New study discovers possible early detection method for elusive ovarian cancer
University of Minnesota Medical School researchers say Pap tests play a role
2021-02-09
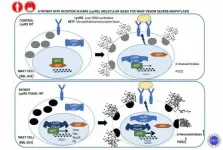
(Press-News.org) A study led by researchers at the University of Minnesota Medical School found a way to detect the presence of ovarian cancer in patients using Pap test samples, normally used to detect cervical cancer. Currently, no early warning system exists for ovarian cancer, which in 2021, is estimated to kill more than 13,700 women, according to the American Cancer Society.
"It is known as a 'silent killer' since women with early stages of ovarian cancer have symptoms that can often be confused with other ailments. Women are typically diagnosed when the cancer has progressed so far that other organs are involved, requiring major surgery and chemotherapy," said Amy Skubitz, PhD, senior author of the study and professor in the Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology. She is also the director of the Ovarian Cancer Early Detection Program at the U of M Medical School. "We set out to identify the proteins present in Pap test samples and cervical swabs to determine whether or not the same proteins are present in ovarian cancer tumor tissues."
This study, published in the journal Clinical Proteomics, found that:
The Pap test and swab samples contained proteins that were also found in the primary tumor of a woman with high-grade serous ovarian cancer;
More than 2,000 proteins were detected in all three sample types collected, suggesting potential biomarker candidates;
Pap test samples, which are already used to detect cervical cancer, may eventually be used to detect ovarian cancer.
"This study is proof of concept that these biospecimens, the Pap test and a swab of the cervix, could be developed for use in the detection of ovarian cancer biomarkers prior to surgery, but it does warrant further investigation," said Skubitz, who is also a member of the Masonic Cancer Center. "Our next step will be to use quantitative mass spectrometry to determine if these proteins or peptides are detected at higher levels in ovarian cancer Pap tests or swabs compared to controls. Their presence alone is not sufficient for diagnosis."
Skubitz also sees an opportunity for this method to be translated into a self-administered, at-home test, where swabs could be collected by women at home and sent to a central laboratory for analysis of proteins that would diagnose ovarian cancer.
INFORMATION:
This project was supported by funding from the Minnesota Ovarian Cancer Alliance, the Cancurables Foundation, Charlene's Light: A Foundation for Ovarian Cancer and the Department of Defense Ovarian Cancer Research Program Pilot Award #W81XWH-16-1-0070.
About the University of Minnesota Medical School
The University of Minnesota Medical School is at the forefront of learning and discovery, transforming medical care and educating the next generation of physicians. Our graduates and faculty produce high-impact biomedical research and advance the practice of medicine. Visit med.umn.edu to learn how the University of Minnesota is innovating all aspects of medicine.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-09
Russian researchers from HSE University have studied a hypothesis regarding the capability of the visual system to automatically categorize objects (i.e., without requiring attention span). The results of a simple and beautiful experiment confirmed this assumption. The paper was published in the journal Scientific Reports. The study was supported by a Russian Science Foundation grant.
Humans receive a lot of information from the environment through their vision. Every day, we face a flow of varied visual stimuli. At the same time, information processing requires cognitive resources. Like a computer processor, the human brain has limited capacity in terms of the data it is able to process and save ...
2021-02-09
Anaphylaxis is a systemic allergic reaction that can affect the skin, the gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The most severe form of anaphylaxis is anaphylactic shock, which features hypotension and can cause death. This reaction can have several causes, such as allergic reactions to food, medicines or insect venom.
The molecular mechanisms that cause the severity of these kinds of reactions is still unknown. In a study led by researchers of the University of Barcelona and IDIBAPS, researchers analyzed the mutation of a gen detected in a patient who suffered from recurrent anaphylactic shocks caused ...
2021-02-09
Growing the right crop in the right place within an impaired watershed can achieve significant water quality improvements, according to Penn State researchers, who conducted a novel study in the drainage of a Susquehanna River tributary in an agricultural area in southeastern Pennsylvania.
The research may reveal a potential path for restoring the troubled Chesapeake Bay, said Patrick Drohan, associate professor of pedology in the College of Agricultural Sciences and one of the study's authors. The bay -- which long has been impaired in large part by nutrients and sediment washing off crop fields and getting into surface waters that feed it -- needs bold solutions, such as changing cropping systems, he suggested.
"Other than when wastewater treatment plants came into compliance ...
2021-02-09
BROOKLYN, New York, Monday, February 8, 2021 -- A holy grail for orthopedic research is a method for not only creating artificial bone tissue that precisely matches the real thing, but does so in such microscopic detail that it includes tiny structures potentially important for stem cell differentiation, which is key to bone regeneration.
Researchers at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering and New York Stem Cell Foundation Research Institute (NYSF) have taken a major step by creating the exact replica of a bone using a system that pairs biothermal imaging with a heated "nano-chisel." In a study, "Cost and Time Effective Lithography of Reusable Millimeter Size Bone Tissue Replicas with Sub-15 nm Feature Size on a Biocompatible ...
2021-02-09
A team of researchers from the Laboratory of Biophysics at NUST MISIS, Lomonosov Moscow State University and D. Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia has summarized metal-containing diagnostic agents for positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging of Alzheimer's disease (AD). According to the researchers, metal-containing radiopharmaceuticals are not only highly effective for detecting early markers of Alzheimer's disease, but also synchrotron-independent and ...
2021-02-09
Bats are the only mammals that can actively fly. Some species travel over one hundred kilometres on their nocturnal excursions in search of food. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior in Radolfzell have now discovered that European free-tailed bats use uplifting winds for their ascents - a behaviour that was previously known only from birds. To do this, they tracked the bats using mini GPS loggers and then linked the flight data to weather data. The animals can thus gain altitude of well over 1,000 metres without expending much energy. The results ...
2021-02-09
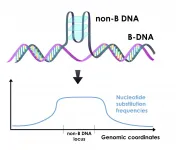
DNA sequences that can fold into shapes other than the classic double helix tend to have higher mutation rates than other regions in the human genome. New research shows that the elevated mutation rate in these sequences plays a major role in determining regional variation in mutation rates across the genome. Deciphering the patterns and causes of regional variation in mutation rates is important both for understanding evolution and for predicting sites of new mutations that could lead to disease.
A paper describing the research by a team of Penn State scientists is available online in the journal Nucleic Acids Research.
"Most of the time we think about DNA as the classic ...
2021-02-09
A 'biological age' score predicts that being male, overweight, a smoker and having depression all contribute to biological aging, a study published today in eLife reports.
Aging can be measured in different ways. While chronological age is measured by date of birth, scientists have developed a range of measurements to determine our biological age. These include measuring the length of telomeres (little caps on the end of our chromosomes that shorten as we grow older), chemical changes to our DNA (epigenetics), and changes to the proteins and metabolites in our bodies ...
2021-02-09
According to the Education Act, schools in the ethnically divided Bosnia and Herzegovina must teach students "democratic ideals in a multicultural society." But according to new research from the University of Copenhagen, the opposite happens: Segregated schools perpetuate ethnic divisions between Croats, Serbs and Bosniaks, making reconciliation after the 1992-1995 wars extremely difficult.
25 years ago, the warring factions in the war in former Yugoslavia signed a peace agreement. Bosnia and Herzegovina, where 100,000 people lost their lives during the war, is now an independent state comprising the Bosnian-Croatian Federation and the Republika Srpska. It is a division that ...
2021-02-09
Social conflicts, from policy debates to family disagreements, can easily devolve into angry words and personal attacks. Such heated confrontations, however, seldom resolve disagreements and can entrench opposing views.
A better approach to resolving interpersonal disagreements is to embrace characteristics that psychological scientists associate with wisdom, like intellectual humility, diverse viewpoints, and open-mindedness.
But applying these elements of wisdom can be difficult, especially during confrontations. The trick, according to new research published ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study discovers possible early detection method for elusive ovarian cancer
University of Minnesota Medical School researchers say Pap tests play a role