(Press-News.org) Berkeley -- The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic last year led to a devastating loss of jobs and income across the global south, threatening hundreds of millions of people with hunger and lost savings and raising an array of risks for children, according to new research co-authored at the University of California, Berkeley.
The research, to be published Friday Feb. 5, 2021, in the journal Science Advances, found "staggering" income losses after the pandemic emerged last year, with a median 70% of households across nine countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America reporting financial losses. By April last year, roughly 50% or more of those surveyed in several countries were forced to eat smaller meals or skip meals altogether, a number that reached 87% for rural households in the West African country of Sierra Leone.
"In the early months of the pandemic, the economic downturn in low- and middle-income countries was almost certainly worse than any other recent global economic crisis that we know of, whether the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s, the Great Recession that started in 2008, or the more recent Ebola crisis," said END
Pandemic caused 'staggering' economic, human impact in developing counties, research says
Falling incomes, smaller meals, educational setbacks among consequences
2021-02-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fingerprint for the formation of nitrous oxide emissions
2021-02-05
Scientists led by Eliza Harris and Michael Bahn from the Institute of Ecology at the University of Innsbruck have succeeded in studying emissions of the greenhouse gas N2O under the influence of environmental impacts in an unprecedented level of detail. The study, which has now been published in Science Advances, is thus also a starting point for the creation of models that could predict future trends in the greenhouse gas emission dynamics of ecosystems under global climate change.
Nitrous oxide (N2O) is a potent greenhouse gas whose atmospheric growth rate has accelerated over the past decade. The largest share of anthropogenic N2O emissions results from the fertilization of soils with nitrogen, which is converted into N2O via various abiotic ...
Genes for face shape identified
2021-02-05
Genes that determine the shape of a person's facial profile have been discovered by a UCL-led research team.
The researchers identified 32 gene regions that influenced facial features such as nose, lip, jaw, and brow shape, nine of which were entirely new discoveries while the others validated genes with prior limited evidence.
The analysis of data from more than 6,000 volunteers across Latin America was published today in Science Advances.
The international research team, led from UCL, Aix-Marseille University and The Open University, found that one of the genes appears ...
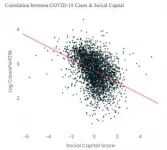
US counties with more social capital have fewer COVID-19 infections and deaths
2021-02-05
US counties with more social capital have fewer COVID-19 infections and deaths - perhaps because these communities have greater concern for the health of others.
INFORMATION:
Article Title: "How social capital helps communities weather the COVID-19 pandemic"
Funding: This research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research [CIHR, FRN-170368; PI: Cary Wu].
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0245135
...
Women's voices in the media still outnumbered by those of men - study
2021-02-05
New research from Simon Fraser University shows that women's voices continue to be underrepresented in the media, despite having prominent female leaders across Canada and internationally. Researchers in SFU's Discourse Processing Lab found that men outnumber women quoted in Canadian news media about three to one. The findings from the team's Gender Gap Tracker study were published this week in the journal PLOS ONE.
The research team collected data from seven major Canadian media outlets from October 2018 to September 2020. Over the two-year period, 29 per cent of people ...
New microscopy concept enters into force
2021-02-05
The development of scanning probe microscopes in the early 1980s brought a breakthrough in imaging, throwing open a window into the world at the nanoscale. The key idea is to scan an extremely sharp tip over a substrate and to record at each location the strength of the interaction between tip and surface. In scanning force microscopy, this interaction is -- as the name implies -- the force between tip and structures on the surface. This force is typically determined by measuring how the dynamics of a vibrating tip changes as it scans over objects deposited on a substrate. A common analogy is tapping a finger across a table and sensing objects placed ...
Gap between the 'haves' and 'have nots' widened by the COVID pandemic, an IU study found
2021-02-05
A new study by Indiana University found women, younger individuals, those with lower levels of formal education, and people of color are being hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal, found that Black adults were three times as likely as whites to report food insecurity, being laid off, or being unemployed during the pandemic. Additionally, residents without a college degree were twice as likely to report food insecurity (compared to those with some college) while those not completing high school are four times as likely to report it, compared ...
COVID-19 transmission extremely low at group of North Carolina day camps
2021-02-05
Cases of symptomatic COVID-19 were extremely low among children and staff at a network of YMCA summer camps held last year in North Carolina that took precautions like masking and physical distancing, with close to zero transmissions occurring at the camps, according to researchers at Duke Health, Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian.
In the camps' 2020 sessions, there were 19 cases of COVID-19 among 5,344 staff and 1,486 youth, only two of which were linked to possible on-site transmission at a group of YMCA of the Triangle camps, at a time ...
Breakthrough in quantum photonics promises a new era in optical circuits
2021-02-05
The modern world is powered by electrical circuitry on a "chip"--the semiconductor chip underpinning computers, cell phones, the internet, and other applications. In the year 2025, humans are expected to be creating 175 zettabytes (175trillion gigabytes) of new data. How can we ensure the security of sensitive data at such a high volume? And how can we address grand-challenge-like problems, from privacy and security to climate change, leveraging this data, especially given the limited capability of current computers?
A promising alternative is emerging quantum communication and computation technologies. For this to happen, however, it will require the widespread ...
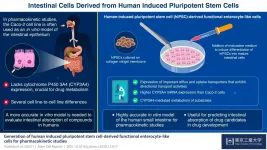
Today's stem cell special: Small intestine on a plate!
2021-02-05
Enterocytes, which line the epithelium of the small intestine, are the sites of absorption and metabolism of most orally consumed medications. For this reason, studies on the absorption of novel oral drugs rely on in vitro or animal models to accurately recreate the environment of the small intestine. Currently, scientists widely use the human colon cancer cell line Caco-2 as a model of the intestinal epithelium. However, this has its drawbacks: Caco-2 cells have been derived from the colon; therefore, they more closely resemble the colon than the small intestine. For example, these cells do not express cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), a protein critical for drug metabolism that is abundantly expressed in the small intestine. Moreover, Caco-2 ...
Grape consumption may protect against UV damage to skin
2021-02-05
Fresno, CA - A recent human study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found that consuming grapes protected against ultraviolet (UV) skin damage.1 Study subjects showed increased resistance to sunburn and a reduction in markers of UV damage at the cellular level. 2 Natural components found in grapes known as polyphenols are thought to be responsible for these beneficial effects.
The study, conducted at the University of Alabama, Birmingham and led by principal investigator Craig Elmets, M.D., investigated the impact of consuming whole grape powder - equivalent to 2.25 cups of grapes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
Physical function is a crucial predictor of survival after heart failure
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
Produce hydrogen and oxygen simultaneously from a single atom! Achieve carbon neutrality with an 'All-in-one' single-atom water electrolysis catalyst
[Press-News.org] Pandemic caused 'staggering' economic, human impact in developing counties, research saysFalling incomes, smaller meals, educational setbacks among consequences