(Press-News.org) Feb. 10, 2021 - A new paper published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society describes a "virtual" recovery program for sepsis patients that may also help post-COVID-19 patients and survivors of other serious illnesses.
In " END
Virtual post-sepsis recovery program may also help recovering COVID-19 patients
2021-02-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
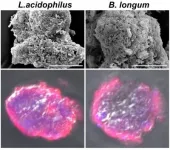
Smectite promotes probiotic biofilm formation in gut for cancer immunotherapy
2021-02-10
Scientists from Nanjing University and the University of Macau have devised a new approach to extend the survival of transplanted probiotics in vivo, enhancing the efficacy of cancer chemo-/immunotherapies in mice. The paper entitled "Smectite promotes probiotic biofilm formation in the gut for cancer immunotherapy" appears online today in Cell Reports.
The gut contains trillions of symbiotic bacteria. Disturbing the balance of intestinal flora may increase the occurrence of major diseases, including cancers. The gut microbiome plays an essential role in regulating the host immunity, which has inspired strategies to modulate intestinal microorganisms ...
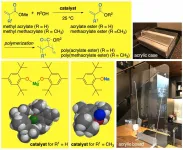
Industrial compound gets eco-friendly reaction
2021-02-10
Nagoya University scientists have developed a chemical reaction that produces high yields of a compound used in a wide variety of industries, without needing high temperatures or toxic catalysts. The approach was described in the journal ACS Catalysis and offers a practical and sustainable solution for industrial (meth)acrylate (= acrylate or methacrylate) ester synthesis.
(Meth)acrylate esters are used in industrial coatings and masonry, and to make plastics, dyes and adhesives. But the chemical process for making them from methyl (meth)acrylates ...
Sleep keeps teens on track for good mental health
2021-02-10
As families settle back into a new school year, sleep experts at the University of South Australia are reminding parents about the importance of teenagers getting enough sleep, cautioning them that insufficient sleep can negatively affect their mental health.
In a new research paper, UniSA sleep experts Dr Alex Agostini and Dr Stephanie Centofanti confirm that sleep is intrinsically linked to mental health, but is commonly overlooked by health practitioners as a contributing factor.
Dr Agostini says it's imperative that parents and medical practitioners ...
Response to cancer immunotherapy may be affected by genes we carry from birth
2021-02-10
For all their importance as a breakthrough treatment, the cancer immunotherapies known as checkpoint inhibitors still only benefit a small minority of patients, perhaps 15 percent across different types of cancer. Moreover, doctors cannot accurately predict which of their patients will respond.
A new study finds that inherited genetic variation plays a role in who is likely to benefit from checkpoint inhibitors, which release the immune system's brakes so it can attack cancer. The study also points to potential new targets that could help even more patients unleash their immune system's natural power to fight ...
Obesity contributes to up to half of new diabetes cases annually in the United States
2021-02-10
DALLAS, Feb. 10, 2021 — Reducing the prevalence of obesity may prevent up to half of new Type 2 diabetes cases in the United States, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association. Obesity is a major contributor to diabetes, and the new study suggests more tailored efforts are needed to reduce the incidence of obesity-related diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, affecting more than 31 million Americans, according to the U.S. Centers ...
New improved dog reference genome will aid a new generation of investigation
2021-02-10
Researchers at Uppsala University and the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences have used new methods for DNA sequencing and annotation to build a new, and more complete, dog reference genome. This tool will serve as the foundation for a new era of research, helping scientists to better understand the link between DNA and disease, in dogs and in their human friends. The research is presented in the journal Communications Biology.
The dog has been aiding our understanding of the human genome since both genomes were released in the early 2000s. At that time, a comparison of both genomes, and two others, revealed that the human genome contained circa 20,000 genes, down ...
Why Black men's prostate cancer may be more responsive to immunotherapy
2021-02-10
Increased level of plasma cells linked to improved cancer survival
1,300 prostate tumor samples studied
Immunotherapy-based precision medicine clinical trials being developed
CHICAGO--- Black men die more often of prostate cancer yet, paradoxically, have greater survival benefits from immunotherapy treatment. A new Northwestern Medicine study discovered the reason appears to be an increase of a surprising type of immune cell in the tumor. The findings could lead to immune-based precision medicine treatment for men of all races with localized aggressive and advanced prostate cancer.
In the new study, Northwestern scientists showed tumors from Black men and men ...
Lipid epoxides target pain, inflammatory pathways in neurons
2021-02-10
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- When modified using a process known as epoxidation, two naturally occurring lipids are converted into potent agents that target multiple cannabinoid receptors in neurons, interrupting pathways that promote pain and inflammation, researchers report. These modified compounds, called epo-NA5HT and epo-NADA, have much more powerful effects than the molecules from which they are derived, which also regulate pain and inflammation.
Reported in the journal Nature Communications, the study opens a new avenue of research in the effort to find alternatives to potentially addictive opioid pain killers, researchers say.
The ...
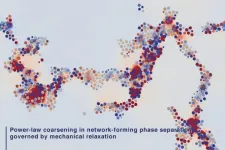
Discovery of a new law of phase separation
2021-02-10
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Institute of Industrial Science at The University of Tokyo investigated the mechanism of phase separation into the two phases with very different particle mobilities using computer simulations. They found that slow dynamics of complex connected networks control the rate of demixing, which can assist in the design of new functional porous materials, like lithium-ion batteries.
According to the old adage, oil and water don't mix. If you try to do it anyway, you will see the fascinating process of phase separation, in which the two immiscible liquids spontaneously "demix." In this case, the minority phase always forms droplets. Contrary to this, the researchers ...
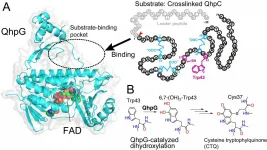
The chemistry lab inside cells
2021-02-10
Osaka, Japan - Investigators from the Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research at Osaka University, together with Hiroshima Institute of Technology, have announced the discovery of a new protein that allows an organism to conduct an initial and essential step in converting amino acid residues on a crosslinked polypeptide into an enzyme cofactor. This research may lead to a better understanding of the biochemistry underlying catalysis in cells.
Every living cell is constantly pulsing with an array of biochemical reactions. The rates of these reactions are controlled by special proteins called enzymes, which catalyze specific processes that would otherwise take much longer. A number of enzymes require specialized molecules called "cofactors," which can help shuttle electrons ...