(Press-News.org) Scientists studying forest dwelling butterflies in Central and South America have discovered that changes in the way animals perceive and process information from their environment can support the emergence of new species. The study led by the University of Bristol, and published today [9 February] in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), has implications for how new species might evolve and the underappreciated role of changes in the brain.
The international team, led by Dr Stephen Montgomery from the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Bristol, compared the brain morphology of two distinct but closely related lineages of butterfly that occur in distinct tropical forest habitats. The first, including the species Heliconius cydno, lives in deeper forests, where the canopy light levels are low. Its sister lineage, including a species called Heliconius melpomene, lives around the forest edges, where light is much more abundant. Despite their ecological differences, these species are very closely related and can still produce viable offspring, suggesting they sit right at the brink of being new species.
The team found substantial differences in the brains of forest edge and deep forest species, with the latter investing more in parts of the brain that process visual information. By collecting butterflies across south and central America, as well as rearing captive individuals under controlled conditions at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Panama, the researchers showed that differences in brain morphology have accumulated in a way consistent with natural selection.
Dr Stephen Montgomery, Senior Research Fellow at Bristol, said: "These butterflies aren't separated by huge distances, nor are they distantly related, but their brain structure is finely tuned to the specific habitats they occupy, and we think this process helps keep the two lineages apart, allowing them to become distinct species."
Similar differences were seen when the team examined the how highly different genes were expressed in the brain.
Matteo Rossi, a PhD student at LMU Munich, explained: "Based on the pattern of gene expression in brain tissue we can accurately cluster individuals into the correct species. The expression of genes driving these differences evolve fast, and seem to be located in regions of the genome that are most distinct between the two species."
To further explore these effects the team produced hybrid offspring between forest edge and deep forest species. They found these hybrids showed intermediate brain morphologies and patterns of gene expression in the brain.
Dr Richard Merrill, also from LMU Munich, said: "Our study is exciting because it suggests that hybrids in the wild might be behavioural misfits in both habitats, and suffer the consequences."
The researchers believe that the work may imply adaptations in the brain play an underappreciated role in speciation across environments.
"We're used to thinking about behaviour being important in speciation, but behavioural evolution must have a neural basis, but we're only just beginning to unpick this kind of process" added Dr Stephen Montgomery.
The team also hope their work illustrates how important it is to protect habitat complexity in tropical forests.
"The forest is a tapestry of different conditions, with different structures, resources and cues. This work illustrates how closely species evolve to occupy these different micro-habitats, supporting high numbers of species in seemingly small areas" said Dr Owen McMillan, a co-author from the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Panama, "if we want to protect the diversity of species in these areas, we have to protect the forests in a way that supports their natural variability."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded with support from the Royal Commission for the Great Exhibition of 1851, The Leverhulme Trust, British Ecological Society, the Natural Environment Research Council, the DFG and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute.
BOSTON -- Hospitals across the United States have gone to great lengths to implement infection control measures to prevent transmission of SARS-CoV-2. And yet, as the pandemic has unfolded, many health care settings have experienced clusters of cases, with the virus spreading among patients, staff or both. Some clusters have been easily traced back to break rooms and shared meals. But other clusters have been challenging to trace and contain. In September 2020, Brigham and Women's Hospital detected a cluster of infections that would ultimately include 14 patients and 38 staff members. The hospital rapidly activated its incident command structure in order to coordinate a controlled response to contain the cluster. Steps taken included widespread ...
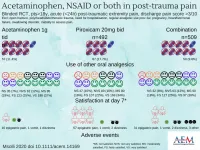
DES PLAINES, IL -- The combination of a high?dose NSAID with paracetamol does not increase the analgesic effect compared to paracetamol alone. Researchers also found that paracetamol alone is superior to high?dose NSAID alone for posttraumatic extremity pain. These are the findings of a study titled Acetaminophen, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or combination of both analgesics in acute post-trauma pain: a randomized controlled trial, to be published in the February 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
According to the study, taking into account its superior efficacy ...
Today, the average American is unlikely to spend time worrying about malaria. Although the disease is commonly perceived to be restricted to other parts of the world, it played a significant role in shaping American history. It even helped turn the tide of the American Revolutionary War by infecting so many British soldiers that General Cornwallis was forced to surrender at Yorktown.
First-year students in a 2019 introductory seminar class led by Erin Mordecai, an assistant professor of biology in the School of Humanities and Sciences (H&S), delved ...
Samara Polytech chemists investigated the potential anticarcinogenic effects of extracts obtained from plant materials of lingonberry, raspberry, black chokeberry, grapes, Krasnodar green tea, ginseng, fireweed and coffee, and also evaluated their effect on the growth and viability of colon cancer cells. The research was carried out within the framework of the state assignment for fundamental research No. 0778-2020-0005, its results were published Dec. 29, 2020 in the journal Proceedings of Universities. Applied Chemistry and Biotechnology (DOI: https://doi.org/10.21285/2227-2925-2020-10-4-613-626).
Prevention is the most cost-effective and long-term strategy for controlling this disease. It is now well known ...
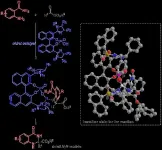
A lot of our medicines and other bioactive drugs are based on chemical structures called "enantiomers"-- molecules that are mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable. Notable among them are chiral N,N-acetals contained in diuretic drugs like bendroflumethiazide and thiabutazide, used to treat high blood pressure and edema. Because an enantiomer and its mirror image version often have different biological activities, with only one of them having pharmacological utility, an "enantioselective" or asymmetric synthesis yielding the desired enantiomer in greater amounts is highly desirable.
In the case of N,N-acetals, several studies have demonstrated their enantioselective preparation from aldehydes, aldimines, or enamines. However, in all these cases, ...
CLEVELAND (Feb. 9)--A study led by Case Western Reserve University researchers found that patients with dementia were at a significantly increased risk for COVID-19--and the risk was higher still for African Americans with dementia.
Reviewing electronic health records of 61.9 million adults in the United States, researchers found the risk of contracting COVID-19 was twice as high for patients with dementia than for those without it--while among those with dementia, African Americans had close to three times the risk of being infected with COVID-19 as Caucasians did.
In addition, patients with dementia who ...
KEY STUDY FINDINGS INCLUDE:
2.9% of U.S. adults report a current peanut allergy.
About one in six adults with a peanut allergy developed it after age 18.
Approximately one in five adults with peanut allergy report visiting the emergency department for food allergy treatment each year.
Patients who developed their peanut allergy during adulthood are less likely to report having an epinephrine auto-injector prescription than those who developed their peanut allergy during childhood, despite similar frequencies of severe reactions among both groups.
CHICAGO --- Peanut allergy affects at least 4.5 million adults in the U.S., many of whom report developing their ...
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and other institutions have identified a novel strategy that can eliminate bacteria in a specific location before they cause an infection. The strategy uses a phage, a virus that infects and destroys bacteria, that can specifically locate in the same place the bacteria live in the gastrointestinal tract. The proximity between phage and bacteria facilitates the phage's attack and subsequent elimination of the bacteria.
This strategy has the potential of becoming a game changer in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria ...
DALLAS, Feb. 9, 2021 -- Participants in a two-year, lifestyle intervention/weight-loss program provided through health coaches at their primary care center were able to lower their blood sugar and improve their cholesterol levels, according to new research published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation Journal. Researchers with the PROmoting Successful Weight Loss in Primary CarE in Louisiana (PROPEL) Trial reported previously that participants also reduced body weight by an average of 5% and note that patients who lost more weight experienced greater improvements in their heart disease risk factors.
"Our results demonstrate lifestyle intervention and weight-loss programs can be successful for people in underserved, low-income ...
DALLAS, Feb. 9, 2021 -- Dietary information from three large, well-known heart disease studies suggests drinking one or more cups of caffeinated coffee may reduce heart failure risk, according to research published today in Circulation: Heart Failure, an American Heart Association journal.
Coronary artery disease, heart failure and stroke are among the top causes of death from heart disease in the U.S. "While smoking, age and high blood pressure are among the most well-known heart disease risk factors, unidentified risk factors for heart disease remain," according to David P. Kao, M.D., senior author of the study, assistant professor of cardiology and medical director at the Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine at the University of Colorado School of Medicine ...