Hydrogen peroxide, universal oxidizing agent, high-efficiency production by simple process
Computer simulation-based catalyst development for hydrogen peroxide production with selectivity of 95%. Development of the platinum-gold alloy catalyst facilitating hydrogen peroxide direct synthesis from hydrogen and oxygen at room temperature and atmo
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) Hydrogen peroxide is used as a disinfectant, after dilution in water, to treat wounds. It is widely used across the industry as an eco-friendly oxidizing agent for impurity removal from semiconductors, waste treatment, etc. Currently, it is mainly produced by the sequential hydrogenation and oxidation of anthraquinone (AQ). However, this process is not only energy intensive and requires large-scale facilities, but AQ is also toxic.
As an alternative to the AQ process, hydrogen peroxide direct synthesis from hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) using a palladium (Pd) catalyst was proposed. However, the commercialization of the technology has been challenging becausethe amount of water (H2O) formed is more than hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) during the process.*
*In the case of the Pd catalyst, 40% of hydrogen peroxide and 60% of water were maximally produced.
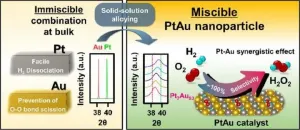
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that a joint research team of Dr. Sang Soo Han and Dr. Donghun Kim (Computational Science Research Center), Dr. Seung Yong Lee (Materials Architecture Research Center), and Professor Kwan-Young Lee at Korea University (Korea University, President Jin Taek Chung) developed a platinum-gold alloy catalyst for hydrogen peroxide production based on a computer simulation. Hydrogen peroxide selectivity can be increased to 95% by using this catalyst, compared with only 30-40% for a palladium catalyst, which indicates that mostly hydrogen peroxide on the developed Pt-Au catalyst can be produced with a small amount of water.
The joint research team between KIST and Korea University developed a new type of Pt-Au alloyed nanoparticle catalyst. Although it is difficult to homogeniously mix Pt and Au to develop an alloyed catalyst due to the intrinsic immiscibility of the metals, the researchers could successfully synthesize nanoparticles in the form of alloys by forcibly reducing **precursors of Pt and Au. Also, using this method, the content of each metal particle could be controlled by adjusting the amount of precursors of Pt and Au.
**Precursor: a substance from which the final specific substances is obtained by metabolism or chemical reactions
Hydrogen peroxide can be produced anywhere without large equipment by simply injecting both hydrogen gas and oxygen gas into an aqueous solution using the catalyst developed by the researchers. Unlike the Pd catalyst, the catalyst developed by the joint researchers can produce hydrogen peroxide up to 95% even at ambient temperature (10 ?C) and atmospheric pressure (1 atm). In addition, a catalytic reaction can be maintained for longer than 8 h, resulting from the structural stability of the catalyst.
The researchers clearly established the crystal structure of Pt-Au alloy nanoparticles by performing additional computer simulations, which is difficult to solve using general material analysis techniques. Furthermore, the catalytic reaction mechanism via compuater simulations was proposed at the atomic level in which the reason why the catalytic performance for hydrogen peroxide production is increased iswith increasing Au content was also clarified.
Sang Soo Han, Head of the Center at KIST, said, "it is important that the developed catalysts provide an eco-friendly hydrogen peroxide production option that can be applied without any limitation of manufacturing sites. Therefore, commercialization for the hydrogen peroxide direct synthesis would be greatly accelerated by overcoming the limitation of Pd catalysts with the low selectivity" and "the time and cost for the development of novel catalysts, mainly explored through trial and error, could be considerably reduced through computer simulations".
INFORMATION:
This study was conducted by the Creative Materials Discovery Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).The research results were published in the latest issue of an international journal 'Acta Materialia' in the field of materials science.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine have developed and validated a short questionnaire to help patients report symptoms and assist healthcare providers in assessing the severity of symptoms, and in monitoring and adjusting treatment accordingly.
The tool, called SymTrak-8, is a shorter version of the SymTrak-23. The questionnaire tracks symptoms such as pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, memory problems, anxiety and depression in older adults, enabling clinicians to provide better care for the diseases causing the symptoms.
"These symptoms are commonly reported in primary care, but they can be a sign of a variety of different diseases, so tracking them is important," said Kurt ...
2021-02-16
Teens may be more likely to use marijuana after legalization for adult recreational use
PISCATAWAY, NJ - Adolescents who live in California may be more likely to use marijuana since adult recreational marijuana use was legalized in 2016, according to a new report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
"The apparent increase in marijuana use among California adolescents after recreational marijuana legalization for adult use in 2016 is surprising given the steady downward trend in marijuana use during years before legalization," says lead researcher Mallie J. ...
2021-02-16
A new first-of-its-kind study has questioned whether pub operators can effectively and consistently prevent COVID-19 transmission - after researchers observed risks arising in licensed premises last summer.
Led by the University of Stirling, the research was conducted in May to August last year in a wide range of licensed premises which re-opened after a nationwide lockdown, and were operating under detailed guidance from government intended to reduce transmission risks.
While observed venues had made physical and operational modifications on re-opening, ...
2021-02-16
A technology that is widely used by commercial genetic testing companies is "extremely unreliable" in detecting very rare variants, meaning results suggesting individuals carry rare disease-causing genetic variants are usually wrong, according to new research published in the BMJ.
After hearing of cases where women had surgery scheduled after wrongly being told they had very rare genetic variations in the gene BRCA1 that could significantly increase risk of breast cancer, a team at the University of Exeter conducted a large-scale analysis of the technology using data from nearly 50,000 people. They found that the technology wrongly identified ...
2021-02-16
Recreational drinking, smoking, and drug use is linked to premature heart disease in young people, particularly younger women, finds research published online in the journal Heart.
Those who regularly use 4 or more substances are 9 times as likely to be affected, the findings indicate.
The numbers of new cases of heart disease (atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease) have been increasing in young adults, but the potential role of recreational substance use isn't entirely clear.
To probe this further, the researchers explored whether the recreational use of tobacco, cannabis, alcohol, and illicit drugs, such as amphetamine and cocaine, might be linked to prematurely and extremely prematurely furred up arteries.
They drew on information supplied ...
2021-02-16
Ageism, sexism, and Western ideals of the nuclear family have excluded grandmothers from national and international policy initiatives to save newborn lives in the Global South, suggests an analysis published in the online journal BMJ Global Health.
This is despite published research indicating that they are a valuable and influential resource for children's health and survival in many cultures, the study author points out.
Around three out of 4 newborn deaths in the Global South occur in the first week of life--40% of them on the first day, and most of them at home.
But ...
2021-02-16
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Zika vaccine candidate shows promise in phase I trial
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-5306
Editorial: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-0397
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
The Zika virus candidate, Ad26.ZIKV.001, a replication-incompetent human adenovirus serotype 26 (ad26) vector showed ...
2021-02-15
A new paper refines estimates of when herbivorous dinosaurs must have traversed North America on a northerly trek to reach Greenland, and points out an intriguing climatic phenomenon that may have helped them along the journey.
The study, published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is authored by Dennis Kent, adjunct research scientist at Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, and Lars Clemmensen from the University of Copenhagen.
Previous estimates suggested that sauropodomorphs -- a group of long-necked, herbivorous dinosaurs that eventually included Brontosaurus and Brachiosaurus ...
2021-02-15
Experts have devised a novel approach to selecting photos for police lineups that helps witnesses identify culprits more reliably.
In a paper published by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers - from the University of California San Diego and Duke University in the United States and the University of Birmingham in the U.K. - show for the first time that selecting fillers who match a basic description of the suspect but whose faces are less similar, rather than more, leads to better outcomes than traditional approaches in the field.
The counterintuitive technique improves eyewitness performance by about 10 percent.
"In ...
2021-02-15
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT researchers have invented a new type of amputation surgery that can help amputees to better control their residual muscles and sense where their "phantom limb" is in space. This restored sense of proprioception should translate to better control of prosthetic limbs, as well as a reduction of limb pain, the researchers say.
In most amputations, muscle pairs that control the affected joints, such as elbows or ankles, are severed. However, the MIT team has found that reconnecting these muscle pairs, allowing them to retain their normal push-pull ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Hydrogen peroxide, universal oxidizing agent, high-efficiency production by simple process
Computer simulation-based catalyst development for hydrogen peroxide production with selectivity of 95%. Development of the platinum-gold alloy catalyst facilitating hydrogen peroxide direct synthesis from hydrogen and oxygen at room temperature and atmo