RUDN University mathematician suggested a scheme for solving telegraph equations
2021-02-11
(Press-News.org) A mathematician from RUDN University suggested a stable difference scheme for solving inverse problems for elliptic-telegraph and differential equations that are used to describe biological, physical, and sociological processes. The results of the study were published in the Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations journal.
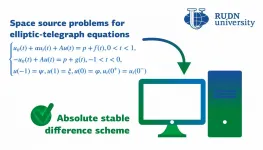
Elliptic equations are a class of differential equations in partial derivatives that are used, among other things, to model time-independent processes. Telegraph equations are presented in a nonstationary form. They were initially obtained for a telegraph communication line, but today they are also used to model the movement of insects, the flow of blood through veins, and the changes underwent by building materials. Moreover, they can be inversed, i.e. used to find a source of changes based on known process characteristics, for example, to identify a cause of material damage or to create an optic tomography image for the purposes of medical diagnostics. It is often difficult to obtain accurate solutions for problems like that, therefore, the initial problem is reduced to a system of simpler equations that provide an answer with a certain degree of approximation to the correct one. A mathematician from RUDN University suggested an algorithm to obtain inverse problem solutions for elliptic-telegraph equations using a computer.
"The more complex a modeled system, the more unknown parameters it contains, and the more difficult are the calculations. However, despite the complexity of the task, modern computers can be used to search for approximate solutions to differential equations. We aimed to obtain absolute stable difference schemes for the approximate solution of the space identification problem for the elliptic?telegraph equations. Our work could help further implement these methods into the modeling of various processes," said Prof. Allaberen Ashyralyev, a PhD in Physics and Mathematics from the Department of Higher Mathematics, RUDN University.
One way to obtain an approximate solution is to replace the initial problem with difference schemes. The studied area is turned into a grid with a given step size, and functions are replaced with nod values. The mathematician suggested a difference scheme and then studied it both analytically and numerically. The first method was used to confirm the absolute stability of the scheme, and the second (a numerical experiment, i.e. an equation that the scheme was applied to) - to support the results of the analysis. The scientist managed to demonstrate that the scheme was absolute stable and independent from the chosen calculation step size.
"Similar elliptic-telegraph equations are used to model biological systems, sociological phenomena, and engineering processes. An absolute stable difference scheme could help specialists better study these issues," added Prof. Allaberen Ashyralyev from RUDN University.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-11
PHOENIX -- A Mayo Clinic team, led by Rahmi Oklu, M.D., Ph.D., a vascular and interventional radiologist at Mayo Clinic, in collaboration with Samir Mitragotri, Ph.D., of Harvard University, report the development of a new ionic liquid formulation that killed cancer cells and allowed uniform distribution of a chemotherapy drug into liver tumors and other solid tumors in the lab. This discovery could solve a problem that has long plagued drug delivery to tumors and provide new hope to patients with liver cancer awaiting a liver transplant. The preclinical study results are published in Science Translational Medicine.
Dr. Oklu, study author and director of Mayo Clinic's ...
2021-02-11
Two international studies of a consortium including more than a dozen institutions the world over, including Empa, published today in the journal Nature show levels of CFC-11 emissions, one of many chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) chemicals once widely used in refrigerators and insulating foams, are back on the decline - less than two years after their shock resurgence in the wake of suspected rogue production in eastern China was widely publicized.
"The findings are very welcome news and hopefully mark an end to a disturbing period of apparent regulatory breaches", says Luke Western from the University of Bristol, a ...
2021-02-11
Cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) is characterized by damage to the blood vessels and parenchyma in the brain. It presents as a multitude of symptoms, which makes the diagnosis difficult. Matters are complicated further when SVD sets in along with other comorbidities with similar symptoms. Therefore, accurate diagnosis at an early stage of disease progression helps in defining better prognosis and management strategies for patients with cerebral SVD.
A team of researchers from the United Kingdom set out to review more than 10,000 studies on clinical diagnosis, risk factors, progression, and intervention ...
2021-02-11
Experts have spent decades warning us about the rising rates of childhood obesity, which has become an epidemic among recent generations in many places around the world, including Spain. The transition from the traditional Mediterranean diet to the consumption of processed foods with low nutritional value is a key contributor, with child-targeted advertising also partly to blame. According to the Breakfast Food Advertisements in Mediterranean Countries: Products' Sugar Content in Adverts from 2015 to 2019 report produced by UOC Faculty of Information and Communication Sciences professor and researcher, Mireia Montaña, the majority of breakfast products ...
2021-02-11
In recent years, active, self-propelled particles have received growing interest amongst the scientific community. Examples of active particles and their systems are numerous and very diverse, ranging from bacterium films to flocks of birds or human crowds. These systems can demonstrate unusual behavior, which is challenging to understand or model.
To this end, large-scale models of active particles were being scrutinised by experts at Leicester, in order to understand basic principles underlying active particle dynamics and apply them in a scenario of an evacuation strategy for customers in crowded place. Unexpectedly, the 'super-particles' milling in a circular motion were stumbled upon ...
2021-02-11
There's a reason that ideas--even erroneous ones--catch fire on social media or in popular culture: groupthink.
New research co-authored by Berkeley Haas Asst. Prof. Douglas Guilbeault shows that large groups of people all tend to think alike, and also illustrates how easily people's opinions can be swayed by social media--even by artificial users known as bots.
In a series of experiments, published in the journal Nature Communications, Guilbeault and co-authors Damon Centola of the University of Pennsylvania and Andrea Baronchelli of City University London created an online game that asked numerous people to identify ...
2021-02-11
Just as beneficial microbes in the human gut can be affected by antibiotics, diet interventions and other disturbances, the microbiomes of other animals can also be upset. In a rare study published this week, Andrea Jani, a researcher with the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), determined the skin microbiome of an endangered frog was altered when the frogs were infected by a specific fungus, and it didn't recover to its initial state even when the frog was cured of the infection.
All animals host symbiotic microbes--many ...
2021-02-11
WASHINGTON--Chinese people are more likely to face high blood pressure and other health risks as a result of higher body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference than people from other racial and ethnic groups, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society's END ...
2021-02-11
SINGAPORE, 10 February 2021 - Researchers studying an enzyme in fruit fly larvae have found that it plays an important role in waking up brain stem cells from their dormant 'quiescent' state, enabling them to proliferate and generate new neurons. Published in the journal EMBO Reports, the study by Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, could help clarify how some neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism and microcephaly occur.
Quiescent neural stem cells in the fruit fly larval brainPr-set7 is an enzyme involved in maintaining genome stability, DNA repair and cell cycle regulation, as well as ...
2021-02-11
Modern telecommunication systems rely on satellites to relay signals across the globe quickly and reliably, enabling users to send messages across the world in an instant, watch live television, or - more recently - hold conference calls with global partners right from the kitchen table!
Communications satellites use high-frequency radio waves to transmit data, with antennas acting as a two-way interface, converting electric current provided by the transmitter into radio waves, and vice versa when paired with a receiver. Antennas are therefore vital pieces of equipment, without which satellites and ground receivers would be practically useless. However, despite advances in modern satellite design and performance, antenna technology remains a limiting factor for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] RUDN University mathematician suggested a scheme for solving telegraph equations