professor Fernandez Lynch, who is a lawyer and bioethics expert, adds: "SARS-CoV-2 HICS should not be allowed to proceed in any setting in which there have not been adequate provisions made for compensating research-related harms, as well as other efforts to minimize risk and promote social value.
"Our hope going forward is that our analysis will serve both to ease concerns about payment in these studies, should they proceed, and to advance the broader project of ensuring ethical payment to participants in all clinical research."
The framework the team has developed is split into two-parts. The first focuses on three main motives for payment: 'reimbursement' (for out-of-pocket expenses), 'compensation' (which includes payment for time, burden, inconvenience of isolating, etc.), and 'incentive' (to broaden the range of individuals willing to consider participation). The second part considers appropriate compensation in the event any harm materializes - ranging from injury to death.
In developing the framework, the team paid special attention to public trust, acknowledging that "research payments could affect public trust in several ways". Ultimately, they conclude that "the best way to promote trust in HICS is by helping the public understand why this design can be both scientifically important and ethically acceptable".
"HICS can proceed only when strict research and ethical standards are satisfied," says co-author Thomas Darton, from the Department of Infection, Immunity and Cardiovascular Disease at The University of Sheffield.
Dr Darton is a HICS researcher, although he does not work with the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
He states: "If the risks associated with these studies are unreasonable in relation to their potential benefits, payment for participation cannot help achieve ethical acceptability. But if the research is otherwise ethical, it doesn't become unethical simply because payment is offered."
Another factor the team considered is whether COVID-19 HICS would be "uniquely risky" and how that should influence payment levels.
Ultimately, they concluded that "the ethical concerns about payment for these studies are the same as those for payment in all clinical research".
"Although certainly relevant to considerations regarding the ethical acceptability of HICS, including the importance of planning for research-related harm, heightened risks do not support adopting a novel framework for HICS payment as compared to other types of research," adds co-author Emily Largent, the Emanuel and Robert Hart Assistant Professor of Medical Ethics at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania.
Limitations of the project include the team's perspectives being "limited to the Global North". They state, therefore, that additional considerations may be relevant when research is conducted elsewhere.
The team also declined to identify a payment amount or even a range that would be appropriate for HICS or SARS-CoV-2 HICS. "Stakeholders must take the final step between conceptual guidance and actual payment offers on their own," the paper concludes. "This means that there may be several different payment offers that could be justified, but the framework can help determine which offers are ethically appropriate," says Professor Fernandez Lynch.
INFORMATION:
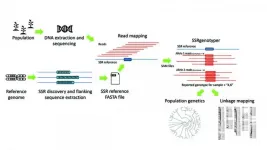
SSRgenotyper is a newly developed, free bioinformatic tool that allows researchers to digitally genotype sequenced populations using simple sequence repeats (SSRs), a task that previously required time-consuming lab-based methods.
Reporting in a recent issue of Applications in Plant Sciences, the tool's developers designed the program to seamlessly integrate with other applications currently used for the detection and analysis of SSRs.
Simple sequence repeats are short chains of repeating nucleotides that are prone to mutation. The variability of these DNA sequences makes them ideal for genetic analyses to distinguish between individuals and are often the marker of choice for paternity and forensic testing.
In research fields, SSRS have ...
American actor Robin Williams had a neurodegenerative brain disease called dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): a distressing disease, with symptoms in common with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). But unlike these two conditions, DLB also entails prominent mood and cognitive swings, sleep disorders, and vivid, sometimes terrifying, visual hallucinations. It is now thought that Robin Williams, whose diagnosis was only ascertained post-mortem, was likely driven to suicide, in 2014, by the terrifying hallucinatory experiences he suffered for years - and about which he never told anyone, not even his wife. Susan Schneider Williams recounted the tragic story in an editorial published in the journal ...
As a new presidential administration takes steps to examine options to control the spread of COVID-19 through increased testing, epidemiologists at The University of Texas at Austin and other institutions have a new analysis that shows the value of having all people in the U.S. tested on a regular, rotating basis to slow the spread of the novel coronavirus and the loss of life from COVID-19. The team's model is outlined in a paper published online today in The Lancet Public Health.
With the introduction of accurate and inexpensive rapid tests, researchers say there is an optimal testing schedule that minimizes costs as well ...
Weekly COVID-19 testing, with two-week isolation of positive cases, is the most cost-effective strategy to mitigate spread of the virus in the USA when transmission is high in affected areas until vaccines are widely available.
When transmission rates are low to moderate, monthly testing and a one-week isolation period is the most cost-effective approach.
Monthly population testing is more cost-effective than the current strategy of testing only people showing symptoms and their close contacts.
Weekly COVID-19 testing, coupled with a two-week isolation period for positive cases, may be the most cost-effective strategy to tackle the ...
A biologist from RUDN University confirmed that selenium nanoparticles and garlic extract can effectively reduce the negative impact of stress on the health of grass carp in the breeding industry. The results of his study were published in the Journal of the World Aquaculture Society.
Grass carp or Ctenopharyngodon Idella is a valuable commercial fish type. In order to increase productivity, fish farms tend to breed more and more fish in small reservoirs. This extreme population density causes stress in carps that negatively affects their health, namely, reduces immunity, slows down growth, suppresses digestion, and interferes with intestinal functions. To mitigate ...
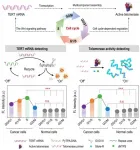
Cancer is a significant cause of death worldwide and many efforts have been devoted to the development of methods for early detection. Telomerase are considered as a tumor biomarker for early diagnosis because the telomerase of more than 80% immortalized cells are reactivated and provides the sustained proliferative capacity of these cells, but the telomerase activity are not detectable in normal somatic cells. Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein complex that is thought to add telomeric repeats onto the ends of chromosomes during the replicative phase (S ...
DETROIT - Wayne State University School of Medicine researchers have reported that zinc supplements for men and women attempting to conceive either naturally or through assisted reproduction during the COVID-19 pandemic may prevent mitochondrial damage in young egg and sperm cells, as well as enhance immunity against the virus.
In "Potential Role of Zinc in the COVID-19 Disease Process and its Probable Impact on Reproduction," published in Reproductive Sciences, Husam Abu-Soud, Ph.D., associate professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology and the C.S. Mott Center for Growth and Development, ...
Sexual assault and sexual harassment are significant problems in the U.S. military and military service academies in the United States. In 2018, 15.8% of female and 2.4% of male cadets and midshipmen across the military service academies reported unwanted sexual contact in the past year. This unwanted behavior can contribute to a variety of negative mental and behavioral health outcomes.
While the military service academies have implemented multiple sexual assault prevention programs and social marketing campaigns to improve awareness of and response to sexual assault, prevention initiatives have been hindered by an absence of evidence ...
Gun violence among children is lower in states with more gun laws, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The study, published in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence, examined youth gun and weapon carrying data from 2005 and 2017 across several states. Researchers found the rates of youths carrying guns was higher in states and lower in states with more gun laws. According to researchers, this phenomenon could be associated with large urban areas and more significant safety concerns within these areas.
Louisiana and Arkansas reported the highest percentages of youth reporting gun carrying behavior in 2017 and 2013 respectively, with 12.7 percent and 12.5 percent respectively. These two states had 13 gun laws in place while the lowest rates of gun carrying among ...
If you're about to buy something online and its only customer review is negative, you'd probably reconsider the purchase, right? It turns out a product's first review can have an outsized effect on the item's future -- it can even cause the product to fail.
Shoppers, retailers and manufacturers alike feel the effects of customer reviews. Researchers at the University of Florida's Warrington College of Business looked at the influence of the first review after noticing the exact same products getting positive reviews on one retailer's website but negative reviews on others, said Sungsik Park, Ph.D., who studied the phenomenon ...