New test provides fast and accurate diagnosis of liposarcomas
Emerging technologies harnessed to develop a faster, cheaper, and more accurate test for these hard-to-diagnose tumors, researchers report in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics
2021-02-04
(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, February 4, 2021 - Researchers have leveraged the latest advances in RNA technology and machine learning methods to develop a gene panel test that allows for highly accurate diagnosis of the most common types of liposarcoma. It quickly and reliably distinguishes benign lipomas from liposarcomas and can be performed in laboratories at a lower cost than current "gold standard" tests. The new assay is described in The Journal of Molecular Diagnosis, published by Elsevier.
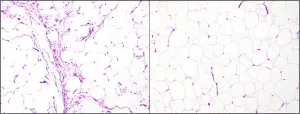
"Liposarcomas are a type of malignant cancer that is difficult to diagnose because, even under a microscope, it is hard to differentiate liposarcomas from benign tumors or other types of cancer that need different treatments," explains lead investigator Torsten Owen Nielsen, MD, PhD, Genetic Pathology Evaluation Centre, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. "Many liposarcomas look like their benign and relatively common counterparts, lipomas. Diagnostic delay and uncertainty cause severe stress for patients, and misdiagnosis can have many consequences including delayed or inadequate treatment or unnecessary surgical procedures and long-term postoperative follow up."
Among the current recommended diagnostic tests for liposarcomas, immunohistochemistry (IHC) is inaccurate and hard to interpret, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is relatively expensive, as well as labor- and equipment-intensive. In this study, investigators explored whether NanoString technology, ideal for analyzing even poor-quality RNA, could allow for more rapid and cost-efficient diagnosis of liposarcomas through gene expression.
The investigators utilized data from the Cancer Genome Atlas, a catalog of genetic information from over 20,000 cancer samples, to identify the 20 most common genes that are overexpressed in liposarcomas. Probes for these genes were designed by NanoString bioinformatics and run on a set of "training samples" that included lipomas and liposarcomas. Analysis of the NanoString results showed clear separation of lipoma from liposarcoma cases.
A machine learning model was developed to determine the probability that a given sample was positive for liposarcoma and was then applied to 45 retrospective cases to determine boundaries for positive and negative predictions. The test was subsequently applied in a real-world clinical setting. A molecular technologist with no knowledge of the clinical, histologic, IHC, or FISH information about the cases was asked to identify each sample as liposarcoma or not liposarcoma from the NanoString test results. The same samples were examined by specialist pathologists using standard testing.
The retrospective and prospective cases probed by the NanoString assay had a 93 percent success rate and agreed with standard tests 97.8 percent of the time. Results from the NanoString assay were available in 36 hours, whereas it took between one to two weeks to get FISH results. NanoString costs amounted to US$270 per case, factoring in reagents, labor, and equipment maintenance.
Advances in biotechnology have shown great promise in other cancers such as breast cancer. "We applied these new technologies to improve patient care in areas where existing diagnostic methods were inaccurate, slow, or costly and saw substantial improvements. There is no patent on this test; anyone can apply the method we describe, and we are happy to help others get set up to run it at their own institution," says Dr. Nielsen.
First author Xiu Qing (Jenny) Wang, a fourth year medical student at the University of British Columbia, adds that accurate and fast diagnosis can be critical for patients who are dealing with what are often difficult and quite large tumors. "I am proud to be part of a team that has made significant progress in bringing this test closer to clinical reality."
This group previously published a NanoString-based assay for sarcomas bearing diagnostic fusion oncogenes, which is now in clinical use. However, the most common type of liposarcoma carries a different type of mutation (gene amplifications) and so was not covered. Thus, the current study not only expands the types of sarcoma that can be diagnosed accurately with NanoString-based diagnostics, but also shows how a different category of mutation can be detected. This strategy may help develop diagnostics for other types of cancer.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-04
An assessment published this week in the journal The Lancet HIV provides new insight about an initiative to integrate treatment of opioid use disorder along with HIV in Vietnam.
The study marks one of the first scientifically robust assessments of a new model of treating HIV in lower or middle income countries where injection drug use is a major cause of HIV infection. It also suggests the importance of building support for peer and community connections to tackle the opioid epidemic that continues to ravage the United States in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study was led by scientists and physicians at Hanoi Medical University and Oregon Health & Science University.
"Our study suggests that countries that ...
2021-02-04
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Egg cells start out as round blobs. After fertilization, they begin transforming into people, dogs, fish, or other animals by orienting head to tail, back to belly, and left to right. Exactly what sets these body orientation directions has been guessed at but not seen. Now researchers at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) have imaged the very beginning of this cellular rearrangement, and their findings help answer a fundamental question.
"The most interesting and mysterious part of developmental biology is the origin of the body axis in animals," said researcher Tomomi Tani. An MBL scientist in the Eugene Bell Center at the time of the research, Tani is now with Japan's National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology.
The work by Tani and ...
2021-02-04
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Chemical manufacturers frequently use toxic solvents such as alcohols and benzene to make products like pharmaceuticals and plastics. Researchers are examining a previously overlooked and misunderstood phenomenon in the chemical reactions used to make these products. This discovery brings a new fundamental understanding of catalytic chemistry and a steppingstone to practical applications that could someday make chemical manufacturing less wasteful and more environmentally sound.
The study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign researcher David Flaherty, University of Minnesota, Twin Cities researcher Matthew Neurock and Virginia Tech researcher Ayman Karim is published in the journal Science.
Combining ...
2021-02-04
For more than a century, optical coatings have been used to better reflect certain wavelengths of light from lenses and other devices or, conversely, to better transmit certain wavelengths through them. For example, the coatings on tinted eyeglasses reflect, or "block out," harmful blue light and ultraviolet rays.
But until now, no optical coating had ever been developed that could simultaneously reflect and transmit the same wavelength, or color.
In a paper in Nature Nanotechnology, researchers at the University of Rochester and Case Western Reserve University describe a new class of optical coatings, so-called Fano Resonance Optical Coatings (FROCs), that can be used on filters to reflect and transmit colors of remarkable purity.
In addition, ...
2021-02-04
The rapid development of silicon-based transistors leads to its integration getting closer to the limit of Moore's law. Graphene is expected to become the next generation of mainstream chip materials due to its ultra-high carrier mobility. However, it is difficult to obtain a high on/off current ratio for intrinsic graphene-based transistor owing to the absence of bandgap. Graphene nanoribbons, which possess a tunable bandgap and unique optoelectrical properties, have attracted extensive attention and exploration.
Nowadays, the preparation of graphene nanoribbons is underdeveloped, and common strategies include the clip of carbon materials (graphene films, carbon nanotubes, or graphite) ...
2021-02-04
When we think about the links to the future - the global transition to solar and wind energy, tactile virtual reality or synthetic neurons - there's no shortage of big ideas. It's the materials to execute the big ideas - the ability to manufacture the lithium-ion batteries, opto-electronics and hydrogen fuel cells - that stand between concept and reality.
Enter two-dimensional materials, the latest step in innovation. Consisting of a single layer of atoms, two-dimensional materials like graphene and phosphorene exhibit new properties with far-reaching potential. With a capability to be combined like Lego bricks, these materials ...
2021-02-04
CLEVELAND--Researchers at Case Western Reserve University, using artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze simple tissue scans, say they have discovered biomarkers that could tell doctors which lung cancer patients might actually get worse from immunotherapy.
Until recently, researchers and oncologists had placed these lung cancer patients into two broad categories: those who would benefit from immunotherapy, and those who likely would not.
But a third category--patients called hyper-progressors who would actually be harmed by immunotherapy, including a shortened lifespan after treatment--has begun ...
2021-02-04
PITTSBURGH, Feb. 4, 2021 - Researchers at UPMC Hillman Cancer Center and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) demonstrate that changing the gut microbiome can transform patients with advanced melanoma who never responded to immunotherapy--which has a failure rate of 40% for this type of cancer--into patients who do.
The results of this proof-of-principle phase II clinical trial were published online today in Science. In this study, a team of researchers from UPMC Hillman administered fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) and anti-PD-1 immunotherapy to melanoma patients ...
2021-02-04
Despite living in the same part of the Mojave Desert, and experiencing similar conditions, mammals and birds native to this region experienced fundamentally different exposures to climate warming over the last 100 years, a new study shows; small mammal communities there remained much more stable than birds, in the face of local climate change, it reports. The study presents an integrative approach to understanding the climate vulnerability of biodiversity in rapidly warming regions. Exposure to rising temperature extremes threatens species worldwide. It is expected to push many ever closer toward extinction. Thus, understanding ...
2021-02-04
The soundscapes of the Anthropocene ocean are fundamentally different from those of pre-industrial times, becoming more and more a raucous cacophony as the noise from human activity has grown louder and more prevalent. In a Review, Carlos Duarte and colleagues show how the rapidly changing soundscape of modern oceans impacts marine life worldwide. According to the authors, mitigating these impacts is key to achieving a healthier ocean. From the plangent songs of cetaceans to grinding arctic sea ice, the world's oceans' natural chorus is performed by a vast ensemble of geological (geophony) and biological (biophony) sounds. However, for more than a century, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New test provides fast and accurate diagnosis of liposarcomas
Emerging technologies harnessed to develop a faster, cheaper, and more accurate test for these hard-to-diagnose tumors, researchers report in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics