(Press-News.org) Scientists like the John A. Moran Eye Center's Paul S. Bernstein, MD, PhD, know a special class of lipids, or fatty acids, found in the retina of the eye and in just a few other parts of the body play an important role in maintaining vision.
But it's been difficult to study whether giving these lipids, called very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (VLC-PUFAs), to patients as a supplement could prevent blinding eye diseases like age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and some inherited retinal diseases. Made in the body by the ELOVL4 enzyme but rarely consumed as part of a normal diet, VLC-PUFAs weren't commercially available in enough quantities for animal or human research.
Now Bernstein and colleagues from the University of Utah's Chemistry Department have changed the paradigm, inventing a method for synthesizing large enough quantities of VLC-PUFAs to evaluate their potential sight-preserving properties. The method and the results of the first study to use it were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) this week.
The study determined that VLC-PUFA supplementation increased levels of the lipids in the retina and also improved visual function in normal mice and in mice with a defect in the ELOVL4 enzyme. While Bernstein says there's more work to be done, the results are an exciting first step.
"Synthesizing VLC-PUFAs opens up a whole new area of study, and these first results are very promising," said Bernstein, the paper's corresponding author. "Our results raise interesting questions about how orally administered VLC-PUFAs improve vision, how they are carried in the bloodstream, and how they are selectively targeted to the retina. The VLC-PUFA formulation, dosage, and timing of the intervention first need to be optimized, and then the underlying mechanisms will need to be defined."
Organic Chemistry Professor Jon D. Rainier, PhD, a co-author on the research, said the group is confident it can synthesize additional VLC-PUFA variants.
"There are a number of VLC-PUFA variants that are present in the human eye," said Rainier, second author on the research. "So far we have only made one member of this family, but we are confident that our new synthetic method will enable us to both synthesize and study the other variants and by doing that get a much better idea of what it is that each of the individual VLC-PUFAs do."
INFORMATION:
Bernstein's laboratory focuses on the biochemistry and biophysics of nutritional interventions against inherited and acquired ocular disorders. Bernstein, Moran's vice-chair for clinical and basic science research and the Val A. and Edith D. Green Presidential Professor of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, helped develop the protective AREDS2 supplement formulation for patients with age-related macular degeneration.
Additional authors on the PNAS study, Retinal Bioavailability and Functional Effects of a Synthetic Very-Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid in Mice, were: Aruna Gorusupudi, Rameshu Rallabandi, Binxing Li, Ranganathan Arunkumar, J. David Blount, Gergory T. Rognon, Fu-Yen Chang, Alexander Wade, Steven Lucas, and John C. Conboy.
The research was supported by a Knights Templar Career Starter Grant, a University of Utah Center on Aging Seed Grant, a Foundation Fighting Blindness Grant, a Carl Marshall Reeves and Mildred Almen Reeves Foundation Grant, and departmental core grants from Research to Prevent Blindness and the National Institutes of Health.
In nuclear physics so-called magic number are such nuclear proton and/or neutron numbers, for which the nucleus is more stable compared to neighboring isotopes on the nuclear chart. Researchers in both experimental and theoretical nuclear physics from University of Jyväskylä, Finland, took part of international research team, which studied the nuclear charge radii of potassium isotopes. Isotopes were studied by using the collinear resonance ionization spectroscopy technique. The results indicated that the potassium isotope with a neutron number of 32 does not conform with criteria of magic neutron number. The results were published in Nature Physics journal on January 2021.
Far from the stable ...
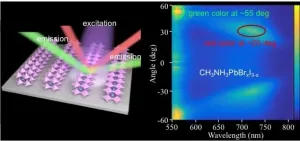
Lead halide perovskites, with high refractive index and excellent optoelectronic property, have been used in both constructing high-quality optical resonators/lasers and fabricating high-efficiency light-emitting devices for advanced displays. Lenticular printing provides an illusion of depth and shows varying images upon view angles, which is considered as a promising approach towards future stereoscopic displays. To realize lenticular-printing-based display, it is required to modulate the outcoupling direction of emission light rather than that of incident light. Ideally, the lenticular-lens-like structures would be integrated into the active layer of light-emitting devices. Therefore, the hybrid perovskite becomes a promising candidate for ...
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine found that while most individuals responded to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) natural reinfection with a typical sustained antibody response associated with protection, a few individuals surprisingly responded atypically, not being able to sustain the antibody response, which declined to levels that made the individuals susceptible to RSV reinfection.
The researchers highlight in their study, published in the journal Vaccine, that their findings point at a subpopulation of people who also may not maintain an antibody response to vaccines and suggest the need to characterize patient-specific responses to respiratory viral infections, such as COVID-19.
"RSV is ...
Anyone who's been to a concert knows that something magical happens between the performers and their instruments. It transforms music from being just "notes on a page" to a satisfying experience.
A University of Washington team wondered if artificial intelligence could recreate that delight using only visual cues -- a silent, top-down video of someone playing the piano. The researchers used machine learning to create a system, called Audeo, that creates audio from silent piano performances. When the group tested the music Audeo created with music-recognition ...
Researchers from the University of Ottawa have discovered that plants may be able to control the genetics of their intimate root symbionts - the organism with which they live in symbiosis - thereby providing a better understanding of their growth.
In addition to having a significant impact on all terrestrial ecosystems, their discovery may lead to improved eco-friendly agricultural applications.
We talked to research lead Nicolas Corradi, Associate Professor in the Department of Biology and Research Chair in Microbial Genomics at the University of Ottawa, ...
LA JOLLA, CA--As the opioid epidemic raged on with an even greater force during COVID-19, the Scripps Research laboratory of chemist Kim Janda, PhD, has been working on new therapeutic interventions that may be able to prevent the bulk of deaths from opioid overdose.
Janda and his team have developed experimental vaccines that have shown in rodents to blunt the deadly effects of fentanyl--which has been driving the boom in opioid deaths--as well as its even more fatal cousin, carfentanil, a growing source of overdoses and a chemical terrorist threat.
"Synthetic opioids are not only extremely deadly, but also addictive and easy to manufacture, making them a formidable public health threat, especially when the coronavirus crisis is negatively impacting mental health," says Janda, the Ely ...
A team of researchers led by Columbia University has developed a unique platform to program a layered crystal, producing imaging capabilities beyond common limits on demand.
The discovery is an important step toward control of nanolight, which is light that can access the smallest length scales imaginable. The work also provides insights for the field of optical quantum information processing, which aims to solve difficult problems in computing and communications.
"We were able to use ultrafast nano-scale microscopy to discover a new way to control our crystals with light, turning elusive photonic properties on and off at will," said Aaron Sternbach, postdoctoral researcher ...
Army scientists evaluated three nonhuman primate species as potential models of SARS-CoV-2 airborne infection, according to results published online this week in PLOS ONE. Their work demonstrates that any of these species may be useful for testing vaccines and therapies in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, which has resulted in over 104 million cases and more than 2 million deaths worldwide in the past year.
Given the global impact of COVID-19, experts are working rapidly to develop medical countermeasures, and testing in animal models is critically important to evaluate the efficacy of these products. Recent studies suggest that aerosol ...
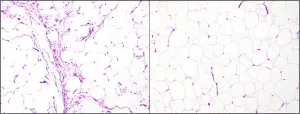
Philadelphia, February 4, 2021 - Researchers have leveraged the latest advances in RNA technology and machine learning methods to develop a gene panel test that allows for highly accurate diagnosis of the most common types of liposarcoma. It quickly and reliably distinguishes benign lipomas from liposarcomas and can be performed in laboratories at a lower cost than current "gold standard" tests. The new assay is described in The Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, published by Elsevier.
"Liposarcomas are a type of malignant cancer that is difficult to diagnose because, even under a microscope, it is hard to differentiate liposarcomas from benign tumors or other types ...
An assessment published this week in the journal The Lancet HIV provides new insight about an initiative to integrate treatment of opioid use disorder along with HIV in Vietnam.
The study marks one of the first scientifically robust assessments of a new model of treating HIV in lower or middle income countries where injection drug use is a major cause of HIV infection. It also suggests the importance of building support for peer and community connections to tackle the opioid epidemic that continues to ravage the United States in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study was led by scientists and physicians at Hanoi Medical University and Oregon Health & Science University.
"Our study suggests that countries that ...