Origami powered by light
Pitt and CMU researchers develop high-torque light-powered actuator
2021-02-10
(Press-News.org) If you watch the leaves of a plant long enough, you may see them shift and turn toward the sunlight through the day. It happens slowly, but surely.
Some man-made materials can mimic this slow but steady reaction to light energy, usually triggered by lasers or focused ambient light. New research from the University of Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University has discovered a way to speed up this effect enough that its performance can compete against electrical and pneumatic systems.
"We wanted to create machines where light is the only source of energy and direction," explained M. Ravi Shankar, professor of industrial engineering and senior author of the paper. "The challenge is that while we could get some movement and actuation with light-driven polymers, it was too slow of a response to be practical."
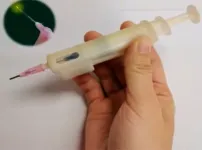
When the polymer sheet is flat, the light animates it slowly, curving or curling over time. The researchers found that by forming the polymer into a curved shape, like a shell, the bending action happened much more quickly and generated more torque.
"If you want to move something, like flip a switch or move a lever, you need something that will react quickly and with enough power," said Shankar, who holds a secondary appointment in mechanical engineering and materials science. "We found that by applying a mechanical constraint to the material by confining it along on the edges, and embedding judiciously thought-out arrangements of molecules, we can upconvert a slow response into something that is more impulsive."
The researchers used a photoresponsive azobenzene-functionalized liquid crystalline polymer (ALCP) film that is 50 micrometers thick and several millimeters in width and length. A shell-like geometry was created by confining this material along its edges to create a curve. Shining light on this geometry folds the shell at a crease that spontaneously nucleates. This folding occurs within tens of milliseconds and generates torque densities of up to 10 newton-meters per kilogram (10Nm/kg). The light driven response is magnified by about three orders-of-magnitude in comparison to the material that was flat.
"The outcomes of the project are very exciting because it means that we can create light powered actuators that are competitive with electrical actuators," said Kaushik Dayal, coauthor and professor of civil and environmental engineering at CMU.
"Our approach towards scaling up the performance of light-driven polymers could reinvent the design of fully untethered soft robots with numerous technological applications," added lead author and post-doctoral researcher at CMU Mahnoush Babaei.
INFORMATION:
The paper, "Torque-dense Photomechanical Actuation," (DOI: 10.1039/D0SM01352H) was published in the journal Soft Matter.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-10
CORVALLIS, Ore. - The Columbia River basin will see an increase in flooding over the next 50 years as a result of climate change, new modeling from Oregon State University indicates.
The magnitude of flooding - the term used to describe flooding severity - is expected to increase throughout the basin, which includes the Columbia, Willamette and Snake rivers and hundreds of tributaries. In some areas, the flooding season will expand, as well.
"The flood you're used to seeing out your window once every 10 years will likely be larger than it has been in the past," said the study's lead author, Laura Queen, a research assistant at OSU's Oregon Climate Change Research Institute. ...
2021-02-10
A team of scientists from Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University with their colleagues from the Institute of Ecology and Genetics of Microorganisms of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Perm) studied the effect of trophoblastic β1-glycoprotein in the blood of pregnant women on pro-inflammatory immune cells. Thanks to trophoblastic β1-glycoprotein, a woman's body does not adversely react to the fetus and supports its normal development until birth. It turned out that trophoblastic β1-glycoproteins also suppressed the development of pro-inflammatory lymphocytes ...
2021-02-10
Exposure to some odorless, colorless and tasteless gases, such as nerve agents, can be toxic or even lethal. And having the ability to detect other types of vapors could save people from eating spoiled or rotten food. Easy-to-use portable devices could, therefore, go a long way toward protecting the public. Now researchers reporting in ACS Materials Letters have created a pen-like sensor that changes color when exposed to harmful gases.
Humans can't detect many toxic vapors, such as poisonous nerve agents or volatile amines released from spoiled foods, so a sensor that can notice these gases' very minute concentrations would be useful. Fluorescence-based sensors are a potential solution because they are inexpensive and can reveal trace amounts of compounds. However, some fluorescing ...
2021-02-10
CHICAGO --- Northwestern University's Noshir Contractor will discuss team problem-solving and human systems integration for Mars exploration at the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual meeting.
At a AAAS press briefing at 12 p.m. ET, Wednesday, Feb. 10, Contractor will discuss recent findings and opportunities for social science research on astronauts as exploration advances into deep space. The embargo will lift at the time of the press briefing.
In addition, he will present "Pairing Teams for, and (Re)pairing Teams During, Long-Duration Space Exploration" at 1 p.m. ET on Thursday, Feb. 11 ...
2021-02-10
Political polarization is having far-reaching impacts on American life, harming consumer welfare and creating challenges for people ranging from elected officials and policymakers to corporate executives and marketers.
That's one of the conclusions of a new scholarly paper by researchers from the University of Wyoming and five other universities across the country. The paper appears in the Journal of Public Policy & Marketing of the American Marketing Association.
"I think we're all aware of how political polarization has affected our elections and system of government, but the impacts go far beyond the political arena," ...
2021-02-10
Oncotarget recently published "Evaluation of cancer-derived myocardial impairments using a mouse model" which reported that Myocardial damage in cancer patients is emphasized as a cause of death; however, there are not many murine cachexia models to evaluate cancer-derived heart disorder.
Using the mouse cachexia model that they established previously, the authors investigated myocardial damage in tumor-bearing mice.
When rat cardiomyoblasts were treated with mouse cachexia model ascites and subjected to flux analysis, both oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis were suppressed, and the cells were in a quiescent state.
These results are in good agreement with those previously reported on cancerous myocardial damage.
The established mouse cachexia ...
2021-02-10
Amsterdam, NL, February 10, 2021 - Neuroplasticity, the remarkable ability of the brain to modify and reorganize itself, is affected by or in response to excessive alcohol, whether through individual consumption or exposure in the womb. It is now well accepted that the birth and integration of new neurons continue beyond development and into adulthood. New discoveries and insights on how alcohol impacts this and other plastic processes are discussed in " END ...
2021-02-10
10th of February, Wednesday, Hong Kong - Deep Longevity, a fully-owned subsidiary of Regent Pacific (SEHK:0575.HK), specializing in the development and the application of next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) for aging and longevity research, today announced the publication of an article in Lancet Healthy Longevity titled "The potential of rapalogs to enhance resilience against SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduce the severity of COVID-19".
While the pandemic continues to unfold, targeted therapeutic solutions for COVID-19 are still not established. The extremely rapid development of various vaccines as a preventative approach provides ...
2021-02-10
New Rochelle, NY, February 9, 2021--The rapid upscaling of a telemonitoring program in which health care providers performed daily telemedicine check-ins on COVID-19 patients faced a unique set of challenges. How these were resolved, and early outcomes are reported in the peer-reviewed journal Telemedicine and e-Health, Click here to read the article now.
"Kaiser Permanente's Virtual Home Care Program (VHCP) was able to rapidly establish a telemedicine-based program for the management of COVID-19 positive patients in the DC and Baltimore Metro regions. Preliminary data suggest that such a program may be effective ...
2021-02-10
Mini-Neptunes and super-Earths up to four times the size of our own are the most common exoplanets orbiting stars beyond our solar system. Until now, super-Earths were thought to be the rocky cores of mini-Neptunes whose gassy atmospheres were blown away. In a new study published in The Astrophysical Journal, astronomers from McGill University show that some of these exoplanets never had gaseous atmospheres to begin with, shedding new light on their mysterious origins.
From observations, we know about 30 to 50 percent of host stars have one or the other, and the two populations appear in about equal proportion. But where did they come from?
One theory is that most exoplanets ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Origami powered by light
Pitt and CMU researchers develop high-torque light-powered actuator