New tool predicts the success of extubating patients on intensive mechanical ventilation
The study show a potential reduction of the current rate of reintubation from 9% to 1% by using machine learning tools; data from a thousand intensive-care patients with respiratory difficulties has been processed and analyzed to create this tool
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) Almost half the patients admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) require invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), a medical procedure that guarantees a sufficient supply of oxygen to their organs and tissues. The therapy involves connecting patients to a machine that substitutes their spontaneous breathing. In recent months it has been in general use in intensive-care patients affected by COVID-19.
Although it can often save a patient's life, invasive mechanical ventilation is not risk-free: there can be accidental injury during intubation or extubation or the muscles involved in the breathing process can atrophy. So the doctors responsible for intensive-care patients have to find a balance between keeping patients intubated as long as they cannot breathe for themselves and not keeping them intubated any longer than necessary so that they can start their recovery. In accordance with current criteria, an extubation is regarded to have failed if patients have to be intubated again (reintubation) within 48 hours of having withdrawn invasive mechanical ventilation.
To prevent as many reintubations as possible, a multidisciplinary research team consisting of the research group Ecommfit, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering of the Universitat Rovira i Virgili and ICU doctors from the Joan XXIII University Hospital-Pere Virgili Institute of Health Research has developed a mathematical model that makes it possible to predict the result of an extubation practised in a critical adult patient on invasive mechanical ventilation.
The study was carried out with a massive, heterogeneous set of data from a variety of sources such as patient monitoring equipment, demographic data (age, sex, weight, etc.), clinical data obtained on admission to the ICU and records of incidents by the medical staff. By using machine learning techniques, researchers have been able to determine the complex relation between all these variables and create models that can reveal part of the complexity of all that is happening within the patient.
The research team from the ICU of the Joan XXIII University Hospital, led by Maria Bodí (head of the ICU) and the data scientist Josep Gómez collected data from approximately 1,000 patients with breathing difficulties who had been admitted to the ICU in the previous five years. Subsequently this data was processed and analysed by a research group from the Department of Mechanical Engineering led by Alexandre Fabregat.
The results of the study, published in the journal Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, show that the current rate of reintubation of 9% can be reduced to 1%, thus minimising the risk for patients. The team is now focusing on incorporating this model into the ICU monitoring systems so that it can be readily accessed and used for fast predictions. When it has been fully developed, the model will be tested to show its effectiveness.
INFORMATION:
Bibliographical reference: Alexandre Fabregat, Mónica Magret, Josep Anton Ferré, Anton Vernet, Neus Guasch, Alejandro Rodríguez, Josep Gómez, María Bodí, "A Machine Learning decision-making tool for extubation in Intensive Care Unit patients", Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2020, 105869, ISSN 0169-2607, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105869.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
A NEW study from the University of Chichester has shed light on how people coped psychologically with the sudden and life-changing disruption caused by COVID-19.
This new publication, by Chichester's Professor Laura Ritchie and PhD candidate Benjamin Sharpe, in collaboration with Professor Daniel Cervone of the University of Illinois at Chicago, provides a unique snapshot into people's understanding of their goals and self-beliefs amidst a shared, unexpected alteration of the daily landscape during lockdown.
Ritchie and colleagues collected their ...
2021-02-16
HOUSTON - (Feb. 15, 2021) - Collagen is the king of biological proteins, and now it has a SCEPTTr.
That's the handle of an algorithm developed by Rice University scientists who study natural and synthetic versions of collagen, which accounts for about a third of the body's proteins and forms the fibrous glue in skin, bones, muscles, tendons and ligaments.
The program -- full name, Scoring function for Collagen-Emulating-Peptides' Temperature of Transition -- accurately predicts the stability of collagen triple helices, the primary structure that forms fibrils.
The Rice team led by chemist and bioengineer Jeffrey ...
2021-02-16
According to some estimates, chronic pain affects up to 40% of Americans, and treating it frustrates both clinicians and patients--a frustration that's often compounded by a hesitation to prescribe opioids for pain.
A new study from the University of Michigan School of Dentistry confirms that a low dose of a drug called naltrexone is a good option for patients with orofacial and chronic pain, without the risk of addiction, said first author Elizabeth Hatfield, a clinical lecturer in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Hospital Dentistry.
Naltrexone is a semisynthetic opioid first developed in ...
2021-02-16
HOUSTON - (Feb. 15, 2021) - Rice University engineers have suggested a colorful solution to next-generation energy collection: Luminescent solar concentrators (LSCs) in your windows.
Led by Rafael Verduzco and postdoctoral researcher and lead author Yilin Li of Rice's Brown School of Engineering, the team designed and built foot-square "windows" that sandwich a conjugated polymer between two clear acrylic panels.
That thin middle layer is the secret sauce. It's designed to absorb light in a specific wavelength and guide it to panel edges lined with solar cells. Conjugated polymers are chemical compounds ...
2021-02-16
Researchers from the University of Southampton and Université Laval, Canada, have successfully measured for the first time back-reflection in cutting-edge hollow-core fibres that is around 10,000 times lower than conventional optical fibres.
This discovery, published this week in The Optical Society's flagship Optica journal, highlights yet another optical property in which hollow-core fibres are capable of outperforming standard optical fibres.
Research into improved optical fibres is key to enable progress in numerous photonic applications. Most notably, these would improve Internet performance ...
2021-02-16
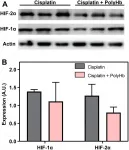
Oncotarget recently published "Polymerized human hemoglobin increases the effectiveness of cisplatin-based chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer" which reported that unfortunately, a significant portion of NSCLC patients relapse due to cisplatin chemoresistance.
Administration of hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers is a promising strategy to alleviate hypoxia in the tumor, which may make cisplatin more effective.
The R-state PolyHb administered in this study is unable to deliver O2 unless under severe hypoxia which significantly limits its oxygenation potential.
In vitro sensitivity studies indicate that the administration of PolyHb increases the effectiveness of cisplatin under ...
2021-02-16
BOSTON -- While PCR testing has been used widely for COVID-19 diagnosis, it only provides information on who is currently infected. Antibody testing can tell who has been previously exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, a metric that is essential for tracking spread across a population. It may also, as a study recently published in the journal Nature Communications shows, hold the key to understanding the immune response to the virus.
Led by Galit Alter, PhD, Core Member of the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, this study found that while antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 may be a good way to measure exposure to the virus, their presence alone wasn't enough to determine if a person had long-lasting protection. Instead, antibody effector functions associated ...
2021-02-16
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Radiomics--the extraction of very detailed quantitative features from medical images--provides a refined understanding of how cocaine use and other risk factors affect the course of coronary artery disease, according to a study published in Radiology. Researchers said the study shows the power of radiomics to improve understanding of not just cardiovascular disease, but cancer and other conditions as well.
Coronary artery disease typically develops over time as plaque builds up inside the arteries. This process, known as atherosclerosis, ...
2021-02-16
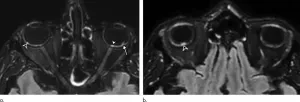
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Researchers using MRI have found significant abnormalities in the eyes of some people with severe COVID-19, according to a study published in the journal Radiology. The study results support the need for eye screening in these patients to provide appropriate treatment and management of potentially severe ophthalmological manifestations of COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected more than 100 million people since it began early in 2020. While the virus primarily attacks the lungs, it has been linked with eye abnormalities ...
2021-02-16
Launched in 1988, the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) stands out as one of the largest, internationally coordinated global public health major projects conducted to date, with cumulative spending of over $16.5 billion for 1988-2018, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). More than 30 years later, stubborn outbreaks of wild poliovirus still occur in Afghanistan and Pakistan, where cases have been increasing since 2018. The global eradication of polio continues to be an elusive goal.
A special issue of the journal Risk Analysis, titled "Global Poliovirus Risk Management and Modeling," looks at the current status of polio eradication ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New tool predicts the success of extubating patients on intensive mechanical ventilation
The study show a potential reduction of the current rate of reintubation from 9% to 1% by using machine learning tools; data from a thousand intensive-care patients with respiratory difficulties has been processed and analyzed to create this tool