Synthetic protein quality control system in bacteria
2021-02-08
(Press-News.org) On Feb 5th, Seoul National University, College of Engineering (Dean Kookheon Char) announced that Professor Sang Woo Seo's research team (Dr. Jina Yang and Mr. Yong Hee Han (graduate student)) at School of Chemical and Biological Engineering has developed a synthetic protein quality control system to enhance full-length translation in bacteria. This technology is expected to increase the efficiency of the production of biopharmaceuticals, industrial enzymes, and bio-based chemicals.
Recombinant proteins are used in various industrial fields from protein drugs such as insulin to industrial proteins such as laundry detergents. Since proteins can perform their functions only with full-length and proper 3D structure, recombinant protein production using microbial cell factories requires several protein purification steps. To enhance the yield of the production process, strain improvement techniques have been developed to increase the target protein expression level or to supplement the insufficient amino acids in a cell. However, since transcription and translation steps occur in the same place at the same time in bacteria, truncated mRNA can be served as a template for translation by ribosome resulting in the production of incomplete polypeptides.
The Protein Quality Control system (ProQC), developed by Prof. Seo's research team, is a synthetic gene expression cassette that allows ribosomes to only use intact mRNA as a template. In eukaryotic expression systems, the translation process is initiated after the transcription process is completed. By mimicking this, when the transcription process is completed, the cis-trigger element at the 3'end of mRNA can hybridize with Toehold switch at the 5'end and expose ribosome binding sites for the translation. Also, the mRNA becomes circular ensuring efficient re-initiation of ribosomes.
By applying the ProQC system to various protein expressions, the bacterial cells synthesized more full-length proteins (up to 250%). In addition, when the enzymes in the biochemical synthesis pathways were expressed under the control of the ProQC system, the target metabolite production levels were also increased more than two times.
Professor Sang Woo Seo said, "The gene expression system developed in this study allows bacteria to selectively translate intact mRNA to synthesize high-quality proteins by themselves. Also, as this technology is applied to a new level of regulation, there will be synergies when used with existing recombinant protein production strategies. It will dramatically improve the efficiency of the microbial cell factory-based recombinant protein and biochemical production."
INFORMATION:
The study, which was published online in Nature Chemical Biology on February 5th (KST), was conducted with the support from the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program, C1 Gas Refinery Program, and the Basic Research Laboratory Project through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
Information
Title: Synthetic protein quality control to enhance full-length translation in bacteria
Journal: Nature Chemical Biology (2021)
DOI: 10.1038/s41589-021-00736-3
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41589-021-00736-3
First authors: Jina Yang (SNU Researcher), Yong Hee Han (SNU graduate student)
Corresponding author: Sang Woo Seo (SNU Professor)
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-08
Against the background of global warming, extreme heat days (EHDs) occur frequently and greatly threaten human health and societal development. Therefore, it is of great importance to understand the variation of EHDs.
Previous studies have indicated that the frequency of EHDs is mainly modulated by the mean state of temperature, and thus the frequency of EHDs mostly presents an increasing trend.
"However, the variability of the daily maximum temperature also plays an important role in the interdecadal change of extreme heat days over Northeast China," says Ms. Liu Wenjun, a Master's student from the group of Dr. Ruidan Chen in the School of Atmospheric Sciences ...
2021-02-08
Researchers from Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) and the Faculty of Medicine at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CU Medicine) have jointly developed the Spermine Risk Score which, coupled with the use of a urine test, provides a non-invasive and more reliable method for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. In a study conducted by the researchers, about 37% of the patients, who were ultimately found to have no prostate cancer, can avoid undergoing a prostate biopsy procedure. The findings have just been published in the scientific journal Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases.
Demand for more reliable and non-invasive diagnosis
Prostate cancer is the third most common and the fourth most fatal cancer for the male ...
2021-02-08
Which bananas end up in your shopping basket-- the uniformly yellow ones or those with brown spots?
If you are like most people, you skip the spotted ones and select those that are perfectly yellow. This is because emotions play an an oversized role in our shopping decisions, according to a new study by Danish and Swedish researchers.
"We choose food based upon an expectation of what it will taste like that is bound to our feelings. So, if we expect a brown banana to not match the taste of a yellow one, we opt for the latter," explains Karin Wendin, an associate professor at University of Copenhagen's Department of Food Science, and one of the researchers behind the study.
Approximately 716,000 tonnes ...
2021-02-08
A team of researchers led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a new material, that when electricity is applied to it, can flex and bend forty times more than its competitors, opening the way to better micro machines.
Conversely, when it is bent, it generates electricity very effectively and could be used for better "energy harvesting" - potentially recharging batteries in gadgets just from everyday movements.
The novel material is both electrostrictive and piezoelectric. Its electrostrictive properties means it can change shape when an electric current is applied, while piezoelectric means the material can convert pressure into electric charges.
When an electric field is applied, the atoms that make up electrostrictive ...
2021-02-08
Although SGLT-2 inhibitors are central to the treatment of diabetes, their exact mode of action was hitherto unknown. In a study conducted by a research group led by Peter Wolf, Martin Krssak and Michael Krebs from MedUni Vienna's Department of Medicine III, magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) was used to show that there is a direct correlation between the elimination of glucose via the kidneys and new glucose production in the liver. A single dose of the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin gives rise to a beneficial regulation mechanism, in which glucose loss due to drug-induced SGLT-2 inhibition is exactly balanced out by an equal increase in new glucose production in the liver. The study has been published in the leading journal Diabetes Care.
Dapagliflozin is a drug from the group ...
2021-02-08
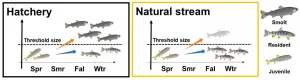
Researchers at the Kobe University Graduate School of Science have revealed that when captive-bred juvenile red-spotted masu salmon are released into natural streams, very few individuals become migrants.
Red-spotted masu salmon was an important fish species for the fishing industry in the rivers of west Japan, however in recent years their numbers are declining rapidly. The results of this research offer important suggestions for stocking practices and the management of river environments.
The research group consisted of graduate school students TANAKA Tatsuya and UEDA Rui and Associate Professor SATO Takuya. The results were published in Biology Letters ...
2021-02-08
[Background]
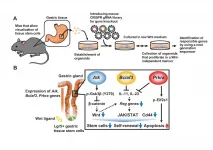
The human body consists of about 60 trillion cells that are renewed day by day to maintain homeostasis of body tissues. In particular, cells of the digestive tract are renewed completely within several weeks thanks to vigorous proliferation where tissue stem cells of every tissue play critical roles in supplying those cells. Tissue stem cells play essential roles in various phenomena such as histogenesis and recovery from damage by producing differentiated cells while dividing. They do this by producing identical cells (self-renewal) or by differentiating into other types of cells. The research team led by Profs. Murakami and Barker of the Cancer Research Institute, Kanazawa University revealed ...
2021-02-08
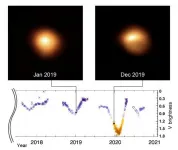
Betelgeuse is normally one of the brightest, most recognizable stars of the winter sky, marking the left shoulder of the constellation Orion. But lately, it has been behaving strangely: an unprecedentedly large drop in its brightness has been observed in early 2020 (Figure 1), which has prompted speculation that Betelgeuse may be about to explode.
To find out more, an international team of scientists, including Ken'ichi Nomoto at the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU), conducted a rigorous examination of Betelgeuse. They concluded that the star is in the early core helium-burning phase (which is more than 100,000 ...
2021-02-08
A study reveals the genetic factors that may expose or protect people with Down syndrome from SARS-CoV-2 infection, as well as the prognosis of COVID-19.
Their findings, which are published in the journal Scientific Reports, follow previous studies showing a tenfold mortality risk of COVID-19 for people with Down syndrome, adding further evidence to boost existing calls for priority vaccination of the medically vulnerable group.
The researchers analysed all publicly available Down syndrome transcriptomic data to uncover alterations that might affect SARS-CoV-2's infection and disease progression.
TMPRSS2, a gene that codes for an enzyme critical for aiding the entry of SARS-CoV-2 in human cells, had 60% higher levels ...
2021-02-08
A study carried out at the University of Helsinki indicates that agricultural activity confuses the mechanisms that regulate the occurrence of plant diseases in nature. A wider variety of virus species was found in meadows close to agricultural fields compared to those located in natural surroundings, with the richness of plant species having no effect on the number of virus species. However, maintaining biodiversity is worthwhile, as plant richness did reduce the number of viral infections in the meadows.
An increasing share of the global land area is used for agricultural purposes, with more and more of the remaining area located at the boundary between agricultural and natural land, also known as the agro-ecological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Synthetic protein quality control system in bacteria