Study finds even the common house sparrow is declining
Citizen scientists provide the research data
2021-02-11
(Press-News.org) Ithaca, NY--The European House Sparrow has a story to tell about survival in the modern world. In parts of its native range in Europe, House Sparrow numbers are down by nearly 60%. Their fate in the U.S. and Canada is less well known. A new study by Cornell Lab of Ornithology scientists aims to clarify the status of this non-native species, using 21 years of citizen science data from the Cornell Lab's Project FeederWatch. The results are published in the Wilson Journal of Ornithology.
"We wanted to find out where and how much House Sparrows might be declining here," explains lead author Liam Berigan, who did this work while at the Cornell Lab and who is now a Ph.D. student at the University of Maine. "We also explored whether the declines would match up with an increase in hawk populations, as is true in European studies. Surprisingly, they didn't."
FeederWatchers record observations during the non-breeding season when House Sparrows gather in flocks. Reports from nearly 12,500 sites were used and cross-referenced with the National Land Cover database to determine whether the U.S. sightings came from rural or urban locations.
Findings for the U.S. and Canada:
Winter flocks in urban areas were larger than flocks in rural areas.
House Sparrows declined in urban areas but remained stable in rural areas.
The study found that declines in House Sparrow populations were no greater when Sharp-shinned or Cooper's Hawks were also present.
From 1995 to 2016, the proportion of FeederWatch sites reporting House Sparrows declined by 7.5% and mean flock sizes declined by 22%.
House Sparrows were introduced in Brooklyn in 1851. They expanded rapidly to become one of the most common species in the U.S. and Canada. Latest estimates peg the population at 82 million individuals. The global breeding population is estimated at 740 million (Partners in Flight).
"When even a bird as common as the House Sparrow is experiencing population declines, this is probably a reflection on the state of the environment," says Berigan. "In Europe, a lack of urban green space and nesting sites are threats. It's likely some of those same factors are at work in North America and contribute to House Sparrow declines here."
INFORMATION:
Reference:
Liam A. Berigan, Emma I. Greig, David N. Bonter. Urban House Sparrow (Passer domesticus) populations decline in North America. Wilson Journal of Ornithology. February 2021.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-11
The CIPD is today launching a new research report, co-authored by the University of Bath's Dr Luke Fletcher, to highlight how LGBT+ workers tend to have a more negative experience of work.
'Inclusion at work: Perspectives on LGBT+ working lives' draws on data from the CIPD's UK Working Lives Survey and a separate survey of trans workers to explore their perspectives on working life, hence the intentional use of LGB+ rather than LGBT, in the research findings:
Over 40% of LGB+ workers experienced a conflict at work over a twelve-month period, compared with 29% of heterosexual workers. Conflicts typically involve being undermined/ humiliated or discriminatory behaviour aimed at a protected characteristic.
More than half (55%) of trans workers surveyed said they had experienced conflict ...
2021-02-11
A commercially available genomic test may help oncologists better determine which patients with recurrent prostate cancer may benefit from hormone therapy, according to new research from the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and 15 other medical centers.
Researchers studied prostate cancer samples from 352 participants in the NRG/RTOG 9601 clinical trial, which compared radiation therapy alone with radiation therapy combined with hormone therapy. The investigators found that the Decipher test, which measures the activity of 22 genes among seven known cancer pathways, independently estimated the participants' risk of metastasis, death from prostate cancer and overall ...
2021-02-11
The PCR test is the most accurate tool to identify SARS-CoV-2. However, valid results are often available only after days. Moreover, the laboratory must be well equipped, have trained personnel and sufficient financial resources. All of this is usually a problem in Africa. A portable suitcase could help. In cooperation with several African universities, scientists at Leipzig University have found that this mini-laboratory provides test results that are almost as good as a PCR test - and almost in real time. The researchers have now published their findings in the journal "Analytical Chemistry".
The compact case could provide rapid coronavirus test results in regions of ...
2021-02-11
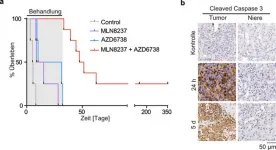
Neuroblastomas are malignant solid tumours that occur mainly in early childhood. They arise from degenerated immature cells of the sympathetic nervous system.
One prognostic marker to assess the malignancy of the tumour is the MYCN oncogene. High-risk neuroblastoma patients often have amplification of MYCN, i.e. very high levels of this protein, which drives uncontrolled tumour growth. Conversely, inhibiting MYCN or its function could be a promising therapeutic opportunity.
An important step towards this direction was taken by an international research project led by scientists ...
2021-02-11
A urine test based on University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center research could have avoided one third of unnecessary prostate cancer biopsies while failing to detect only a small number of cancers, according to a validation study that included more than 1,500 patients. The findings appear in the March issue of the Journal of Urology.
The MyProstateScore test, which is being commercialized by LynxDX, a U-M startup company, measures levels of cancer-specific genes in a patient's urine. It is based on U-M research that discovered that half of all prostate tumors harbor a certain ...
2021-02-11
Among firearm-owning individuals who died by suicide, handgun ownership was associated with greater odds of having died by self-inflicted gunshot wound rather than by another method, according to a Rutgers researcher.
The study, published in the Archives of Suicide Research, surveyed surviving loved ones of 121 handgun and shotgun owners who died by suicide -- 93 of whom died with a firearm and 28 who died through other means -- and asked about the numbers and types of firearms the individuals had and the circumstances of their deaths.
The researchers found that 77 percent of those who died using a firearm, as well as 61 percent of those who died using another method, owned a handgun. They also found that 88.8 percent of individuals who only owned handguns used a firearm in their ...
2021-02-11
Superconductors -- materials that conduct electricity without resistance -- are remarkable. They provide a macroscopic glimpse into quantum phenomena, which are usually observable only at the atomic level. Beyond their physical peculiarity, superconductors are also useful. They're found in medical imaging, quantum computers, and cameras used with telescopes.
But superconducting devices can be finicky. Often, they're expensive to manufacture and prone to err from environmental noise. That could change, thanks to research from Karl Berggren's group in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
The researchers are developing a superconducting nanowire, which could enable more efficient superconducting electronics. The ...
2021-02-11
It is no secret that U.S. politics is polarized. An experiment conducted by MIT researchers now shows just how deeply political partisanship directly influences people's behavior within online social networks.
Deploying Twitter bots to help examine the online behavior of real people, the researchers found that the likelihood that individuals will follow other accounts on Twitter triples when there appears to be a common partisan bond involved.
"When partisanship is matched, people are three times more likely to follow other accounts back," says MIT professor David Rand, co-author of a new paper detailing the study's results. "That's a really big effect, and clear evidence of how important a role partisanship plays."
The finding helps reveal ...
2021-02-11
A new largescale genetic analysis has found biological mechanisms that contribute to making people more susceptible to muscle weakness in later life, finding that diseases such as osteoarthritis and diabetes may play a large role in susceptibility.
As we get older we lose muscle strength, and in some people this severe weakness impacts their ability to live everyday lives, a condition called sarcopenia. Around 10 per cent of people over 50 experience sarcopenia. Many causes thought to impact likelihood of developing this weakness, which is linked to higher death rates.
In a genetic analysis of over 250,000 people aged over 60 from UK Biobank and 21 other cohorts, an international team led by researchers at the University of Exeter ...
2021-02-11
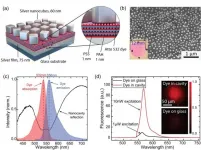
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have created a new plasmonic metasurface that achieves record high light efficiency over the entire centimeter-scale metasurface. The advance makes the new nanostructured thin film practical for use in a variety of applications from light-based communication to fluorescence-based biosensing.
"The major obstacles for using plasmonic structures for practical applications is that they are either too inefficient or their nanoscale properties aren't easily scalable to larger sizes," said research team leader Maiken H. Mikkelsen from Duke University. "We designed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study finds even the common house sparrow is declining
Citizen scientists provide the research data