(Press-News.org) BOSTON -- While PCR testing has been used widely for COVID-19 diagnosis, it only provides information on who is currently infected. Antibody testing can tell who has been previously exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, a metric that is essential for tracking spread across a population. It may also, as a study recently published in the journal Nature Communications shows, hold the key to understanding the immune response to the virus.
Led by Galit Alter, PhD, Core Member of the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, this study found that while antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 may be a good way to measure exposure to the virus, their presence alone wasn't enough to determine if a person had long-lasting protection. Instead, antibody effector functions associated with long-lasting protection, like virus neutralization and T cell responses, were only seen if the immune response included high levels of antibodies against a part of the virus called the receptor binding domain.
"Essentially," says Alter, who is also a professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School (HMS), "this study indicates that it's not simply the presence or absence of antibodies that matter; rather, the amount and type of antibodies may play a defining role in the development of a protective immune response."
This data came from a cohort of adults who had mild or asymptomatic cases of COVID-19 (unusual among the studies that started in the early days of the pandemic), the result of a collaboration with SpaceX, an aerospace manufacturer and space transportation services company that was seeking data-driven ways to protect its essential workforce.
The project began in April of 2020 and, along with Alter and her group, included Anil Menon, MD, Medical Director at SpaceX; Doug Lauffenberg, Ford Professor of Biological Engineering, Chemical Engineering, and Biology at MIT; Elon Musk, CEO of SpaceX; and Eric Nilles, MD, Director of the Program on Infectious Diseases and Epidemics at the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative.
"This collaboration with SpaceX that has pulled together immunologists, epidemiologists, molecular and computational biologists and infectious disease modelers is a fantastic example of teamwork across institutions and disciplines, and I'm delighted to see this first publication from these efforts," says Nilles, who is also a professor at HMS and an attending physician at the Brigham and Women's Hospital.
Though the original goal of the study was to measure antibody levels over time, when reports of reinfection began surfacing, Alter's team realized their samples may hold much more valuable information than they originally thought.
"In early spring, we weren't sure if asymptomatic infection could drive long-lived antibodies," says Alter, "nor whether they possessed the capability to neutralize or kill the virus."
The team did know, however, that 120 of their study participants had experienced mild or asymptomatic COVID-19 which had resulted in the development of COVID-19 antibodies. By using sophisticated techniques to delve into these antibody responses, they discovered that individuals who had developed a larger number of antibodies, associated with stronger symptoms in case of mild COVID-19, had also developed immune functions associated with natural immune protection.
"Once you hit a certain threshold of these antibodies, it's like a switch turns on and we can observe antibody effector functions," says Yannic Bartsch, PhD, a Ragon postdoctoral fellow and first author on the study. "These functions were not observed in individuals with lower antibody binding titers, and the level of protection from reinfections is uncertain in these individuals."
Though more work remains to be done, this is an important first step in understanding natural immunity to SARS-CoV-2. With limited availability of COVID-19 vaccines, understanding asymptomatic infection, natural immunity, and who, exactly, is at risk for reinfection, is vital to an effective, successful global vaccine rollout.
INFORMATION:
This work was funded by donations from Nancy Zimmerman, Mark and Lisa Schwartz, an anonymous donor (financial support), and Terry and Susan Ragon, as well as the SAMANA Kay MGH Research Scholars award, and funding from the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard, the Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness (MassCPR), the NIH (3R37AI080289-11S1, R01AI146785, U19AI42790-01, U19AI135995-02, U19AI42790-01, 1U01CA260476 - 01, CIVIC75N93019C00052), the Gates Foundation Global Health Vaccine Accelerator Platform funding (OPP1146996 and INV-001650), the Musk Foundation, and the Translational Research Institute for Space Health through NASA Cooperative Agreement NNX16AO69A.
About the Ragon Institute
The Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard was established in 2009 with a gift from the Phillip T. and Susan M. Ragon Foundation, with a collaborative scientific mission among these institutions to harness the immune system to combat and cure human diseases. Focusing on global infectious diseases, the Ragon Institute draws scientists, clinicians and engineers from diverse backgrounds and areas of expertise to study and understand the immune system with the goal of benefiting patients. For more information, visit http://www.ragoninstitute.org
About the Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. In August 2020, Mass General was named #6 in the U.S. News & World Report list of "America's Best Hospitals."
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Radiomics--the extraction of very detailed quantitative features from medical images--provides a refined understanding of how cocaine use and other risk factors affect the course of coronary artery disease, according to a study published in Radiology. Researchers said the study shows the power of radiomics to improve understanding of not just cardiovascular disease, but cancer and other conditions as well.
Coronary artery disease typically develops over time as plaque builds up inside the arteries. This process, known as atherosclerosis, ...
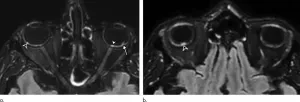
OAK BROOK, Ill. - Researchers using MRI have found significant abnormalities in the eyes of some people with severe COVID-19, according to a study published in the journal Radiology. The study results support the need for eye screening in these patients to provide appropriate treatment and management of potentially severe ophthalmological manifestations of COVID-19.
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected more than 100 million people since it began early in 2020. While the virus primarily attacks the lungs, it has been linked with eye abnormalities ...
Launched in 1988, the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) stands out as one of the largest, internationally coordinated global public health major projects conducted to date, with cumulative spending of over $16.5 billion for 1988-2018, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). More than 30 years later, stubborn outbreaks of wild poliovirus still occur in Afghanistan and Pakistan, where cases have been increasing since 2018. The global eradication of polio continues to be an elusive goal.
A special issue of the journal Risk Analysis, titled "Global Poliovirus Risk Management and Modeling," looks at the current status of polio eradication ...
Earth is home to millions of known species of plants and animals, but by no means are they distributed evenly. For instance, rainforests cover less than 2 percent of Earth's total surface, yet they are home to 50 percent of Earth's species. Oceans account for 71 percent of Earth's total surface but contain only 15 percent of Earth's species. What drives this uneven distribution of species on Earth is a major question for scientists.
In a paper published February 16 in the Journal of Biogeography an international team of researchers led by Jacob S. Suissa, Ph.D. Candidate in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, ...
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) physicians and scientists presented new research at the 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology Genitourinary Cancers Symposium held virtually February 11-13. Notably, MSK medical oncologist Robert Motzer, MD, presented encouraging data from a phase III randomized study that assessed two new treatment combinations as first-line treatments that may prolong survival in people with advanced kidney cancer. Dr. Motzer's findings were also published on February 13 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In this large, international trial involving 200 sites across 20 countries, Dr. Motzer and a team of investigators ...
Using advanced RNA sequencing, scientists have identified two unique subtypes of a prominent mutation present in many patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) - called NPM1 - that could help predict survival and improve treatment response for patients whose leukemic cells bear the mutation.
In research published Feb. 16, in Nature Communications, a team led by Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Senior Scientists, Drs. Benjamin Haibe-Kains, Aaron Schimmer and Mark Minden, have discovered that within the NPM1 mutation of AML there exists two unique subtypes, one of which can be effectively treated with drugs already in use.
It is the first study to classify within the common NPM1 mutant form of AML two subtypes, one being "primitive" and the other ...
Most people infected with SARS-CoV-2 are able to recover from the disease at home - even if they might experience very stressful disease progressions. Some have no symptoms at all. But about ten percent of those affected become so severely ill that they have to be treated in a hospital. The assumption that a weak immune system is behind a severe progression is short-sighted. Especially with critical progressions, the immune system works under intense pressure, but does not manage to control the virus.
A Berlin research group has now observed how SARS-CoV-2 uses an immune system defense mechanism to increasingly hijack ...
Computing - Modeling COVID dynamics
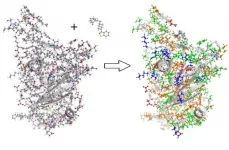
To better understand the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have harnessed the power of supercomputers to accurately model the spike protein that binds the novel coronavirus to a human cell receptor.
These simulations also shed light on the ligand molecules that can inhibit such binding, pointing the way to potential drug therapies.
An ultrafast quantum chemical modeling method provides information about the critical electronic interactions between protein and ligand chemicals, going beyond the classical interaction models that are normally employed in computational drug discovery.
The findings will enable accurate predictions of the performance of currently available inhibitors ...
The University of Kent has led a study highlighting the urgent need for the UK's Government and renewable energy industries to give vital attention to decommissioning offshore wind turbines approaching their end of live expectancy by 2025. The research reveals that the UK must decommission approximately 300 and 1600 early-model offshore wind turbines by 2025 and 2030, respectively.
Urgent focus is needed now to proactively use the remaining years until turbines installed in the 1990s and early 2000s are no longer safely functional in 2025, to prevent safety lapses, potentially huge costs and the irretrievable loss of the skillset required for safe decommission.
The research shows that these original turbines have an approximate lifetime of 20 to 25 years, but this expectation ...
Atropisomers are a class of stereoisomers (chemical compounds that differ in spatial arrangement of atoms) arising from restricted rotation around a single bond and have various applications in chemistry. To date, most research on atropisomers has focused on "biaryl atropisomers" (due to the rotational restriction around a carbon-carbon bond), but it is also possible for atropisomers to arise from rotational restrictions around a nitrogen-carbon (N-C) bond. These N-C axially chiral compounds are found in various natural products and bioactive compounds and thus have promising applications in medicine ...