Going the distance--insights into how cancer cells spread
2021-02-12
(Press-News.org) Most tumors consist of a heterogenous mix of cells. Genetic mutations found only in some of these cells are known to aid with the spread and progression of cancer. However, oncologists often find that when tumors metastasize to distant organs, they retain this heterogenous nature--a phenomenon termed "polyclonal metastasis". The mechanism by which non-metastatic cells accompany the metastatic cells is ambiguous. Now, Masanobu Oshima and his research team have used mouse models to explain how non-metastatic cells begin their long commute.
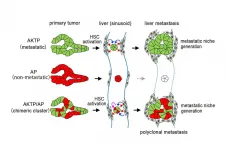
The team has previously developed various cancerous mutants of mice and analyzed them closely to reveal which cancer cells inherently spread and which do not. It was found that cells with four mutations, colloquially termed AKTP, were the most fatal. When these cells were transplanted into the spleens of mice, they migrated to and formed colonies in the livers within 3 days. In contrast, cells with two mutations, AK and AP, could not traverse this distance. To replicate polyclonal metastasis, AP cells were then co-transplanted with AKTP cells, and voila, both cell types indeed moved into the livers. Instead, when AP cells were injected into the blood (without prior exposure to the AKTP cells) they could not metastasize. Certain processes seemed to be at play when the cells were incubated together.
Next, AKTP cells within the liver tumors were killed to see how closely that affected the AP cells. The AP cells continued thriving and grew into larger tumors suggesting they did not need the AKTP cells anymore. Thus, at some point in the journey from the spleen to the liver the AP cells turned dangerous. To identify this point, the researchers traced back the chain of events. Within a day after transplantation, AKTP clusters were found in the sinusoid vessel, a major blood vessel supplying the liver. By 14 days, this cluster transformed into a mass termed as a "fibrotic niche". The same mass was observed with a mix of AP and AKTP cells, but not with AP cells alone. What's more, within this mass AKTP cells were activating hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). HSCs are responsible for scarring of liver tissue. Activated HSCs then set up the perfect environment for AP cells to proliferate infinitely. Harboring the AP cells within the fibrotic environment was, therefore, a key step.
"These results indicate that non-metastatic cells can metastasize via the polyclonal metastasis mechanism using the fibrotic niche induced by malignant cells," conclude the researchers. Targeting this fibrotic niche might be a promising strategy to keep the spread of solid tumors in check.
INFORMATION:
Background
Polyclonal metastasis: Solid tumors such as breast and colorectal cancer are famous for spreading notoriously. These tumor cells break off from the point of origin and migrate via the bloodstream into distant organs to set up shop. It is often found that such metastatic tumors are genetically diverse in nature. However, the role of cancer mutations in conferring tumors metastatic is still unclear. Older theories have suggested that genetic alterations are the sole key to turning cells metastatic. However, the study depicted here shows that other mechanisms are also at play.
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and the fibrotic niche: HSCs are specialized cells of the liver responsible for scarring and wound healing mechanisms when activated. Upon activation, (after events such as liver damage) HSCs start proliferating and induce fibrotic tissue within the liver. Thus, their activation by AKTP cells resulted in development of the fibrotic niche, an environment particularly favorable for tumor proliferation. END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-12
New research shows that hurricane maximum wind speeds in the subtropical Atlantic around Bermuda have more than doubled on average over the last 60 years due to rising ocean temperatures in the region.
Hurricanes intensify by extracting energy from the warm ocean surface via air-sea heat fluxes, so a warmer ocean can lead to more intense hurricanes.
Improving predictions of wind speeds from hurricanes will help determine the right level of response in advance of the storm and potentially limit the resulting damage in Bermuda.
Between 1955 and ...
2021-02-12
Hydrogen for energy use can be extracted in an environmentally friendly way from water and sunlight, using photocatalytic composite polymer nanoparticles developed by researchers at Uppsala University. In laboratory tests, these "polymer dots" showed promising performance and stability alike. The study has been published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
How we are to meet future demand for sustainable energy is a much-debated question. One feasible way to go is hydrogen, which can be produced from renewable resources: water and solar energy. But the process ...
2021-02-12
Cisplatin is one of the most effective chemotherapy agents, used in just under half of pediatric cancer cases. Permanent hearing loss is a common side effect of this medication, but until now, studies have been too small and too varied to accurately characterize this risk. Today in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, investigators at Children's Hospital Los Angeles published results of the largest study of cisplatin-induced hearing loss to date. The study establishes the first benchmarks for the prevalence of hearing loss, and reveals that the risk of hearing loss is affected not only by how much drug is given, but by how that drug is delivered--dosing schedules, complementary treatments, and more. These findings will allow oncologists to deliver more information ...
2021-02-12
If you're poor and terminally ill in southern Mexico, there's far less chance you'll get the painkillers you need for palliative care than your cousins in more prosperous regions, particularly those pharmacy-rich areas along Mexico-U.S. border, say UCLA researchers and colleagues who studied opioid dispensing levels across the country.
What's more, the researchers' paper in the journal The Lancet Public Health suggests it's likely that some of the opioids intended for Mexican citizens are ending up in American pockets.
Despite a Mexican government initiative launched in 2015 to improve access to prescription opioids among palliative care patients, the country has seen only a marginal increase in dispensing levels, and inequities in dispensing ...
2021-02-12
A novel computer algorithm, or set of rules, that accurately predicts the orbits of planets in the solar system could be adapted to better predict and control the behavior of the plasma that fuels fusion facilities designed to harvest on Earth the fusion energy that powers the sun and stars.
The algorithm, devised by a scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), applies machine learning, the form of artificial intelligence (AI) that learns from experience, to develop the predictions. "Usually in physics, you make observations, create a theory based on those observations, and then use that theory to predict new observations," said PPPL physicist Hong Qin, author of a paper detailing ...
2021-02-12
Monash University researchers have uncovered the barrier to β-cell (beta cell) regeneration that could pave the way for improved treatments for diabetes and diseases that involve organ and tissue damage.
The human body doesn't repair itself very well, with our liver the only organ that can regenerate efficiently. We have limited capacity to regenerate new cells or tissue after birth as the genes involved in development are switched off.
This process happens through DNA methylation, a biological process where chemicals (methyl groups) are written on DNA and modify the way the gene functions. ...
2021-02-12
A team of researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) used a quantum computer to successfully simulate an aspect of particle collisions that is typically neglected in high-energy physics experiments, such as those that occur at CERN's Large Hadron Collider.
The quantum algorithm they developed accounts for the complexity of parton showers, which are complicated bursts of particles produced in the collisions that involve particle production and decay processes.
Classical algorithms typically used to model parton showers, such ...
2021-02-12
An international research team led by Professor Kari Rissanen of the University of Jyvaskyla (Finland) and Professor Antonio Frontera of the University of Balearic Islands (Spain) has demonstrated that positively charged iodine (termed iodonium) is able to favorably interact with a silver cation (Ag+), overcoming the strong electrostatic repulsion. The research was published online in Chem -journal 8th of February 2021.
It is well known and intuitive that iodide (I-) has a strong affinity for Ag+. For instance, AgI is one of the most insoluble inorganic salts ...
2021-02-12
When we listen to speech sounds, the information that enters our left and right ear is not exactly the same. This may be because acoustic information reaches one ear before the other, or because the sound is perceived as louder by one of the ears. Information about speech sounds also reaches different parts of our brain, and the two hemispheres are specialised in processing different types of acoustic information. But how does the brain integrate auditory information from different areas?
To investigate this question, lead researcher Basil Preisig from the University of Zurich collaborated with an international team of scientists. In an earlier study, the team discovered that the brain integrates information about speech sounds by 'balancing' the rhythm of gamma waves across ...
2021-02-12
Most countries introduced school closures during the spring of 2020 despite substantial uncertainty regarding the effectiveness in containing SARS-CoV-2. In Sweden, upper-secondary schools moved online while lower-secondary schools remained open. A comparison of parents with children in the final year of lower-secondary and first year of upper-secondary school shows that keeping the former open had limited consequences for the overall transmission of the virus. However, the infection rate doubled among lower-secondary teachers relative to upper-secondary ones. The infection rate among partners of lower-secondary teacher was 30 percent higher than among their upper-secondary counterparts.
On March 18, 2020, Swedish ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Going the distance--insights into how cancer cells spread