(Press-News.org) BOSTON -- Sleep and health are inextricably connected. New research from investigators at Brigham and Women's Hospital explores the connection between sleep disturbances and deficiencies among older adults and risk of dementia and death, finding that risk of dementia was double among participants who reported getting less than five hours of sleep compared to those who reported 7-8 hours of sleep per night. The team also found associations between sleep disturbance and sleep deficiency with overall risk of death. Results are published in Aging.
"Our findings illuminate a connection between sleep deficiency and risk of dementia and confirm the importance of efforts to help older individuals obtain sufficient sleep each night," said lead author, Rebecca Robbins, PhD, of the Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders.
To investigate the connection between quality and quantity of sleep and risk of dementia and death, Robbins and colleagues used nationally representative data collected from older adults participating in the National Health and Aging Trends Study (NHATS). NHATS is a longitudinal study of Medicare beneficiaries 65 years and older. Survey data from NHATS participants has been collected annually since 2011.
A sample of 2,610 participants answered sleep questionnaires in 2013 and 2014. The researchers examined participants' answers about several characteristics of sleep disturbance and deficiency, including alertness, nap frequency, how long it took participants to fall asleep, sleep quality (good/very good, fair, very poor/poor), sleep duration and snoring. They also collected information (from health care proxies as needed) about patient outcomes such as dementia and death from any cause for up to five years after the survey.
Overall, they found a strong relationship between several sleep disturbance and deficiency variables and incident dementia over time. Routinely taking 30 minutes or longer to fall asleep was associated with a 45 percent greater risk for incident dementia. Routinely experiencing a difficulty in maintaining alertness, routinely napping, reporting poor sleep quality, and sleeping five or fewer hours per night was also associated with increased risk of death.
"This prospective study reveals that sleep deficiency at baseline, when the average age of participants was 76 years old, was associated with double the risk of incident dementia and all-cause mortality over the next 4 to 5 years," said senior author, Charles Czeisler, MD, PhD, FRCP, FAPS, chief of the Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders. "These data add to the evidence that sleep is important for brain health and highlight the need for further research on the efficacy of improving sleep and treating sleep disorders on the risk of Alzheimer's disease and mortality."
The authors call for further study of the causal relationship between sleep and dementia and death, as insights may lead to a new lens through which to view sleep among older adults.
"Our study demonstrates that very short sleep durations and poor-quality sleep in the elderly increase the risk of developing dementia and earlier death. There should be increased focus on obtaining healthy sleep in older adults," said second author Stuart Quan, MD, of the Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders.
INFORMATION:
Funding for this work was provided by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (R01OH011773); the NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (K01HL150339 and
R56HL151637), and the Brigham Research Institute Fund to Sustain Research Excellence.
Paper cited: Robbins R et al. "Examining sleep deficiency and disturbance and their risk for incident dementia and all-cause mortality in older adults across 5 years in the United States" Aging DOI: 10.18632/aging.202591
Brigham Health, a global leader in creating a healthier world, consists of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Brigham and Women's Faulkner Hospital, the Brigham and Women's Physicians Organization and many related facilities and programs. With more than 1,000 inpatient beds, approximately 60,000 inpatient stays and 1.7 million outpatient encounters annually, Brigham Health's 1,200 physicians provide expert care in virtually every medical and surgical specialty to patients locally, regionally and around the world. An international leader in basic, clinical and translational research, Brigham Health has nearly 5,000 scientists, including physician-investigators, renowned biomedical researchers and faculty supported by over $700 million in funding. The Brigham's medical preeminence dates back to 1832, and now, with 19,000 employees, that rich history is the foundation for its commitment to research, innovation, and community. Boston-based Brigham and Women's Hospital is a teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School and dedicated to educating and training the next generation of health care professionals. For more information, resources, and to follow us on social media, please visit brighamandwomens.org.
Combination of pine scent and ozone as super source of particulate emissions from coniferous forests
Scientists have managed to figure out why conifer forests produce so many fine particles into the atmosphere. Aerosol particles are particularly abundant when ?-pinene, the molecule responsible for the characteristic pattern of pine trees reacts with atmospheric ozone.
Atmospheric aerosol particles affect the Earth's climate by forming clouds, but at the same time they also pollute the air, thereby increasing mortality.
Aerosol particles in the atmosphere have their origins in many sources. The significant amount of aerosol particles in the atmosphere is caused ...
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common neurological disease in young adults, affecting more than 2 million individuals worldwide, with about 1500 cases in Estonia. About 20% of MS patients experience optic neuritis (ON) as the presenting symptom, but not all ON patients develop MS.
The TalTech gene technology research unit, in collaboration with the laboratory of Protobios OÜ and medical researchers of the University of Helsinki, published their findings in the prestigious journal of EBioMedicine entitled "Identification of two highly antigenic epitope markers predicting multiple sclerosis in optic neuritis patients". The lead author Helle Sadam and co-authors Mariliis Jaago and Annika ...
Ithaca, NY--The European House Sparrow has a story to tell about survival in the modern world. In parts of its native range in Europe, House Sparrow numbers are down by nearly 60%. Their fate in the U.S. and Canada is less well known. A new study by Cornell Lab of Ornithology scientists aims to clarify the status of this non-native species, using 21 years of citizen science data from the Cornell Lab's Project FeederWatch. The results are published in the Wilson Journal of Ornithology.
"We wanted to find out where and how much House Sparrows might be declining here," explains lead author Liam Berigan, who did this work while at the Cornell Lab and who is now a Ph.D. student at the University of Maine. "We also explored whether the declines would match up with an increase in hawk ...
The CIPD is today launching a new research report, co-authored by the University of Bath's Dr Luke Fletcher, to highlight how LGBT+ workers tend to have a more negative experience of work.
'Inclusion at work: Perspectives on LGBT+ working lives' draws on data from the CIPD's UK Working Lives Survey and a separate survey of trans workers to explore their perspectives on working life, hence the intentional use of LGB+ rather than LGBT, in the research findings:
Over 40% of LGB+ workers experienced a conflict at work over a twelve-month period, compared with 29% of heterosexual workers. Conflicts typically involve being undermined/ humiliated or discriminatory behaviour aimed at a protected characteristic.
More than half (55%) of trans workers surveyed said they had experienced conflict ...
A commercially available genomic test may help oncologists better determine which patients with recurrent prostate cancer may benefit from hormone therapy, according to new research from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and 15 other medical centers.
Researchers studied prostate cancer samples from 352 participants in the NRG/RTOG 9601 clinical trial, which compared radiation therapy alone with radiation therapy combined with hormone therapy. The investigators found that the Decipher test, which measures the activity of 22 genes among seven known cancer pathways, independently estimated the participants' risk of metastasis, death from prostate cancer and overall ...
The PCR test is the most accurate tool to identify SARS-CoV-2. However, valid results are often available only after days. Moreover, the laboratory must be well equipped, have trained personnel and sufficient financial resources. All of this is usually a problem in Africa. A portable suitcase could help. In cooperation with several African universities, scientists at Leipzig University have found that this mini-laboratory provides test results that are almost as good as a PCR test - and almost in real time. The researchers have now published their findings in the journal "Analytical Chemistry".
The compact case could provide rapid coronavirus test results in regions of ...
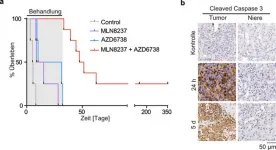
Neuroblastomas are malignant solid tumours that occur mainly in early childhood. They arise from degenerated immature cells of the sympathetic nervous system.
One prognostic marker to assess the malignancy of the tumour is the MYCN oncogene. High-risk neuroblastoma patients often have amplification of MYCN, i.e. very high levels of this protein, which drives uncontrolled tumour growth. Conversely, inhibiting MYCN or its function could be a promising therapeutic opportunity.
An important step towards this direction was taken by an international research project led by scientists ...
A urine test based on University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center research could have avoided one third of unnecessary prostate cancer biopsies while failing to detect only a small number of cancers, according to a validation study that included more than 1,500 patients. The findings appear in the March issue of the Journal of Urology.
The MyProstateScore test, which is being commercialized by LynxDX, a U-M startup company, measures levels of cancer-specific genes in a patient's urine. It is based on U-M research that discovered that half of all prostate tumors harbor a certain ...
Among firearm-owning individuals who died by suicide, handgun ownership was associated with greater odds of having died by self-inflicted gunshot wound rather than by another method, according to a Rutgers researcher.
The study, published in the Archives of Suicide Research, surveyed surviving loved ones of 121 handgun and shotgun owners who died by suicide -- 93 of whom died with a firearm and 28 who died through other means -- and asked about the numbers and types of firearms the individuals had and the circumstances of their deaths.
The researchers found that 77 percent of those who died using a firearm, as well as 61 percent of those who died using another method, owned a handgun. They also found that 88.8 percent of individuals who only owned handguns used a firearm in their ...
Superconductors -- materials that conduct electricity without resistance -- are remarkable. They provide a macroscopic glimpse into quantum phenomena, which are usually observable only at the atomic level. Beyond their physical peculiarity, superconductors are also useful. They're found in medical imaging, quantum computers, and cameras used with telescopes.
But superconducting devices can be finicky. Often, they're expensive to manufacture and prone to err from environmental noise. That could change, thanks to research from Karl Berggren's group in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
The researchers are developing a superconducting nanowire, which could enable more efficient superconducting electronics. The ...