Scientists measure spectral line of Cherenkov radiation in radiant regime
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) The scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with the colleagues from Keysight company have conducted an experiment with an electron beam at the TPU microtron to study a super-radiant regime that occurs when radiation is generated by a train of electron bunches. The research findings obtained by a high-precision measurement of a spectral line width proved that about 8,000 electron bunches in a super-radiant regime form monochromatic Cherenkov radiation. This experiment was conducted for the first time. The fundamental research findings are published in the Scientific Reports academic journal (IF: 4.120, Q1) and can be used for further research on the new sources of radiation in the terahertz range.
A super-radiant regime is a coherent addition of fields from a sequence of radiating charges. With their periodic sequence, radiation for certain wavelengths occurs in phase, resulting in a narrow spectral line. The development of laser technologies as a whole is focused on creating the sources of monochromatic radiation in different ranges of wavelengths.
"Various fields of industry, medicine and science require the sources with narrow spectral lines (sources of highly monochromatic radiation).
For a number of applications, the use of laser technologies does not provide for the required parameters, therefore, recently, new types of sources based on electron radiation have intensively been developing.
In this case, radiation is generated by a beam of electrons that consists of a periodic set of bunches emitted at a certain interval," Alexander Potylitsyn, Professor of the TPU Research School of High-Energy Physics, says.
The main question the scientists posed to themselves was whether it was possible to prove that as the number of bunches increases, their frequency remains constant, the in-phase condition is satisfied and a coherent addition of radiation from each bunch occurs. The TPU scientists performed the measurements at the TPU microtron in the gigahertz range using a special high-precision spectrometry equipment provided by Keysight. The measurements showed that the width of a radiation spectral line was less than 0.01 percent. Based on the measurement result, the scientists defined that the number of coherently radiating sources was approximately 8,000.
"Earlier, similar experiments were conducted using interferometers, standard devices, which have a finite resolution and allow for measuring the width of a spectral line at a 1 percent level.
In most cases, that was sufficient. However, we were interested in going below the 1 percent threshold and the colleagues from Keysight were interested in working with electron accelerators. Our mutual interest turned into such an unexpected result," Alexander Potylitsyn explains.
The authors of the article emphasize that the experiment with electron beams using this kind of equipment was conducted for the first time and is of a fundamental nature. Its results can be used in the development and creation of monochromatic sources of radiation in the extremely demanded terahertz range.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-08
Scientists at HSE University have learned that disagreeing with the opinion of other people leaves a 'trace' in brain activity, which allows the brain to later adjust its opinion in favour of the majority-held point of view. The article was published in Scientific Reports.
We often change our beliefs under the influence of others. This social behavior is called conformity and explains varios components of our behaviour, from voting at elections to fashion trends among teenagers.
Brain research has recently well informed about short-term effects of social influence on decision making. If our choice coincides with the point of view of the people who are important to us, this decision is reinforced in ...
2021-02-08
Reston, VA--A combination of radionuclide therapy and immunotherapy has proven successful in slowing the progression of prostate cancer and increasing survival time, according to new research published in the February issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. The results of the murine study indicate that radionuclide therapy promotes prostate cancer immunogenicity, provoking a cellular response that makes the tumors more receptive to immunotherapy.
"Prostate cancer is generally viewed as an immunological cold cancer in which immunotherapies only have moderate success," said Katharina Lückerath, PhD, assistant professor of preclinical ...
2021-02-08
Geoscientists have released a video that for the first time shows the uninterrupted movement of the Earth's tectonic plates over the past billion years.
The international effort provides a scientific framework for understanding planetary habitability and for finding critical metal resources needed for a low-carbon future.
It reveals a planet in constant movement as land masses move around the Earth's surface, for instance showing that Antarctica was once at the equator.
The video is based on new research published in the March 2021 edition of ...
2021-02-08
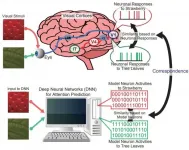
This discovery was made possible by applying the research method for the comparison of the brain activity between monkeys and humans to artificial neural networks. This finding might be helpful not only to understand the cortical mechanism of attentional selection but also to develop artificial intelligence.
Deep neural networks (DNNs), which are used in the development of artificial intelligence, are mathematical models for obtaining appropriate mechanisms to solve specific problems from the training with a large-scale dataset. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying DNNs through ...
2021-02-08
On Feb 5th, Seoul National University, College of Engineering (Dean Kookheon Char) announced that Professor Sang Woo Seo's research team (Dr. Jina Yang and Mr. Yong Hee Han (graduate student)) at School of Chemical and Biological Engineering has developed a synthetic protein quality control system to enhance full-length translation in bacteria. This technology is expected to increase the efficiency of the production of biopharmaceuticals, industrial enzymes, and bio-based chemicals.
Recombinant proteins are used in various industrial fields from protein drugs such as insulin to industrial proteins such as laundry detergents. Since proteins can perform their functions only with full-length and proper 3D structure, recombinant protein production ...
2021-02-08
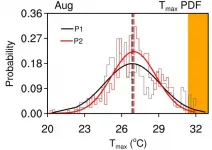
Against the background of global warming, extreme heat days (EHDs) occur frequently and greatly threaten human health and societal development. Therefore, it is of great importance to understand the variation of EHDs.
Previous studies have indicated that the frequency of EHDs is mainly modulated by the mean state of temperature, and thus the frequency of EHDs mostly presents an increasing trend.
"However, the variability of the daily maximum temperature also plays an important role in the interdecadal change of extreme heat days over Northeast China," says Ms. Liu Wenjun, a Master's student from the group of Dr. Ruidan Chen in the School of Atmospheric Sciences ...
2021-02-08
Researchers from Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) and the Faculty of Medicine at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CU Medicine) have jointly developed the Spermine Risk Score which, coupled with the use of a urine test, provides a non-invasive and more reliable method for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. In a study conducted by the researchers, about 37% of the patients, who were ultimately found to have no prostate cancer, can avoid undergoing a prostate biopsy procedure. The findings have just been published in the scientific journal Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases.
Demand for more reliable and non-invasive diagnosis
Prostate cancer is the third most common and the fourth most fatal cancer for the male ...
2021-02-08
Which bananas end up in your shopping basket-- the uniformly yellow ones or those with brown spots?
If you are like most people, you skip the spotted ones and select those that are perfectly yellow. This is because emotions play an an oversized role in our shopping decisions, according to a new study by Danish and Swedish researchers.
"We choose food based upon an expectation of what it will taste like that is bound to our feelings. So, if we expect a brown banana to not match the taste of a yellow one, we opt for the latter," explains Karin Wendin, an associate professor at University of Copenhagen's Department of Food Science, and one of the researchers behind the study.
Approximately 716,000 tonnes ...
2021-02-08
A team of researchers led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a new material, that when electricity is applied to it, can flex and bend forty times more than its competitors, opening the way to better micro machines.
Conversely, when it is bent, it generates electricity very effectively and could be used for better "energy harvesting" - potentially recharging batteries in gadgets just from everyday movements.
The novel material is both electrostrictive and piezoelectric. Its electrostrictive properties means it can change shape when an electric current is applied, while piezoelectric means the material can convert pressure into electric charges.
When an electric field is applied, the atoms that make up electrostrictive ...
2021-02-08
Although SGLT-2 inhibitors are central to the treatment of diabetes, their exact mode of action was hitherto unknown. In a study conducted by a research group led by Peter Wolf, Martin Krssak and Michael Krebs from MedUni Vienna's Department of Medicine III, magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) was used to show that there is a direct correlation between the elimination of glucose via the kidneys and new glucose production in the liver. A single dose of the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin gives rise to a beneficial regulation mechanism, in which glucose loss due to drug-induced SGLT-2 inhibition is exactly balanced out by an equal increase in new glucose production in the liver. The study has been published in the leading journal Diabetes Care.
Dapagliflozin is a drug from the group ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists measure spectral line of Cherenkov radiation in radiant regime