INFORMATION:
Garlic and selenium increase stress resistance in carps, says a RUDN University biologist
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) A biologist from RUDN University confirmed that selenium nanoparticles and garlic extract can effectively reduce the negative impact of stress on the health of grass carp in the breeding industry. The results of his study were published in the Journal of the World Aquaculture Society.
Grass carp or Ctenopharyngodon Idella is a valuable commercial fish type. In order to increase productivity, fish farms tend to breed more and more fish in small reservoirs. This extreme population density causes stress in carps that negatively affects their health, namely, reduces immunity, slows down growth, suppresses digestion, and interferes with intestinal functions. To mitigate these effects and support the immune system of the fish, farmers often use dietary supplements. A biologist from RUDN University confirmed the efficiency of selenium and garlic extract that increase stress resistance in carps.
"Being a component of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase, selenium protects cell membranes from oxidative damage. It is also known to support immunity and gut health in fish. In its turn, garlic increases the growth rate, improves immunity and antioxidant activity, and supports the activity of digestive enzymes in fish. However, until recently, no data on the effect of selenium and garlic extract on the productivity of actively bred young grass carps has been available. Therefore, we decided to research the ability of these substances to mitigate stress," said Morteza Yousefi, PhD, an assistant professor at the Department of Veterinary Medicine, RUDN University.
The team divided 1,008 healthy juvenile grass carps with an average weight of two grams into six groups and put them into 18 48-liter pools with low (24 fish), medium (48 fish), and high (96 fish) population density. Half of the fish received 1 mg of Se nanoparticles and 1 g of garlic per 1 kg of fodder (diet 1), while the other half got twice as much of both supplements (diet 2). After 60 days, the team compared the growth rate, blood composition, and digestive enzyme activity in both groups and broke the data down by population density levels.
The fish from the pools with medium and low population density that received more selenium and garlic grew the most: by 286% and 276%, respectively. The experiment showed that both low and high population density caused a stress reaction in fish that led to the reduction of antioxidant enzyme activity. However, regardless of the density, the levels of cortisol, also known as the hormone of stress, were lower in the group that received diet 2: 30 ng/ml against 40 ng/ml in the group that received diet 1. According to the researchers, adding selenium and garlic to fodder could partially compensate for the stress of breeding in highly populated pools.
"We confirmed that both dietary supplements and population density have a prominent effect on growth rate and food utilization in grass carp. Higher concentrations of selenium and garlic extract in the diet suppress the stress reaction, reduce oxidizing damage and lipid damage, and improve the growth rate, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant properties, and the general state of health of the fish. Moreover, at medium population density, the fish grew bigger than at low or high density. Therefore, these conditions should be considered the most optimal for breeding," added Morteza Yousefi, PhD, an assistant professor at the Department of Veterinary Medicine, RUDN University.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
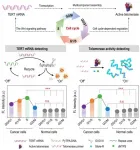
Role of cell cycle on analyzing telomerase activity with a fluorescence off-on system
2021-02-04
Cancer is a significant cause of death worldwide and many efforts have been devoted to the development of methods for early detection. Telomerase are considered as a tumor biomarker for early diagnosis because the telomerase of more than 80% immortalized cells are reactivated and provides the sustained proliferative capacity of these cells, but the telomerase activity are not detectable in normal somatic cells. Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein complex that is thought to add telomeric repeats onto the ends of chromosomes during the replicative phase (S ...
Zinc may help with fertility during COVID-19 pandemic, researchers report
2021-02-04
DETROIT - Wayne State University School of Medicine researchers have reported that zinc supplements for men and women attempting to conceive either naturally or through assisted reproduction during the COVID-19 pandemic may prevent mitochondrial damage in young egg and sperm cells, as well as enhance immunity against the virus.
In "Potential Role of Zinc in the COVID-19 Disease Process and its Probable Impact on Reproduction," published in Reproductive Sciences, Husam Abu-Soud, Ph.D., associate professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology and the C.S. Mott Center for Growth and Development, ...
U.S. Air Force Academy intervention reduces unwanted sexual contact by over 40 percent
2021-02-04
Sexual assault and sexual harassment are significant problems in the U.S. military and military service academies in the United States. In 2018, 15.8% of female and 2.4% of male cadets and midshipmen across the military service academies reported unwanted sexual contact in the past year. This unwanted behavior can contribute to a variety of negative mental and behavioral health outcomes.
While the military service academies have implemented multiple sexual assault prevention programs and social marketing campaigns to improve awareness of and response to sexual assault, prevention initiatives have been hindered by an absence of evidence ...
States with more gun laws have lower youth gun violence, Rutgers study finds
2021-02-04
Gun violence among children is lower in states with more gun laws, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The study, published in the Journal of Youth and Adolescence, examined youth gun and weapon carrying data from 2005 and 2017 across several states. Researchers found the rates of youths carrying guns was higher in states and lower in states with more gun laws. According to researchers, this phenomenon could be associated with large urban areas and more significant safety concerns within these areas.
Louisiana and Arkansas reported the highest percentages of youth reporting gun carrying behavior in 2017 and 2013 respectively, with 12.7 percent and 12.5 percent respectively. These two states had 13 gun laws in place while the lowest rates of gun carrying among ...
The strange impact of the first consumer review
2021-02-04
If you're about to buy something online and its only customer review is negative, you'd probably reconsider the purchase, right? It turns out a product's first review can have an outsized effect on the item's future -- it can even cause the product to fail.
Shoppers, retailers and manufacturers alike feel the effects of customer reviews. Researchers at the University of Florida's Warrington College of Business looked at the influence of the first review after noticing the exact same products getting positive reviews on one retailer's website but negative reviews on others, said Sungsik Park, Ph.D., who studied the phenomenon ...
A personal benefit of social distancing: lower odds of getting COVID-19
2021-02-04
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Considering the greater good by social distancing during a pandemic turns out to have an attractive personal benefit: A new study has found that staying away from others also reduces an individual person's chances of contracting COVID-19.
Researchers presented study participants with virtual behavior scenarios of various public settings - a grocery store, a crowded beach, a crosswalk - and asked them to place themselves or fictional people in those contexts based on their social distancing preferences.
Four months later, the participants were asked if they had tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection or otherwise believed they had been sick with a case of COVID-19.
Statistical analyses ...
Synthesized very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids improved retinal function in mice
2021-02-04
Scientists like the John A. Moran Eye Center's Paul S. Bernstein, MD, PhD, know a special class of lipids, or fatty acids, found in the retina of the eye and in just a few other parts of the body play an important role in maintaining vision.
But it's been difficult to study whether giving these lipids, called very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (VLC-PUFAs), to patients as a supplement could prevent blinding eye diseases like age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and some inherited retinal diseases. Made in the body by the ELOVL4 enzyme but rarely consumed as part of a normal diet, VLC-PUFAs weren't commercially available ...
Charge radii of exotic potassium isotopes challenge nuclear structure theory
2021-02-04
In nuclear physics so-called magic number are such nuclear proton and/or neutron numbers, for which the nucleus is more stable compared to neighboring isotopes on the nuclear chart. Researchers in both experimental and theoretical nuclear physics from University of Jyväskylä, Finland, took part of international research team, which studied the nuclear charge radii of potassium isotopes. Isotopes were studied by using the collinear resonance ionization spectroscopy technique. The results indicated that the potassium isotope with a neutron number of 32 does not conform with criteria of magic neutron number. The results were published in Nature Physics journal on January 2021.
Far from the stable ...
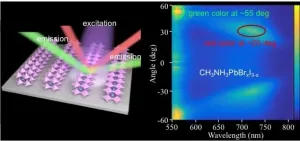
Large-area periodic perovskite nanostructures for lenticular printing laser displays
2021-02-04
Lead halide perovskites, with high refractive index and excellent optoelectronic property, have been used in both constructing high-quality optical resonators/lasers and fabricating high-efficiency light-emitting devices for advanced displays. Lenticular printing provides an illusion of depth and shows varying images upon view angles, which is considered as a promising approach towards future stereoscopic displays. To realize lenticular-printing-based display, it is required to modulate the outcoupling direction of emission light rather than that of incident light. Ideally, the lenticular-lens-like structures would be integrated into the active layer of light-emitting devices. Therefore, the hybrid perovskite becomes a promising candidate for ...
Duration of antibody response varies among adults naturally reinfected with RSV
2021-02-04
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine found that while most individuals responded to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) natural reinfection with a typical sustained antibody response associated with protection, a few individuals surprisingly responded atypically, not being able to sustain the antibody response, which declined to levels that made the individuals susceptible to RSV reinfection.
The researchers highlight in their study, published in the journal Vaccine, that their findings point at a subpopulation of people who also may not maintain an antibody response to vaccines and suggest the need to characterize patient-specific responses to respiratory viral infections, such as COVID-19.
"RSV is ...