Anti-cancer drug's mode of operation deciphered
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) Rituximab, an anti-cancer drug targeting the membrane protein CD20, was the first approved therapeutic antibody against B tumor cells. Immunologists at the University of Freiburg have now solved a mystery about how it works. A team headed by Professor Dr. Michael Reth used cell cultures, healthy cells, and cells from cancer patients to investigate how CD20 organizes the nanostructures on the B cell membrane. If the protein is missing or Rituximab binds to it, the organization of the B cell surface changes. The resting B cell is activated in the process. The team has published the research in the journal PNAS as part of contributions by new members of the National Academy of Science.
B cells are white blood cells and part of the immune system. When they recognize foreign substances, they develop into plasma cells. These produce antibodies that fight off bacteria, viruses or tumor cells. Reth's team used CRISPR/Cas9 gene scissors to remove the gene of CD20 in tumor cell lines and in healthy B cells. The researchers then analyzed on a nanoscale how the proteins on the surface of the B cells form new interactions with other receptors. "These results are based on our research on nanoclusters of membrane proteins and their regulation of immune cells," says Reth.
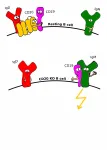
"The protein CD20 keeps apart the B cell antigen receptor of the IgM class and the coreceptor CD19. CD20 thereby ensures the resting state of the B cells," Reth explains. Only when these proteins interact within the membrane and form an IgM/CD19 complex - normally as a reaction to an exogenous antigen - is the immune cell's defense fully activated. Reth's team found that this complex also forms in cells without CD20 or after treatment with Rituximab.
The binding of Rituximab, which is prescribed against B-cell lymphomas as well as B-cell autoimmune diseases, signals to other immune cells to destroy all CD20-bearing B cells. This led the researchers to examine blood from patients during treatment with Rituximab. "We found that CD20 bound by Rituximab on the B cell surface disappears very quickly. These B cells then remain undetected, but are activated by the absence of CD20," explains Kathrin Kläsener, first author of the study.
The B cells thus altered eventually proliferate and can develop into plasma cells. These plasma cells no longer possess CD20 and are therefore no longer accessible to Rituximab. "In the blood tests of relapse patients who have been treated with Rituximab, we also found increased amounts of plasma cells," Kläsener says. "Until now, it was unclear what important function the protein CD20 had and why some patients relapsed after treatment with Rituximab. Now we understand why," Reth explains. "This could help develop even more effective therapies in the future."
INFORMATION:
Michael Reth is Professor of Molecular Immunology and co-speaker of BIOSS - Centre for Biological Signalling Studies He is also a member of the cluster of excellence CIBSS - Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies
Publication:
Kläsener, K., Jellusova, J., Andrieux, G, Salzer, U., Böhler, C., Steiner, S. N., Albinus, J. B., Cavallari, M., Süß, B., Voll, R. E., Boerries, M., Wollscheid, B. and Reth, M. (2021): CD20 as a gatekeeper of the resting state of human B cells. In: PNAS. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2021342118
Contact:
Professor Dr. Michael Reth
Molecular Immunology working group
Institute of Biology III
University of Freiburg
Phone: 0761/203- 2718
michael.reth@bioss.uni-freiburg.de
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
Oncotarget recently published "Melatonin increases overall survival of prostate cancer patients with poor prognosis after combined hormone radiation treatment" which reported that a retrospective study included 955 patients of various stages of prostate cancer who received combined hormone radiation treatment from 2000 to 2019. Comprehensive statistical methods were used to analyze the overall survival rate of PCa patients treated with melatonin in various prognosis groups.
The overall survival rate of PCa patients with favorable and intermediate prognoses treated or not treated ...
2021-02-10
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. (February 10, 2021) - Brain volume, verbal IQ, and overall IQ are lower in children with Type 1 diabetes (T1D) than in children without diabetes, according to a new longitudinal study published in Diabetes Care, a journal of the American Diabetes Association. The nearly eight-year study, led by Nelly Mauras, MD, a clinical research scientist at Nemours Children's Health System in Jacksonville, Florida, and Allan Reiss MD, a Professor at the Stanford University School of Medicine in California, compared brain scans of young children who have T1D with those of non-diabetic children to assess the extent to which glycemic exposure may adversely affect the ...
2021-02-10
It was reported that volume of the brain areas such as superior temporal gyrus and anterior cingulate cortex reduces in schizophrenia but precise change of three-dimensional structure of neuron has remains unclear.
Dr. Itokawa and colleague performed Nanotomography experiments using Fresnel zone plate optics at the BL37XU beamline of the SPring-8 synchrotron radiation facility and at the 32-ID beamline of the Advanced Photon Source (APS) of Argonne National Laboratory.
A total of 34 three-dimensional image datasets of layer V of the BA22 cortex were blinded ...
2021-02-10
The recent review, published in Environment International and led by the University of Tartu, summarises the effect of aquatic pollution on cancer prevalence in wild animals with the help of more than 300 reviewed studies. Authors shed light on understudied yet important fields in cancer research in wild animals - summarising the key effects and pointing to future research avenues to crack the puzzle of why cancer develops in polluted environments.
„What was immediately evident was the bias towards fish in current research into aquatic wildlife cancer. However, given this bias it is especially interesting ...
2021-02-10
Sophia Antipolis, 10 February 2021: A nationwide US study has found increasing death rates from heart disease in women under 65. The research is published in European Heart Journal - Quality of Care and Clinical Outcomes, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The study found that while death rates from cancer declined every year between 1999 and 2018, after an initial drop, heart disease death rates have been rising since 2010.
"Young women in the US are becoming less healthy, which is now reversing prior improvements in heart disease deaths," said senior author Dr. Erin Michos of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, US. "With ...
2021-02-10
Satellite images reveal that the timing of algal blooms in the Red Sea may affect the next haul of sardines and squid by commercial fisheries.
Rising temperatures in the Red Sea have changed the timing of phytoplankton blooms. These microscopic algae form the base of many marine food webs and so are critical to ocean biodiversity and the industries that they support on land, such as fisheries and tourism.
A team led by KAUST climate modeler Ibrahim Hoteit has used satellite images to study the phenology of algal blooms in the northern Red Sea and ...
2021-02-10
A new method has enabled the natural structure of particularly large and complex enzymes to be revealed. Scientists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and TU Berlin have published their findings in the journal Cell Reports. They investigated a multi-enzyme complex that plays an essential role in metabolism and have discovered that it functions differently than previously thought. This will help scientists better understand certain diseases.
Enzymes are a cell's biocatalysts. They accelerate chemical reactions in the body or ensure that these reactions even take place at all. As a result, they play an extremely important role in metabolism. Individual enzymes frequently form a complex with many subunits, as in the case of the ...
2021-02-10
In a study conducted at the University of Helsinki, Finland, 136 adults adhered to one of three study diets for 12 weeks. One of them corresponded to the average Finnish diet, containing roughly 70% animal-derived protein of total protein, while most of the plant-based protein originated from cereal products. In the second study diet, half of the protein was derived from plant products and the other half from animal products, while the third one contained 30% animal protein and 70% plant-based protein of total protein.
Sources of animal protein, both red and white meat as well as dairy products, were partially replaced with plant-based proteins by adding a diverse range of legumes, nuts, ...
2021-02-10
Your breath holds the key to monitoring fat burning, and now a research group from Tohoku University has created a compact and low-cost device that can measure how our body metabolizes fat.
The device uses an ultraviolet lamp to gauge exhaled acetone gas, which is produced in the blood through the metabolic reaction of fat.
"Precise measurements of acetone gas concentration allows us to determine the body's ability to metabolize fat and develop exercise methods for efficient fat burning," says Professor Yuji Matsuura from Tohoku University's Graduate School of Biomedical ...
2021-02-10
Many natural and human-made networks, such as computer, biological or social networks have a connectivity structure that critically shapes their behavior. The academic field of network science is concerned with analyzing such real-world complex networks and understanding how their structure influences their function or behavior. Examples are the vascular network of our bodies, the network of neurons in our brain, or the network of how an epidemic is spreading through a society.
The need for reliable null models
The analysis of such networks often focuses on finding interesting properties and features. For example, does the structure of a particular contact network help diseases spread ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Anti-cancer drug's mode of operation deciphered