Biosensors to detect P. jirovecii, responsible for Pneumocystis pneumonia
This project has detected this atypical fungus, responsible for very serious pneumonia in immunosuppressed patients
2021-02-05
(Press-News.org) The group led by Dr. Enrique J. Calderón - "Clinical Epidemiology and Vascular Risk" at the Institute of Biomedicine of Seville - IBiS/University Hospitals Virgen del Rocío and Macarena/CSIC/University of Seville, also a member of CIBERESP, participated in a project with researchers from CIBER-BBN, in which they developed systems to detect Pneumocystis jirovecii, an atypical fungus responsible for very severe pneumonia in immunosuppressed patients. The results have been published in the journals Nanomaterials and Journal of Fungi, and are the fruit of collaboration with the CIBER-BBN groups led by Dr. Laura Lechuga, Dr. Ramon Eritja and Dr. Ramón Martínez Máñez.
Currently, the detection of the fungus in patients, who may be asymptomatic carriers until they develop pneumonia, uses the PCR technique, which takes several hours and requires adequate facilities and qualified personnel. However, the application of nanotechnology now makes it possible to develop more sensitive and efficient biosensors to detect specific sequences corresponding to pathogens responsible for infectious diseases in a shorter time and without the need for major infrastructure.
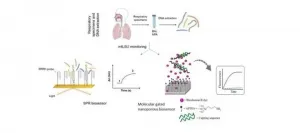
In this case, a specific sequence that corresponds to the gene belonging to the ribosomal subunit (mtLSU rRNA) of the fungus P. jirovecii has been detected using fork-shaped capture probes. These specific probes, "are more efficient and capable of recognising a specific genomic sequence of the fungus and forming very stable triplex structures that can be detected in different biosensor platforms," as Dr. Avignon, a CIBER-BBN researcher at the IQAC-CSIC, points out.
Using an optical biosensor based on SPR technology, Dr. Laura Lechuga's team at ICN2 was able to detect, in real time and without the use of markers, P. jirovecii in bronchoalveolar lavages and nasopharyngeal aspirates with a limit detection at the nM level and all in a matter of minutes.
Likewise, the group headed by Dr. Ramón Martínez-Máñez, scientific director of CIBER-BBN and principal investigator of the IQMA-IDM group at the Universitat Politècnica de València, used the strategy of molecular gates composed of an anodic albumin matrix to develop a sensor capable of efficiently detecting real samples of P. jirovecii without prior amplification steps in just one hour.
"These advances in the diagnosis of PcP have great potential for the development of highly sensitive point-of-care devices using samples taken straight from patients and are applicable in a wide variety of settings," says Dr. Enrique J. Calderón, internist at the Virgen del Rocío University Hospital in Seville and senior lecturer in the Department of Medicine.
The researchers also emphasise that these techniques are very selective and can discriminate patients with other respiratory pathologies derived from other microorganisms, thus enabling a more reliable diagnosis of infectious diseases.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-05
The spinal column consists of 24 vertebrae that provide axial support to the torso and protection to the spinal cord that runs through its central cavity. The vertebrae are connected by means of intervertebral discs. These discs are highly hydrated, flexible and highly mechanically resistant. They allow the column its flexibility and act as shock absorbers during daily activities such as walking, running and in impact situations, such as jumping.
These unique features are made possible by the discs' tissue composition and structure. At its centre, there is a gel-like ...
2021-02-05
At the time of writing, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is seriously threatening human lives and health throughout the world. Before effective vaccines and specific drugs are developed, non-pharmacological interventions and numerical model predictions are essential. To this end, a group led by Professor Jianping Huang from Lanzhou University, China, developed the Global Prediction System of the COVID-19 Pandemic (GPCP).
Jianping Huang is a Professor in the College of Atmospheric Sciences and a Director of the Collaborative Innovation Center for Western Ecological Safety, Lanzhou University, China. He has for a long time been dedicated to studying ...
2021-02-05
The Vlasov-Poisson equations describe many important physical phenomena such as the distribution of gravitating particles in the interstellar space, high-temperature plasma kinetics, and the Landau damping effect. A joint team of scientists from the Mathematical Institute of RUDN University and the Mathematical Institute of the University of Munich suggested a new method to obtain stationary solutions for a system of Vlasov-Poisson equations in a three-dimensional case. The obtained solutions describe the phenomena of stellar dynamics. The results of the study were published in the ...
2021-02-05
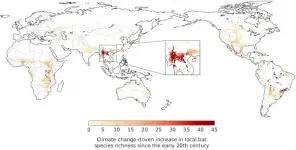
Global greenhouse gas emissions over the last century have made southern China a hotspot for bat-borne coronaviruses, by driving growth of forest habitat favoured by bats.
A new study published today in the journal Science of the Total Environment provides the first evidence of a mechanism by which climate change could have played a direct role in the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that caused the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study has revealed large-scale changes in the type of vegetation in the southern Chinese Yunnan province, and adjacent regions in Myanmar and Laos, over the last century. Climatic changes ...
2021-02-05
Neanderthals' gut microbiota already included some beneficial micro-organisms that are also found in our own intestine. An international research group led by the University of Bologna achieved this result by extracting and analysing ancient DNA from 50,000-year-old faecal sediments sampled at the archaeological site of El Salt, near Alicante (Spain).
Published in Communication Biology, their paper puts forward the hypothesis of the existence of ancestral components of human microbiota that have been living in the human gastrointestinal tract since before the separation between the Homo Sapiens and Neanderthals that occurred more than 700,000 years ago.
"These results allow us to understand which components of the human gut microbiota ...
2021-02-05
New research has identified a nanostructure that improves the anode in lithium-ion batteries
Instead of using graphite for the anode, the researchers turned to silicon: a material that stores more charge but is susceptible to fracturing
The team made the silicon anode by depositing silicon atoms on top of metallic nanoparticles
The resulting nanostructure formed arches, increasing the strength and structural integrity of the anode
Electrochemical tests showed the lithium-ion batteries with the improved silicon anodes had a higher charge capacity and longer lifespan
New research conducted by the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology ...
2021-02-05
USC researchers have developed a new method to counter emergent mutations of the coronavirus and hasten vaccine development to stop the pathogen responsible for killing thousands of people and ruining the economy.
Using artificial intelligence (AI), the research team at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering developed a method to speed the analysis of vaccines and zero in on the best potential preventive medical therapy.
The method is easily adaptable to analyze potential mutations of the virus, ensuring the best possible vaccines are quickly identified -- solutions that give ...
2021-02-05
The early prognosis of high-risk older adults for amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), using noninvasive and sensitive neuromarkers, is key for early prevention of Alzheimer's disease. A recent study, published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, by researchers at the University of Kentucky establishes what they believe is a new way to predict the risk years before a clinical diagnosis. Their work shows that direct measures of brain signatures during mental activity are more sensitive and accurate predictors of memory decline than current standard behavioral testing.
"Many studies have measured electrophysiological rhythms during resting and sleep ...
2021-02-05
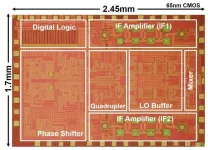
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) and NTT Corporation (NTT) develop a novel CMOS-based transceiver for wireless communications at the 300 GHz band, enabling future beyond-5G applications. Their design addresses the challenges of operating CMOS technology at its practical limit and represents the first wideband CMOS phased-array system to operate at such elevated frequencies.
Communication at higher frequencies is a perpetually sought-after goal in electronics because of the greater data rates that would be possible and to take advantage of underutilized ...
2021-02-05
A new study in Frontiers in Marine Science provides a first-of-its-kind evaluation of which regions of southern European seas are in the most need of fishing restrictions. These areas have persistently shown high numbers of undersized fish and crustaceans, which are typically discarded because they are below the allowable size limit for collection. These findings may offer a strategy for prioritizing conservation efforts and ensuring more sustainable fishery management in the future.
"Natural fish populations need time to reproduce and recover from fishing impacts -- this is the only way to achieve a balance between natural resources and human exploitation," says lead author Dr Giacomo Milisenda, of the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn di Napoli in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Biosensors to detect P. jirovecii, responsible for Pneumocystis pneumonia
This project has detected this atypical fungus, responsible for very serious pneumonia in immunosuppressed patients