INFORMATION:
Notes:
1 In 2019, Google achieved the first demonstration of this type when it sampled from random quantum circuits on their Sycamore chip, made of 53 superconducting qubits. Very recently, Chinese researchers have shown a quantum advantage with boson sampling using an elaborate photonic configuration.
2 At the LIP6 Laboratory (CNRS/Sorbonne University) and the Institut de Recherche en Informatique Fondamentale (CNRS/University of Paris)
The quantum advantage: a novel demonstration
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) Is a quantum machine really more efficient than a conventional machine for performing calculations? Demonstrating this 'advantage' experimentally is particularly complex and a major research challenge around the world1. Scientists from the CNRS2, the University of Edinburgh (Scotland) and the QC Ware, Corp., (France and USA) have just proved that a quantum machine can perform a given verification task in seconds when the same exercise would take a time equivalent to the age of the universe for a conventional computer. For this demonstration, they combined a complex interactive algorithm that solves a certain type of mathematical problem with limited information and a simple experimental photonics system that can be made in all advanced photonics laboratories. Their work was published on 8 February 2021 in Nature Communications.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does Goal 7 Energy for All need a rethink?
2021-02-08
Goal 7 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aims to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all by 2030. Yet according to new research by Copenhagen Business School the poor planning and execution of decarbonisation strategies in emerging markets challenges the aims of Goal 7.
"In the effort to produce renewable energy and decarbonise their economies, emerging countries have neglected the effect on marginalised populations, which could ultimately prove unsustainable for all," says Assistant Professor Jacobo Ramirez from the ...
'Multiplying' light could be key to ultra-powerful optical computers
2021-02-08
An important class of challenging computational problems, with applications in graph theory, neural networks, artificial intelligence and error-correcting codes can be solved by multiplying light signals, according to researchers from the University of Cambridge and Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology in Russia.
In a paper published in the journal Physical Review Letters, they propose a new type of computation that could revolutionise analogue computing by dramatically reducing the number of light signals needed while simplifying the search for the best mathematical solutions, allowing for ultra-fast optical computers.
Optical or ...
Machine learning could aid mental health diagnoses
2021-02-08
A way of using machine learning to more accurately identify patients with a mix of psychotic and depressive symptoms has been developed by researchers at the University of Birmingham.
Patients with depression or psychosis rarely experience symptoms of purely one or the other illness. Historically, this has meant that mental health clinicians give a diagnosis of a 'primary' illness, but with secondary symptoms. Making an accurate diagnosis is a big challenge for clinicians and diagnoses often do not accurately reflect the complexity of individual experience or indeed neurobiology.
Clinicians diagnosing psychosis, for example, would frequently regard depression as a secondary illness, with implications for treatment decisions which focus more on ...
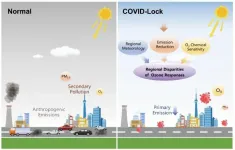
New research reveals drivers of regionally different ozone responses to the COVID-19
2021-02-08
The outbreak of COVID-19 raised a question about the relationship between anthropogenic emissions and air pollution, which has aroused heated discussion. Research on air-quality changes caused by the lockdowns in different areas shows similar substantial reductions in primary emissions. However, regional disparities exist in responses of secondary pollutants to emissions reduction, especially fine particulate matter and ozone (O3).
Professor Ding Aijun and his team from Nanjing University explored global air-quality changes during COVID-19 lockdowns and regional disparities in O3 responses to emission reductions. They integrated multiple observational datasets, including global air quality ...
Beyond secretion of insulin,the novel function of β cell in regulating glucose homeostasis
2021-02-08
In a new study published in Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, Chen-Yu Zhang's group and Antonio Vidal-Puig's group at University of Cambridge report that pancreatic β cells secrete miR-29 family members (miR-29a, miR-29b and miR-29c) in response to high levels of free fatty acids (FFAs). These β cell-derived miR-29s are delivered to the liver, promoting insulin resistance and enhancing hepatic glucose output.
Over 100 years after insulin was discovered, it was believed that pancreatic β cells only secreted a single hormone--insulin. Pancreatic β cell-derived insulin regulates glucose homeostasis by binding with the insulin receptors located in the liver, skeletal ...
Scientists measure spectral line of Cherenkov radiation in radiant regime
2021-02-08
The scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with the colleagues from Keysight company have conducted an experiment with an electron beam at the TPU microtron to study a super-radiant regime that occurs when radiation is generated by a train of electron bunches. The research findings obtained by a high-precision measurement of a spectral line width proved that about 8,000 electron bunches in a super-radiant regime form monochromatic Cherenkov radiation. This experiment was conducted for the first time. The fundamental research findings are published in the Scientific Reports academic journal (IF: 4.120, Q1) and can be used for further research on the new sources of radiation in the terahertz range.
A super-radiant regime is a coherent ...
Can the brain resist the group opinion?
2021-02-08
Scientists at HSE University have learned that disagreeing with the opinion of other people leaves a 'trace' in brain activity, which allows the brain to later adjust its opinion in favour of the majority-held point of view. The article was published in Scientific Reports.
We often change our beliefs under the influence of others. This social behavior is called conformity and explains varios components of our behaviour, from voting at elections to fashion trends among teenagers.
Brain research has recently well informed about short-term effects of social influence on decision making. If our choice coincides with the point of view of the people who are important to us, this decision is reinforced in ...
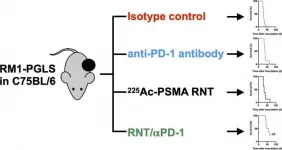
Joint radionuclide therapy-immunotherapy approach effective in prostate cancer model
2021-02-08
Reston, VA--A combination of radionuclide therapy and immunotherapy has proven successful in slowing the progression of prostate cancer and increasing survival time, according to new research published in the February issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. The results of the murine study indicate that radionuclide therapy promotes prostate cancer immunogenicity, provoking a cellular response that makes the tumors more receptive to immunotherapy.
"Prostate cancer is generally viewed as an immunological cold cancer in which immunotherapies only have moderate success," said Katharina Lückerath, PhD, assistant professor of preclinical ...
A billion years in 40 seconds: video reveals our dynamic planet
2021-02-08
Geoscientists have released a video that for the first time shows the uninterrupted movement of the Earth's tectonic plates over the past billion years.
The international effort provides a scientific framework for understanding planetary habitability and for finding critical metal resources needed for a low-carbon future.
It reveals a planet in constant movement as land masses move around the Earth's surface, for instance showing that Antarctica was once at the equator.
The video is based on new research published in the March 2021 edition of ...
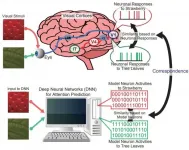
Correspondence between representations in visual cortices and neural networks
2021-02-08
This discovery was made possible by applying the research method for the comparison of the brain activity between monkeys and humans to artificial neural networks. This finding might be helpful not only to understand the cortical mechanism of attentional selection but also to develop artificial intelligence.
Deep neural networks (DNNs), which are used in the development of artificial intelligence, are mathematical models for obtaining appropriate mechanisms to solve specific problems from the training with a large-scale dataset. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying DNNs through ...