Study describes the diversity of genetic changes that cause inherited kidney disease
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) A study has described genetic changes in patients with the most common form of hereditary kidney disease that affects an estimated 12.5 million people worldwide. The research, which focussed on Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) in Ireland, provides insights into PKD that will assist doctors and patients in the management of this of inherited condition.
The study, led by researchers from the RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in the European Journal of Human Genetics.
In the research, a cohort of 169 patients with PKD in Ireland were analysed. The genetic changes were identified in up to 83% of cases. It is the first time that the diversity of genetic causes of PKD in Ireland have been described. The results will better assist doctors in identifying patients who may require transplantation or dialysis. The findings also have important implications for people who have a family history of PKD and are planning a family or considering kidney donation.
"This study is hugely important in providing us with an insight into the genetic landscape of Polycystic Kidney Disease, the most common form of inherited kidney disease in the world," said first author on the study Dr Katherine Benson, School of Pharmacy and Biomolecular Sciences, RCSI.
"Our findings have implications for the prognosis of patients by helping us to further identify why the disease may progress more rapidly in some cases and how we can reduce the burden of inherited kidney disease in future."
INFORMATION:
The study was carried out by a team of researchers and clinician scientists under the supervision of senior authors Prof. Gianpiero Cavalleri, Professor of Human Genetics at RCSI and Prof. Peter Conlon, Associate Professor of Medicine at RCSI and Consultant Nephrologist at Beaumont Hospital.
The study was supported by an Enterprise Partnership Scheme Fellowship Award from The Irish Research Council, in conjunction with Punchestown Kidney Research Fund. The research was also funded by the Beaumont Hospital Foundation and the Royal Irish Academy.
About RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences
Ranked number one globally for Good Health and Well-being in the Times Higher Education (THE) University Impact Rankings 2020, RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences is an international not-for-profit university, with its headquarters in Dublin.
RCSI is exclusively focused on education and research to drive improvements in human health worldwide. It is among the top 250 universities worldwide in the World University Rankings (2020) and its research is ranked first in Ireland for citations. RCSI has been awarded Athena Swan Bronze accreditation for positive gender practice in higher education.
Visit the RCSI MyHealth Expert Directory to find the details of our experts across a range of healthcare issues and concerns. Recognising their responsibility to share their knowledge and discoveries to empower people with information that leads them to better health, these clinicians and researchers are willing to engage with the media in their area of expertise.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-08
Results from a new study which draws on survey data collected during the peak of the first wave of the pandemic suggests that being forced to slow down life, as a consequence of lockdown, has had significant, positive impacts for many people and their families.
The research, recently published in the British Journal of Psychiatry from a team at the University of Bath with international colleagues, analysed survey results from 385 caregivers of children aged 6-16 both in the UK and Portugal. Individuals completed an online questionnaire between 1 May 2020 and 27 June 2020.
This cohort had ...
2021-02-08
Swapping the car for walking, cycling and e-biking even just one day a week makes a significant impact on personal carbon emissions in cities.
'Active transport' - cycling, e-biking or walking - can help tackle the climate crisis according to a new study led by the University of Oxford's Transport Studies Unit and including researchers from Imperial's Centre for Environmental Policy as part of the EU-funded project PASTA: Physical Activity Through Sustainable Transport Approaches.
Meeting greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets requires a significant move away from motorised transport. The team found that shifting to active transport could save as ...
2021-02-08
Molecular iodine, a major emission from the ocean, can quickly convert to iodic oxoacids even under weak daylight conditions. These oxoacids lead rapidly to aerosol particles that significantly affect climate and human health.
Iodine-containing vapors that are emitted from oceans are a major source of aerosol particles. "Despite their importance to the climate, the formation of marine particles has been poorly understood," says Siddharth Iyer, Postdoctoral Researcher in Aerosol Physics Laboratory at Tampere University.
In this research, the formation of aerosol particles form from iodine-containing vapours under marine boundary layer conditions were studied. The experiments were carried out in the ultra-clean CLOUD chamber in CERN, where the nucleation and growth rates as well as ...
2021-02-08
Cells, like humans, cast votes to make decisions as a group. But how do they know what to vote for? Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and King's College London have uncovered how cells actively seek information in order to make faster and better collective decisions to coordinate the growth of new blood vessels. This provides a new basis for understanding intelligence in cells.
The process of how cells precisely and quickly coordinate action when they create new tissue is complex. They must collectively decide which cells should take on specific jobs and ensure that not too ...
2021-02-08
Is a quantum machine really more efficient than a conventional machine for performing calculations? Demonstrating this 'advantage' experimentally is particularly complex and a major research challenge around the world1. Scientists from the CNRS2, the University of Edinburgh (Scotland) and the QC Ware, Corp., (France and USA) have just proved that a quantum machine can perform a given verification task in seconds when the same exercise would take a time equivalent to the age of the universe for a conventional computer. For this demonstration, they combined a complex interactive algorithm that solves a certain type of mathematical problem with limited information and a simple experimental photonics ...
2021-02-08
Goal 7 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aims to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all by 2030. Yet according to new research by Copenhagen Business School the poor planning and execution of decarbonisation strategies in emerging markets challenges the aims of Goal 7.
"In the effort to produce renewable energy and decarbonise their economies, emerging countries have neglected the effect on marginalised populations, which could ultimately prove unsustainable for all," says Assistant Professor Jacobo Ramirez from the ...
2021-02-08
An important class of challenging computational problems, with applications in graph theory, neural networks, artificial intelligence and error-correcting codes can be solved by multiplying light signals, according to researchers from the University of Cambridge and Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology in Russia.
In a paper published in the journal Physical Review Letters, they propose a new type of computation that could revolutionise analogue computing by dramatically reducing the number of light signals needed while simplifying the search for the best mathematical solutions, allowing for ultra-fast optical computers.
Optical or ...
2021-02-08
A way of using machine learning to more accurately identify patients with a mix of psychotic and depressive symptoms has been developed by researchers at the University of Birmingham.
Patients with depression or psychosis rarely experience symptoms of purely one or the other illness. Historically, this has meant that mental health clinicians give a diagnosis of a 'primary' illness, but with secondary symptoms. Making an accurate diagnosis is a big challenge for clinicians and diagnoses often do not accurately reflect the complexity of individual experience or indeed neurobiology.
Clinicians diagnosing psychosis, for example, would frequently regard depression as a secondary illness, with implications for treatment decisions which focus more on ...
2021-02-08
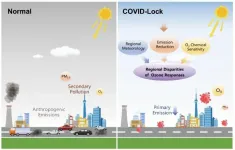
The outbreak of COVID-19 raised a question about the relationship between anthropogenic emissions and air pollution, which has aroused heated discussion. Research on air-quality changes caused by the lockdowns in different areas shows similar substantial reductions in primary emissions. However, regional disparities exist in responses of secondary pollutants to emissions reduction, especially fine particulate matter and ozone (O3).
Professor Ding Aijun and his team from Nanjing University explored global air-quality changes during COVID-19 lockdowns and regional disparities in O3 responses to emission reductions. They integrated multiple observational datasets, including global air quality ...
2021-02-08
In a new study published in Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, Chen-Yu Zhang's group and Antonio Vidal-Puig's group at University of Cambridge report that pancreatic β cells secrete miR-29 family members (miR-29a, miR-29b and miR-29c) in response to high levels of free fatty acids (FFAs). These β cell-derived miR-29s are delivered to the liver, promoting insulin resistance and enhancing hepatic glucose output.
Over 100 years after insulin was discovered, it was believed that pancreatic β cells only secreted a single hormone--insulin. Pancreatic β cell-derived insulin regulates glucose homeostasis by binding with the insulin receptors located in the liver, skeletal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study describes the diversity of genetic changes that cause inherited kidney disease