Can super-Earth interior dynamics set the table for habitability?
Are super-Earths capable of creating conditions that are hospitable for life to arise and thrive?
2021-02-09
(Press-News.org) Washington, DC-- New research led by Carnegie's Yingwei Fei provides a framework for understanding the interiors of super-Earths--rocky exoplanets between 1.5 and 2 times the size of our home planet--which is a prerequisite to assess their potential for habitability. Planets of this size are among the most abundant in exoplanetary systems. The paper is published in Nature Communications.
"Although observations of an exoplanet's atmospheric composition will be the first way to search for signatures of life beyond Earth, many aspects of a planet's surface habitability are influenced by what's happening beneath the planet's surface, and that's where Carnegie researcher's longstanding expertise in the properties of rocky materials under extreme temperatures and pressures comes in," explained Earth and Planets Laboratory Director Richard Carlson.
On Earth, the interior dynamics and structure of the silicate mantle and metallic core drive plate tectonics, and generate the geodynamo that powers our magnetic field and shields us from dangerous ionizing particles and cosmic rays. Life as we know it would be impossible without this protection. Similarly, the interior dynamics and structure of super-Earths will shape the surface conditions of the planet.
With exciting discoveries of a diversity of rocky exoplanets in recent decades, are much-more-massive super-Earths capable of creating conditions that are hospitable for life to arise and thrive?
Knowledge of what's occurring beneath a super-Earth's surface is crucial for determining whether or not a distant world is capable of hosting life. But the extreme conditions of super-Earth-mass planetary interiors challenge researchers' ability to probe the material properties of the minerals likely to exist there.
That's where lab-based mimicry comes in.
For decades, Carnegie researchers have been leaders at recreating the conditions of planetary interiors by putting small samples of material under immense pressures and high temperatures. But sometimes even these techniques reach their limitations.
"In order to build models that allow us to understand the interior dynamics and structure of super-Earths, we need to be able to take data from samples that approximate the conditions that would be found there, which could exceed 14 million times atmospheric pressure," Fei explained. "However, we kept running up against limitations when it came to creating these conditions in the lab. "
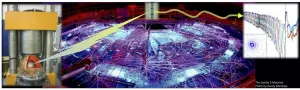
A breakthrough occurred when the team--including Carnegie's Asmaa Boujibar and Peter Driscoll, along with Christopher Seagle, Joshua Townsend, Chad McCoy, Luke Shulenburger, and Michael Furnish of Sandia National Laboratories--was granted access to the world's most powerful, magnetically-driven pulsed power machine (Sandia's Z Pulsed Power Facility) to directly shock a high-density sample of bridgmanite--a high-pressure magnesium silicate that is believed to be predominant in the mantles of rocky planets--in order to expose it to the extreme conditions relevant to the interior of super-Earths.
A series of hypervelocity shockwave experiments on representative super-Earth mantle material provided density and melting temperature measurements that will be fundamental for interpreting the observed masses and radii of super-Earths.
The researchers found that under pressures representative of super-Earth interiors, bridgmanite has a very high melting point, which would have important implications for interior dynamics. Under certain thermal evolutionary scenarios, they say, massive rocky planets might have a thermally driven geodynamo early in their evolution, then lose it for billions of years when cooling slows down. A sustained geodynamo could eventually be re-started by the movement of lighter elements through inner core crystallization.
"The ability to make these measurements is crucial to developing reliable models of the internal structure of super-Earths up to eight times our planet's mass," Fei added. "These results will make a profound impact on our ability to interpret observational data."
INFORMATION:
The project is partially supported by a Carnegie Venture Grant and the U.S. National Science Foundation.
The project is made possible by the Z Fundamental Science Program.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-09
Nutritionists have been touting the health benefits of seafood for years. Dietary guidelines recommend that the average adult get at least two servings of seafood per week. But the push to increase our consumption of seafood can put a strain on the seafood industry and create more waste.
"Many fisheries are fully or overexploited," said Lekelia "Kiki" Jenkins, an associate professor at Arizona State University's School for the Future of Innovation in Society in the College of Global Futures. "We are pushing our fisheries to the brink that they can sustain. Meanwhile, consumers are wasting nearly half of the fish they buy. We need to understand our waste behaviors and put a mechanism into place so that we use what we catch."
Jenkins is researching ways to improve sustainability in ...
2021-02-09
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this review article the authors Yue Li, Zhiyi Chen and Shuping Ge from First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang, China and Tower Health and Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA summarize current state of the art applications of microbubble-cell interactions and sonoporation effects to cellular functions.
Ultrasound combined with microbubble-mediated sonoporation has been applied to enhance drug or gene intracellular delivery. Sonoporation leads to the formation of openings in the cell membrane, triggered by ultrasound-mediated oscillations and destruction of microbubbles. Multiple mechanisms are involved in the occurrence ...
2021-02-09
Announcing a new article publication for BIO Integration journal. In this review article the authors Xiuling Li, Shunung Liang, Chee Hwee Tan, Shuwen Cao, Xiaoding Xu, Phei Er Saw and Wei Tao from Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, China and Center for Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA discuss the potential benefits of four plants endogenous to China and the enhancement of their therapeutic efficacy by nanotechnology intervention.
Plant derived natural products have been used for the treatment of various human diseases long before the intervention of modern medicine. The basis of modern medicine is still inspired by traditional medicine and therapies. However, ...
2021-02-09
LA JOLLA, CA--As new COVID-19 variants begin to throw vaccine efficacy in question, two leading scientists are calling for health agencies to invest in the development of vaccines that would be broadly effective against many different variants and strains of potential pandemic viruses.
In a END ...
2021-02-09
Researchers at the University of Campinas's Chemistry Institute (IQ-UNICAMP) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, have developed a template-free technique to fabricate cilia of different sizes that mimic biological functions and have multiple applications, from directing fluids in microchannels to loading material into a cell, for example. The highly flexible cilia are based on polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles, and their motion can be controlled by a magnet.
In nature, cilia are microscopic hairlike structures found in large numbers on the surface of certain cells, causing currents ...
2021-02-09
Photoplethysmography (PPG) is a simple optical technique used to detect volumetric changes in peripheral blood circulation. It's used in smart watches, for example, to monitor pulse and heart rate, but PPG biosensors are also found in millions of smartphones, but without any current clinical applications.
In a study published online in the February 2021 issue of Chest, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with industry collaborators, found that already embedded PPG in smartphones, in tandem with application software, could be used for remote clinical pulse oximetry to manage chronic cardiopulmonary disease and perhaps initial treatment and monitoring of persons affected in respiratory viral pandemics, such as COVID-19.
"Pulse oximetry monitoring ...
2021-02-09
As governments try to mitigate the spread of COVID-19, many are turning to contact tracing, including apps that track your location and electronic check-in QR codes. But with that technology come questions of personal safety, privacy, trust, control and collective action. So what can be done to improve these large-scale technological system roll-outs without infringing on a citizen's right to privacy?
"These systems are logging your physical social network," said Katina Michael, an Arizona State University professor at the School for the Future of Innovation in Society in the College of Global Futures and the School of Computing, Informatics and Decision Systems Engineering in the Ira A. Fulton Schools of Engineering. "The physical has become more ...
2021-02-09
Beyond the environmental benefits and lower electric bills, it turns out installing solar panels on your house actually benefits your whole community. Value estimations for grid-tied photovoltaic systems prove solar panels are beneficial for utility companies and consumers alike.
For years some utility companies have worried that solar panels drive up electric costs for people without panels. Joshua Pearce, Richard Witte Endowed Professor of Materials Science and Engineering and professor of electrical and computer engineering at Michigan Technological University, has shown the opposite is true -- grid-tied solar photovoltaic (PV) owners are actually subsidizing their non-PV ...
2021-02-09
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- The huge forces generated by the Z machine at Sandia National Laboratories are being used to replicate the gravitational pressures on so-called "super-Earths" to determine which might maintain atmospheres that could support life.
Astronomers believe that super-Earths -- collections of rocks up to eight times larger than Earth -- exist in the millions in our galaxy. "The question before us is whether any of these super planets are actually Earthlike, with active geological processes, atmospheres and magnetic fields," said Sandia physicist Joshua Townsend.
The current ...
2021-02-09
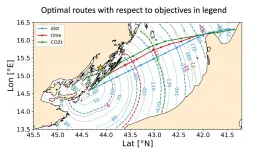
Energy efficiency or carbon intensity (defined as CO2 emissions per transport work, ed.) is a possible point of convergence between the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and EU regulations to cut GHG emissions and decarbonize shipping. Short term measures to increase energy efficiency and achieve carbon intensity savings include voyage optimization.
A new study led by the CMCC Foundation, realized in the framework of the Interreg Italy-Croatia END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Can super-Earth interior dynamics set the table for habitability?
Are super-Earths capable of creating conditions that are hospitable for life to arise and thrive?