(Press-News.org) Tampa, FL (Feb. 10, 2021) - Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), commonly known as angioplasty with a stent, opens clogged arteries and saves lives. Despite its benefit in treating atherosclerosis that causes coronary artery disease, this common minimally-invasive procedure still poses severe complications for some patients.
Angioplasty involves inflating a balloon at the tip of a catheter to compress fatty deposits (plaques) against the artery wall, thereby restoring blood flow to the narrowed or blocked vessels. The image-guided procedure is often combined with the placement of either uncoated stents -- tiny expandable mesh devices- or stents coated with slowly-released antiproliferative drugs. The drug-eluting stents help avert the growth of scar tissue (smooth muscle cell proliferation) in the artery so that the vessel does not eventually close again, known as restenosis.
However, current antiproliferative drugs indiscriminately inhibit the growth of all nearby cells, including the layer of endothelial cells lining the blood vessels. These endothelial cells prevent blood clots (thrombosis) within the stent and the formation of more plaques (neoatherosclerosis), which can trigger a heart attack or sudden cardiac death.
Focused on tackling this treatment complication, University of South Florida Health (USF Health) Morsani College of Medicine researchers recently developed a next-generation nanotherapy. Their preclinical findings are detailed in a study published Feb. 2 in Molecular Therapy.
The nanotherapy comprised of a nontoxic peptide known as p5RHH and a synthetic messenger RNA (mRNA) that carries the genetic instructions, or code, needed by cells to make proteins. By simply mixing up the p5RHH with the mRNA, they spontaneously self assemble into compacted nanoparticles that specifically target the injured regions of the arteries in mouse models mimicking angioplasty. The nanoparticles contain an microRNA switch added to the mRNA.
"One of the main challenges of cardiovascular disease remains the delivery of targeted therapies specifically to the plaque regions and the cells that form plaques, including the smooth muscle cells and inflammatory cells -- without affecting the endothelial cells or the healthy regions," said the study's principal investigator Hana Totary-Jain, PhD, an associate professor of molecular pharmacology physiology at USF Health Morsani College of Medicine.
To do this, the researchers used mRNA that encodes for p27 protein, which blocks cell growth. They added to the mRNA an endothelial cell-specific microRNA to generate a microRNA switch. The design of this microRNA switch allowed the researchers to turn on the mRNA in smooth muscle cells to inhibit their growth and the formation of restenosis. It also enabled them to turn off the mRNA in endothelial cells so these cells could grow uninhibited and quickly heal the damaged blood vessel.
"If we can come up with an antiproliferative therapy that specifically targets the cardiovascular smooth muscles cells and the infiltrating inflammatory cells but spares the endothelial cells - which we've done with the design of our microRNA switches - then we should be able to achieve the therapeutic effects of drug-eluting stents without the downside of thrombosis and neoatherosclerosis," said the paper's lead author John Lockhart, PhD, who worked on the study as a doctoral student at USF Health Molecular Pharmacology and Physiology. Dr. Lockhart is continuing his postdoctoral training at Moffitt Cancer Center.
The latest study builds upon previous research by Dr. Totary-Jain, indicating that a microRNA-based therapy worked better than drug-eluting stents in a rat model of angioplasty. That work used an adenovirus vector to carry the cell-selective therapy to injured arteries. In this study the viral vector was replaced with a nanoparticle alternative - a change needed to avoid safety concerns and advance the therapy toward use in patients.
The investigational nanoparticles were injected into mice with arteries mimicking post-angioplasty vessel injury every three days for two weeks (5 doses total). Mice treated with the nanoparticles containing the miRNA switch had significantly reduced restenosis and completely restored endothelial cell growth in the injured artery, compared to animals treated with nanoparticles containing mRNA without the miRNA switch, the researchers report.
In addition, the nanoparticles efficiently delivered its mRNA cargo, without degradation, solely to regions of the artery where endothelial cells were damaged. The particles did not toxically accumulate either in the cells of healthy organs (the liver, spleen. lungs or kidneys), or in uninjured arteries adjacent to those requiring treatment. The researchers observed no adverse reactions or outcomes in mice treated with the nanoparticles.
Overall, the findings suggest that the miRNA-switch nanoparticles could be applied clinically to selectively prevent restenosis after PCI by specifically targeting areas of endothelial cell damage to allow quicker cell regrowth and repair of injured arteries.
The USF Health researchers next plan to investigate the potential of the microRNA-switch nanoparticles to directly treat atherosclerotic plaques, thereby eliminating the need for PCI.
"Cardiovascular disease is still the number one cause of death," said Dr. Totary-Jain, a member of the USF Health Heart Institute. "This research offers promise for the development of novel biomolecular therapies to advance the fight against coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease,"
One person dies of cardiovascular disease every 36 seconds in the U.S., according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
INFORMATION:
The USF Health research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Samuel Wickline, MD, director of the USF Health Heart Institute, and Hua Pan, PhD, assistant professor at the Heart Institute, collaborated on the study.
USF Health's mission is to envision and implement the future of health. It is the partnership of the USF Health Morsani College of Medicine, the College of Nursing, the College of Public Health, the Taneja College of Pharmacy, the School of Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Sciences, the Biomedical Sciences Graduate and Postdoctoral Programs, and USF Health's multispecialty physicians group. The University of South Florida is a high-impact global research university dedicated to student success. Over the past 10 years, no other public university in the country has risen faster in U.S. News & World Report's national university rankings than USF. For more information, visit health.usf.edu
Tsukuba, Japan -- Economists have been using game theory to study decision-making since the 1950s. More recently, the interdisciplinary field of neuroeconomics has gained popularity as scientists try to understand how economic decisions are made in the brain. Researchers led by Professor Masayuki Matsumoto and Assistant Professor Hiroshi Yamada at the University of Tsukuba in Japan studied populations of neurons across the monkey brain reward network to find out where and when expected value is calculated.
The team trained monkeys to perform a lottery task for a reward. The monkeys saw two pie charts on a computer screen. The colors in the charts told the monkeys the size of the reward and the probability of getting it. ...
Black carbon (BC) is the product of incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuel, and biomass. By strongly absorbing solar radiation, BC can heat the atmosphere, affect its stability, and further deteriorate air quality.
The climatic and environmental effects of BC are determined by its loading in the atmosphere. Scientists find that microphysical characteristics of BC, such as particle size and mixing state, can also influence these effects.
The team pointed out that the reduction of the thickly coated BC would further lead to a decline of solar radiation absorption by atmospheric aerosols, besides the decline resulting from the BC loading ...
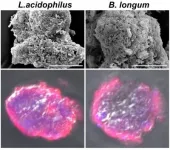
Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI) occurs in the gut and is caused by the Gram-positive, spore-forming anaerobic bacterium, C. difficile when its spores attach to fecal matter and are transferred from hand to mouth by health care workers. Patients undergoing antibiotic treatment are especially susceptible as the microorganisms that maintain a healthy gut are greatly damaged by the antibiotics.
Treatment of rCDI involves withdrawing the causative antibiotics and initiating antibiotic therapy, although this can be very challenging. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is considered an effective alternative therapy as it addresses the issue from the ground up by replacing the damaged microflora with a healthy one through a stool transplant.
However, two deaths caused by antibiotic-resistant ...
Plant nanosensors and Raman spectroscopy are two emerging analytical technologies and tools to study plants and monitor plant health, enabling research opportunities in plant science that have so far been difficult to achieve with conventional technologies such as genetic engineering techniques
The species-independent analytical tools are rapid and non-destructive, overcoming current limitations and providing a wealth of real-time information, such as early plant stress detection and hormonal signalling, that are important to plant growth and yield ...
The percept of time relates to the sense of touch. A new SISSA study "A sensory integration account for time perception" published in PLOS Computational Biology uncovers this connection. "The challenge to neuroscience posed by the sense of time lies, first and foremost, in the fact there do not exist dedicated receptors - the passage of time is a sensory experience constructed without sensors," notes Mathew Diamond, director of the Tactile Perception and Learning Lab. "One might imagine a precise clock in the brain, a sort of stopwatch that registers the start and stop and computes the elapsed ...
A University of Arizona Health Sciences study has estimated total lifetime costs at $736 million for the 10,359 valley fever patients diagnosed in Arizona in 2019, underscoring the economic burden the disease places on the state and its residents.
The prevalence of valley fever, formally known as coccidioidomycosis or cocci, has increased in recent years, from 5,624 cases diagnosed in Arizona in 2014 to 10,359 cases in 2019. There currently are no certain means of prevention or vaccination for the fungal disease, which is caused by spores of Coccidioides, a family of fungi found in soils of the Southwest.
The findings highlight the need ...
Feb. 10, 2021 - A new paper published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society describes a "virtual" recovery program for sepsis patients that may also help post-COVID-19 patients and survivors of other serious illnesses.
In " END ...
Scientists from Nanjing University and the University of Macau have devised a new approach to extend the survival of transplanted probiotics in vivo, enhancing the efficacy of cancer chemo-/immunotherapies in mice. The paper entitled "Smectite promotes probiotic biofilm formation in the gut for cancer immunotherapy" appears online today in Cell Reports.
The gut contains trillions of symbiotic bacteria. Disturbing the balance of intestinal flora may increase the occurrence of major diseases, including cancers. The gut microbiome plays an essential role in regulating the host immunity, which has inspired strategies to modulate intestinal microorganisms ...
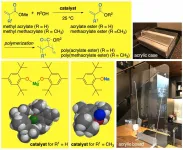
Nagoya University scientists have developed a chemical reaction that produces high yields of a compound used in a wide variety of industries, without needing high temperatures or toxic catalysts. The approach was described in the journal ACS Catalysis and offers a practical and sustainable solution for industrial (meth)acrylate (= acrylate or methacrylate) ester synthesis.
(Meth)acrylate esters are used in industrial coatings and masonry, and to make plastics, dyes and adhesives. But the chemical process for making them from methyl (meth)acrylates ...
As families settle back into a new school year, sleep experts at the University of South Australia are reminding parents about the importance of teenagers getting enough sleep, cautioning them that insufficient sleep can negatively affect their mental health.
In a new research paper, UniSA sleep experts Dr Alex Agostini and Dr Stephanie Centofanti confirm that sleep is intrinsically linked to mental health, but is commonly overlooked by health practitioners as a contributing factor.
Dr Agostini says it's imperative that parents and medical practitioners ...