Compounds from apples may boost brain function
2021-02-11
(Press-News.org) Natural compounds found in apples and other fruits may help stimulate the production of new brain cells, which may have implications for learning and memory, according to a END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Machine-learning how to create better AAV gene delivery vehicles
2021-02-11
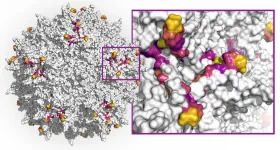
(Boston) -- Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) have become promising vehicles for delivering gene therapies to defective tissues in the human body because they are non-pathogenic and can transfer therapeutic DNA into target cells. However, while the first gene therapy products approved by the Federal Drug Administration (FDA) use AAV vectors and others are likely to follow, AAV vectors still have not reached their full potential to meet gene therapeutic challenges.
First, currently used AAV capsids - the spherical protein structures enveloping the virus' single-stranded DNA genome which can be modified to encode therapeutic genes - are limited in their ability to specifically hone in on the tissue affected by a disease and their wider distribution throughout ...
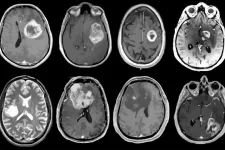
Aggressive brain tumor mapped in genetic, molecular detail
2021-02-11
Glioblastoma is among the most aggressive and devastating of cancers. While rare compared with other cancers, it's the most common type of brain cancer. Even with intensive therapy, relatively few patients survive longer than two years after diagnosis, and fewer than 10% of patients survive beyond five years. Despite extensive studies focused on genomic features of glioblastoma, relatively little progress has been made in improving treatment for patients with this deadly disease.
Now, a new study led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Case Western Reserve University and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has revealed a detailed map of the genes, ...
SARS-CoV-2 screening using CRISPR-based methods
2021-02-11
What The Study Did: This observational study assessed CRISPR-based methods for screening to detect SARS-CoV-2 among asymptomatic college students.
Authors: Carolina Arias, Ph.D., of the University of California, Santa Barbara, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37129)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...
National trends in us otolaryngology surgical volume early in COVID-19 pandemic
2021-02-11
What The Study Did: Changes in otolaryngology surgical volumes in the United States early on in the COVID-19 pandemic are described in this study.
Authors: Anirudh Saraswathula, M.D., M.S., of Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5472)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Pragmatic solutions to counteract regressive effects of COVID-19 pandemic for women in academic oncology
2021-02-11
What The Viewpoint Says: How pandemic-related disruptions may adversely impact progress toward a gender-balanced workforce in academic oncology is described in this article, which also offers possible solutions to mitigate the problem in this specialty.
Authors: Reshma Jagsi, M.D., D.Phil., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.7681)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
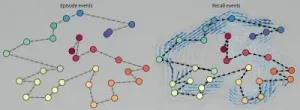
How do our memories take shape?
2021-02-11
Your brain is constantly evaluating which aspects of your experiences to either remember for later, ignore, or forget. Dartmouth researchers have developed a new approach for studying these aspects of memory, by creating a computer program that turns sequences of events from a video into unique geometric shapes. These shapes can then be compared to the shapes of how people recounted the events. The study provides new insight into how experiences are committed to memory and recounted to others. The results are published in Nature Human Behavior and were based on how people remembered the experience of watching an episode of Sherlock, a BBC television show.
"When we represent experiences and memories as shapes, we can use the tools ...
Study identifies never-before-seen dual function in enzyme critical for cancer growth
2021-02-11
Considered the most lethal form of DNA damage, double-strand breaks must be repaired to prevent cell death. In developing therapies for hard-to-treat breast and ovarian cancers in patients with BRCA gene mutations, scientists aim to identify ways to keep cancer cells from using DNA break repair pathways. New findings demonstrate a previously-unknown capability for polymerase theta (pol theta) - a key enzyme in this repair function - that shows promise as a new avenue for treatment development.
The study results are published in Molecular Cell.
Researchers at the University of Vermont (UVM), The University of Texas MD Anderson ...
Protected areas see continued deforestation but at a reduced rate, OSU research shows
2021-02-11
CORVALLIS, Ore. - A survey of more than 18,000 land parcels spanning 2 million square miles across 63 countries shows that a "protected area" designation reduces the rate of deforestation but does not prevent it.
Published today in Nature Ecology and Evolution, the findings are important because most terrestrial species live in forests and because the study suggests that just 6.5% of the Earth's woodlands are truly protected, well below the 2020 target of 17% set by the United Nations' Convention on Biological Diversity.
The findings are also timely given President Biden's recent executive order on climate change, which calls for protecting 30% of the United States' ...
Vaporised crusts of Earth-like planets found in dying stars
2021-02-11
Observations of lithium and potassium around white dwarf stars point to remains of rocky planet crusts
Analysis by astronomers led by University of Warwick shows chemical composition of crusts is very similar to Earth's continental crust
The outer layers of the white dwarfs contain up to 300,000 gigatonnes of rocky debris, which includes up to 60 gigatonnes of lithium and 3,000 gigatonnes of potassium
These white dwarfs are among the oldest stars in our galaxy, and could host one of the oldest planetary systems discovered so far
Remnants of planets with Earth-like crusts have been discovered in the atmospheres of four nearby white dwarf stars by University of Warwick astronomers, offering a glimpse of the planets that may have once orbited ...
Nightly sleep of five hours, less, may increase risk of dementia, death among older adults
2021-02-11
BOSTON -- Sleep and health are inextricably connected. New research from investigators at Brigham and Women's Hospital explores the connection between sleep disturbances and deficiencies among older adults and risk of dementia and death, finding that risk of dementia was double among participants who reported getting less than five hours of sleep compared to those who reported 7-8 hours of sleep per night. The team also found associations between sleep disturbance and sleep deficiency with overall risk of death. Results are published in Aging.
"Our findings illuminate a connection between sleep deficiency and risk of dementia and confirm the importance of efforts to help older individuals obtain ...