Texas Heart Institute develops breakthrough heart ablation evaluation system
The new ex vivo benchtop system is detailed in a study published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Physiology
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) The Texas Heart Institute (THI) has announced that a research team led by Dr. Mehdi Razavi, Director of Electrophysiology Clinical Research & Innovations, has developed a breakthrough new ex vivo benchtop system for evaluating the effects of ablation systems on excised tissues and assessing potential damage to collateral heart tissues. The unique system allows for fast and easy benchtop assessments rather than using costly in vivo tests. Critical findings associated with this innovation are outlined in a study published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Physiology.
The new ablation method evaluated by Dr. Razavi and team is being assessed and used clinically as a promising development to combat the challenge of reducing atrial esophageal fistulas - which are uncommon but often deadly late-stage complications of atrial fibrillation ablation procedures that result from massive thermal injury to the esophagus and surrounding components. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained heart rhythm disorder in clinical cardiology practice worldwide.
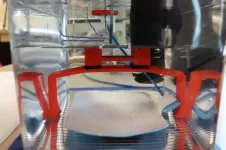
"We created this custom, simple, easy to use fixture to study different ablation settings and the collateral impact of the ablation on the surrounding tissues. It has been useful not only in this particular study, but in many of our other projects as well. It's quite versatile," said Mathews John, Dr. Razavi's Research Engineer III at THI." Our expertise in ablation and access to an extensive set of ablation equipment enabled us to do these experiments in a way that truly mimics what actually happens in a clinical setting."
The most critical finding of the study is that High Power Short Duration (HPSD) ablation protocols may be associated with greater epiesophageal thermal deviations relative to endoluminal measurements. The inaccuracy, in turn, raises the threat of downstream clinical consequences. The results of this ex vivo study support the need for esophageal temperature monitoring, particularly during HPSD ablation.
"Electrophysiology doctors have been utilizing this method previously, but no one has really taken a closer look at the full scope of thermodynamics in play during ablation operations," Dr. Mehdi Razavi noted. He added, "Current technology does not monitor temperature outside of the esophagus during the procedure; it can only monitor temperature changes inside the esophagus itself, which is significant given the fact that major temperature changes occur outside of the organ. To that end, our study sheds light on the problem related to the lack of ability to comprehensively track temperature during these types of procedures and presents an ex vivo method for mitigating this setback."
The study setup detailed in the manuscript was easily modifiable for collaborations with outside companies to evaluate their new devices in order to help them better gather thermodynamic data and validate potential users of the novel technology.
"Overall, our publication demonstrates very interesting findings from the comparison of two different commonly used ablation methods that have been evaluated using this benchtop system and highlights safety measures that should be considered in a clinical setting. The THI Electrophysiology Clinical Research & Innovations team is excited to use this system for further evaluation and characterization of novel cutting-edge ablation systems," Dr. Razavi concluded.
The Texas Heart Institute research presented in the Journal of Cardiovascular Physiology represents a preliminary study of these differences; further studies with larger sample sizes and within vivo characterization will be required to make clinical recommendations.
INFORMATION:
ABOUT TEXAS HEART INSTITUTE (THI)
The Texas Heart Institute, founded by world-renowned cardiovascular surgeon Dr. Denton A. Cooley in 1962, is a nonprofit organization dedicated to reducing the devastating toll of cardiovascular disease through innovative and progressive programs in research, education, and improved patient care. THI's scientists and physicians conduct fundamental biomedical, translational, and clinical research in cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, molecular-based medicine, stem cell and gene therapy, and regenerative medicine both independently and in collaboration with organizations worldwide. As global leaders of patient care for nearly six decades, Texas Heart Institute has been ranked among the top cardiovascular centers in the United States by U.S. News & World Report for the past 30 years. THI is dedicated to spreading awareness and sharing updates on ways to prevent, treat and defeat cardiovascular disease. With over 10 million visitors coming to its website from around the world every year, http://www.texasheart.org is just one of the ways THI is helping to educate people on the importance of heart health. For more information, please visit https://www.texasheart.org.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
Washington, February 10, 2021--After the COVID-19 crisis hit last March, federal student aid applications among potential college freshmen in California dropped 14 percent between mid-March and mid-August, relative to prior years. While there were also initial declines in applications among current undergraduates and graduate students, these quickly recovered and ended 8 percent higher relative to prior years. The findings, published today in Educational Researcher, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association, are from the first academic study conducted on this topic.
Using data from the ...
2021-02-10
ANN ARBOR, Mich. and VANCOUVER, B.C. (February 10, 2021) - After screening more than 1,100 independently assessed, point-of-care COVID-19 tests, researchers at NSF International and Novateur Ventures have identified 5 direct (antigen/RNA) tests for detection of acute infection and 6 indirect (antibody) tests for detection of prior infection that meet the recently published World Health Organization (WHO) "desirable" Target Product Profile (TPP) criteria. The researchers hope their work will help communities and healthcare systems make more informed decisions when choosing rapid, point-of-care COVID-19 ...
2021-02-10
About 1 in 9 mothers suffers from maternal depression, which can affect the mother-infant bond as well as infant development. Touch plays an important role in an infant's socio-emotional development. Mothers who are depressed are less likely to provide their babies with soothing touch, less able to detect changes in facial expressions, and more likely to have trouble regulating their own emotions. In addition, infants of depressed mothers exhibit similar brain functioning patterns as their depressed mothers, which also are linked to temperament characteristics. Infants of depressed mothers are at a high risk of atypical and ...
2021-02-10
NEWPORT, Ore. - Analyzing thousands of genetic markers in albacore tuna from the Pacific Ocean, researchers at Oregon State University have learned that just seven dozen of those markers are needed to determine which side of the equator a fish comes from.
The scientists also discovered that fish from different hemispheres intermingle and sometimes breed with each other.
Published Tuesday in Evolutionary Applications, the findings are an important step toward better understanding the population structure of a species that's a vital and inexpensive source of protein for people around the globe.
Albacore in the North and South Pacific Oceans are currently managed as separate ...
2021-02-10
Overview:
A color illusion that strongly induces color contrast effect has been found by a research team at the Toyohashi University of Technology Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS). The powerful visual illusion clarified a century-old contradiction relating to simultaneous color contrast theory. Through a human psychophysical experiment, the team demonstrated that the presence or absence of flanking contours formed from extremely thin white lines could be used to switch between contradictory visual phenomena (Figure 1), enabling consistent explanation for both discrepant ...
2021-02-10
Tampa, FL (Feb. 10, 2021) - Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), commonly known as angioplasty with a stent, opens clogged arteries and saves lives. Despite its benefit in treating atherosclerosis that causes coronary artery disease, this common minimally-invasive procedure still poses severe complications for some patients.
Angioplasty involves inflating a balloon at the tip of a catheter to compress fatty deposits (plaques) against the artery wall, thereby restoring blood flow to the narrowed or blocked vessels. The image-guided procedure is often combined with the placement of either uncoated stents -- tiny expandable mesh devices- or stents coated with slowly-released antiproliferative ...
2021-02-10
Tsukuba, Japan -- Economists have been using game theory to study decision-making since the 1950s. More recently, the interdisciplinary field of neuroeconomics has gained popularity as scientists try to understand how economic decisions are made in the brain. Researchers led by Professor Masayuki Matsumoto and Assistant Professor Hiroshi Yamada at the University of Tsukuba in Japan studied populations of neurons across the monkey brain reward network to find out where and when expected value is calculated.
The team trained monkeys to perform a lottery task for a reward. The monkeys saw two pie charts on a computer screen. The colors in the charts told the monkeys the size of the reward and the probability of getting it. ...
2021-02-10
Black carbon (BC) is the product of incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuel, and biomass. By strongly absorbing solar radiation, BC can heat the atmosphere, affect its stability, and further deteriorate air quality.
The climatic and environmental effects of BC are determined by its loading in the atmosphere. Scientists find that microphysical characteristics of BC, such as particle size and mixing state, can also influence these effects.
The team pointed out that the reduction of the thickly coated BC would further lead to a decline of solar radiation absorption by atmospheric aerosols, besides the decline resulting from the BC loading ...
2021-02-10
Clostridioides difficile infection (rCDI) occurs in the gut and is caused by the Gram-positive, spore-forming anaerobic bacterium, C. difficile when its spores attach to fecal matter and are transferred from hand to mouth by health care workers. Patients undergoing antibiotic treatment are especially susceptible as the microorganisms that maintain a healthy gut are greatly damaged by the antibiotics.
Treatment of rCDI involves withdrawing the causative antibiotics and initiating antibiotic therapy, although this can be very challenging. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is considered an effective alternative therapy as it addresses the issue from the ground up by replacing the damaged microflora with a healthy one through a stool transplant.
However, two deaths caused by antibiotic-resistant ...
2021-02-10
Plant nanosensors and Raman spectroscopy are two emerging analytical technologies and tools to study plants and monitor plant health, enabling research opportunities in plant science that have so far been difficult to achieve with conventional technologies such as genetic engineering techniques
The species-independent analytical tools are rapid and non-destructive, overcoming current limitations and providing a wealth of real-time information, such as early plant stress detection and hormonal signalling, that are important to plant growth and yield ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Texas Heart Institute develops breakthrough heart ablation evaluation system
The new ex vivo benchtop system is detailed in a study published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Physiology







