(Press-News.org) Aspirin should be favoured over warfarin to prevent blood clotting in children who undergo a surgery that replumbs their hearts, according to a new study.
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published in The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, will have implications for clinicians when prescribing blood thinning medications after Fontan surgery, a complex congenital heart disease operation redirecting blood flow from the lower body to the lungs.
The Fontan procedure is offered to children born with severe heart defects, allowing the child to live with just one pumping heart chamber instead of two.
MCRI Dr Chantal Attard said although the operation couldn't completely 'fix' the heart, most were able to live well into adulthood and have relatively normal lives. But she said those who have the procedure were at an increased risk for blood clots.
"Blood clots are dangerous because they can cause the heart to fail or lead to a stroke. For this reason, all patients are given blood thinning medications, with warfarin and aspirin the most common," she said.
"Warfarin can be affected by food, other medications and illness, so patients must have regular blood tests to check their warfarin levels are safe."
The study involved 121 patients enrolled in the Australian and New-Zealand Fontan (ANZ) Registry. It found stroke was common regardless of which medication the patient took. But patients on warfarin had poorer bone mineral density and were at a higher risk of bleeding.
Dr Attard said the research showed for patients who undergo Fontan surgery, and do not have additional blood clotting risk factors, aspirin should be offered over warfarin.
She said given the need for regular INR monitoring of warfarin, a shift to aspirin would also have a cost benefit to the patient and the healthcare system.
About 70,000 post Fontan patients are alive today, with this number expected to double within two decades.
Carley Clendenning's son Lachie, 7, had the Fontan procedure two years ago after being born with one heart ventricle.
She said the aspirin findings were a relief as the medication was much easier to manage and would benefit other families whose children required the procedure in future.
"Lachie has been taking warfarin ever since his surgery and there are things you have to keep on top of with this medication," she said.
"We have to monitor his blood clotting levels with regular finger prick blood tests at home and watch out for injuries because there is a greater chance of bleeding and bruises.
"In what is already a difficult time for families, this new recommendation will make things a little easier."
INFORMATION:
Researchers from the University of Melbourne, The Royal Children's Hospital, The Children's Hospital at Westmead, The University of Sydney, Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, Western Health, Monash Children's Hospital, Starship Children's Hospital in Auckland, The Royal Melbourne Hospital and the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital also contributed to the study.
Publication: Chantal Attard, Paul T Monagle, Yves d'Udekem, Mark T. Mackay, Julie Briody, Rachael Cordinam, Ebrahim Bani Hassang, Peter Simma, Kathryn Rice, Vera Ignjatovic and the ANZ Fontan Registry Research group. 'Long-term outcomes of warfarin versus aspirin following Fontan surgery,' The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.12.102
*The content of this communication is the sole responsibility of MCRI and does not reflect the views of the NHMRC.
Available for interview:
Dr Chantal Attard
Carley Clendenning's whose son had the Fontan procedure
In a SWOG Cancer Research Network trial that put three targeted drugs to the test, the small molecule inhibitor cabozantinib was found most effective in treating patients with metastatic papillary kidney cancer - findings expected to change medical practice.
These findings will be presented at ASCO's virtual 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium on Feb. 13, 2021 at 1 p.m. ET. The findings will be simultaneously published in The Lancet.
There are currently no effective treatments for metastatic papillary kidney cancer, or metastatic pRCC, a rare subtype of kidney cancer. One study of 38 patients found that the average survival ...
Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab yields better overall survival than single-agent sunitinib when given as first-line therapy in untreated patients with metastatic kidney cancer
The combination also improved progression-free survival and overall response rate
BOSTON - Patients with advanced kidney cancer, who received a targeted drug combined with a checkpoint-blocker immunotherapy agent had longer survival than patients treated with the standard targeted drug, said an investigator from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, reporting results from a phase 3 clinical trial.
The survival benefit demonstrates that an immune checkpoint inhibitor together with a targeted kinase inhibitor drug "is important ...
A test that monitors blood levels of DNA fragments released by dying tumor cells may serve as an accurate early indicator of treatment success in people in late stages of one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer, a new study finds.
Led by NYU Grossman School of Medicine and Perlmutter Cancer Center researchers, the investigation looked at adults with undetectable levels of freely circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) four weeks into drug treatment for metastatic melanoma tumors that cannot be removed surgically (unresectable). The study showed that these patients, all of whom had common genetic changes (BRAFV600 mutations) linked to cancer, were living ...
Peer-reviewed / Review, Survey and Opinion piece
To ensure an effective global immunisation strategy against COVID-19, vaccines need to be produced at scale, priced affordably, and allocated globally so that they are available where needed, and successfully rolled out.
Review of evidence includes a comparison of 26 leading vaccines on their potential contribution to achieving global vaccine immunity, and a new survey of COVID-19 vaccine confidence in 32 countries.
Having new COVID-19 vaccines will mean little if people around the world are unable to get vaccinated in a timely manner. ...
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis demonstrates that a liquid biopsy examining blood or urine can help gauge the effectiveness of therapy for colorectal cancer that has just begun to spread beyond the original tumor. Such a biopsy can detect lingering disease and could serve as a guide for deciding whether a patient should undergo further treatments due to some tumor cells evading an initial attempt to eradicate the cancer.
The study appears online Feb. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology Precision Oncology, a journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
While a few liquid biopsies have been approved ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Scientists have yet to answer the age-old question of whether or how sound shapes the minds of fetuses in the womb, and expectant mothers often wonder about the benefits of such activities as playing music during pregnancy. Now, in experiments in newborn mice, scientists at Johns Hopkins report that sounds appear to change "wiring" patterns in areas of the brain that process sound earlier than scientists assumed and even before the ear canal opens.
The current experiments involve newborn mice, which have ear canals that open 11 days after birth. In human fetuses, the ear canal opens prenatally, at about 20 weeks gestation.
The findings, published online Feb. 12 in END ...
A more aggressive approach to treating acne that marries the disciplines of psychology and dermatology is needed, according to two UC Riverside psychology researchers.
They also assert that women and people with darker skin disproportionately suffer from acne's psychological impacts.
"Acne is pervasive, physically harmless, and painless, so we all-too-often underestimate its impacts as the quintessential nuisance of adolescence and puberty," said UCR psychology professor Misaki Natsuaki, who authored the paper along with Tuppett Yates, also a UCR psychology professor.
The insinuation, including by developmental scientists, can be that hurtful monikers such as "pizza face" and "crater face" are best shrugged off.
But psychological ...
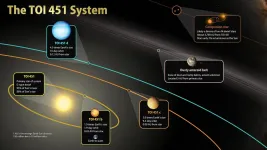
Using observations from NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), an international team of astronomers has discovered a trio of hot worlds larger than Earth orbiting a much younger version of our Sun called TOI 451. The system resides in the recently discovered Pisces-Eridanus stream, a collection of stars less than 3% the age of our solar system that stretches across one-third of the sky.
The planets were discovered in TESS images taken between October and December 2018. Follow-up studies of TOI 451 and its planets included observations made in 2019 and 2020 using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, ...
Masks help protect the people wearing them from getting or spreading SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, but now researchers from the National Institutes of Health have added evidence for yet another potential benefit for wearers: The humidity created inside the mask may help combat respiratory diseases such as COVID-19.
The study, led by researchers in the NIH's National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), found that face masks substantially increase the humidity in the air that the mask-wearer breathes in. This higher level of humidity in inhaled air, the researchers suggest, could help explain why wearing masks has been linked to lower disease severity in people infected with SARS-CoV-2, because hydration of the respiratory ...
A new study published in the journal Science Advances shows that Bantu-speaking communities in the Congo rainforest underwent a major population collapse from 1600 to 1400 years ago, probably due to a prolonged disease epidemic, and that significant resettlement did not restart until around 1000 years ago. These findings revise the population history of no less than seven present-day African countries (Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, and Angola) and challenges the commonly held belief that the settlement of Central Africa by Bantu-speaking communities was a continuous process from about 4000 years ago until the start of the transatlantic ...