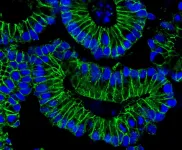
(Press-News.org) Using advanced RNA sequencing, scientists have identified two unique subtypes of a prominent mutation present in many patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) - called NPM1 - that could help predict survival and improve treatment response for patients whose leukemic cells bear the mutation.
In research published Feb. 16, in Nature Communications, a team led by Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Senior Scientists, Drs. Benjamin Haibe-Kains, Aaron Schimmer and Mark Minden, have discovered that within the NPM1 mutation of AML there exists two unique subtypes, one of which can be effectively treated with drugs already in use.
It is the first study to classify within the common NPM1 mutant form of AML two subtypes, one being "primitive" and the other "committed." Furthermore, the research shows that each subtype has a different response to treatment and long-term survival, cracking open opportunities to personalize treatment plans and introduce new targeted therapies in the future.
"Patients with NPM1 mutated AML face a relapse rate of around 40 per cent," says Dr. Schimmer, Research Director and acute leukemia physician at the Princess Margaret, which is part of University Health Network. "While we're getting better at incorporating new monitoring techniques, we're still not at a point where we can adequately predict what side of the curve a patient might fall.
By going deeper with our sequencing, we can better predict outcomes and adjust treatment accordingly for each patient."
NPM1 mutated AML makes up around 30 per cent of all AML cases, but therapeutic discoveries for these patients have been limited.
"While the NPM1 mutation is relatively common, AML is a rare disease to begin with," says Dr. Haibe-Kains, who is also an Associate Professor of Medical Biophysics at the University of Toronto. "Generating enough data to be able to sequence and understand the biology of this mutation is very challenging."
This was made possible in large part thanks to a team led by Dr. Minden, Senior Scientist and medical oncologist, and Andrea Arruda, staff scientist at the Princess Margaret Cancer, who have been collecting samples to enable deeper learning since the mid-1980s thanks to the willingness, generosity and foresight of patients.
"Recognizing those 'needles in a haystack' - the small groups of patients that don't benefit from certain treatments is critically important for improving personalized medicine," says Dr. Minden. "Now we can start to improve outcomes for this more discreet patient population."
An advanced computational model was custom-built to analyze RNA from patient leukemic cells obtained from the Leukemia Live Cell Tissue Bank, along with other data published from NPM1 mutant leukemia studies.
"We developed a unique machine-learning model that was able to clearly discriminate two subtypes of NPM1 mutant AML in datasets collected from patients," says Dr. Haibe-Kains.
These two subtypes both contain mutant AML but they express different genes that can now separate them into two clear subtypes based on their RNA.
The study also suggests that certain drugs already used to treat other types of cancer could be effective in the primitive subtype.
"Once we were able to identify the pattern of each subtype, we analyzed existing pharmacogenomics data to narrow a list of drugs that might be able to target one subtype or the other," explained Dr. Haibe-Kains. "We found two drugs that seemed to effectively target the primitive subtype in the lab, with potential to move to clinical trials in the future."
"This finding could change the way we treat patients," says Dr. Schimmer. "It opens up the opportunity to better refine and time treatments - whether it's the decision for a stem cell transplant early on, or choosing more effective and less toxic therapies throughout the course of treatment.
Our goal with all of our patients is to get better and better outcomes. This is one step towards doing better."
This research was supported by funds from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Orsino Chair in Leukemia Research and the Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation.
ADS has received research funding from Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Medivir AB, and consulting fees/honorarium from Takeda, Novartis, Jazz, and Otsuka Pharmaceuticals. ADS holds stock in Abbvie. ADS, is an inventor on patent applications claiming the use of DNTs for the treatment of AML.
INFORMATION:
About Princess Margaret Cancer Centre
Princess Margaret Cancer Centre has achieved an international reputation as a global leader in the fight against cancer and delivering personalized cancer medicine. The Princess Margaret, one of the top five international cancer research centres, is a member of the University Health Network, which also includes Toronto General Hospital, Toronto Western Hospital, Toronto Rehabilitation Institute and the Michener Institute for Education at UHN. All are research hospitals affiliated with the University of Toronto. For more information: http://www.theprincessmargaret.ca
Most people infected with SARS-CoV-2 are able to recover from the disease at home - even if they might experience very stressful disease progressions. Some have no symptoms at all. But about ten percent of those affected become so severely ill that they have to be treated in a hospital. The assumption that a weak immune system is behind a severe progression is short-sighted. Especially with critical progressions, the immune system works under intense pressure, but does not manage to control the virus.
A Berlin research group has now observed how SARS-CoV-2 uses an immune system defense mechanism to increasingly hijack ...
Computing - Modeling COVID dynamics
To better understand the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have harnessed the power of supercomputers to accurately model the spike protein that binds the novel coronavirus to a human cell receptor.
These simulations also shed light on the ligand molecules that can inhibit such binding, pointing the way to potential drug therapies.
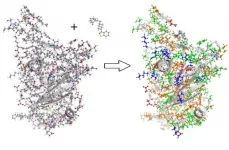
An ultrafast quantum chemical modeling method provides information about the critical electronic interactions between protein and ligand chemicals, going beyond the classical interaction models that are normally employed in computational drug discovery.
The findings will enable accurate predictions of the performance of currently available inhibitors ...
The University of Kent has led a study highlighting the urgent need for the UK's Government and renewable energy industries to give vital attention to decommissioning offshore wind turbines approaching their end of live expectancy by 2025. The research reveals that the UK must decommission approximately 300 and 1600 early-model offshore wind turbines by 2025 and 2030, respectively.
Urgent focus is needed now to proactively use the remaining years until turbines installed in the 1990s and early 2000s are no longer safely functional in 2025, to prevent safety lapses, potentially huge costs and the irretrievable loss of the skillset required for safe decommission.
The research shows that these original turbines have an approximate lifetime of 20 to 25 years, but this expectation ...
Atropisomers are a class of stereoisomers (chemical compounds that differ in spatial arrangement of atoms) arising from restricted rotation around a single bond and have various applications in chemistry. To date, most research on atropisomers has focused on "biaryl atropisomers" (due to the rotational restriction around a carbon-carbon bond), but it is also possible for atropisomers to arise from rotational restrictions around a nitrogen-carbon (N-C) bond. These N-C axially chiral compounds are found in various natural products and bioactive compounds and thus have promising applications in medicine ...
A POSTECH research team has developed a transparent amorphous silicon that transmits visible light - which permits us to distinguish the colors of objects - enabling the development of paper-thin lenses usable in head-mounted displays (HMD) that show virtual and augmented reality images in real time.
A research team - led by Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH's mechanical engineering and chemical engineering departments, and Ph.D. candidate Younghwan Yang and Dr. Gwanho Yoon of the Department of Mechanical Engineering - has developed visibly transparent amorphous silicon by improving the plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) method, a practice widely used by Korean display manufacturers. ...
Tsukuba, Japan - Sleep is very important for athletes, and sleep loss can affect physical performance and cognitive ability. But now, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have identified the prevalence of sleep disorders in visually impaired athletes, as well as specific risk factors associated with lower sleep quality.
In a study published last November in Sleep Medicine, researchers from the University of Tsukuba conducted a survey of 99 visually impaired athletes in Japan and analyzed data from 81 respondents. They found that approximately one-third of the respondents had sleep disorders. Further, higher levels of stress regarding interpersonal relationships ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Statistical modeling developed by Oregon State University researchers has confirmed that changes to melanoma patients' gut microbiome led them to respond to a type of treatment capable of providing long-term benefit.
Findings were published in Science.
The modeling technique invented by Andrey Morgun of the OSU College of Pharmacy and Natalia Shulzenko of Oregon State's Carlson College of Veterinary Medicine is known as transkingdom network analysis.
The human gut microbiome is a community of more than 10 trillion microbial cells from about 1,000 different bacterial species, and transkingdom network analysis integrates ...
Water is a necessity for all life but its availability can be limited. In geographical areas experiencing dry seasons, animals congregate near the few freshwater sources, often reaching large densities. At these sites many animals from different species come to the same spots to drink, potentially operating as key locations for pathogen transmission within and between species. An international team of scientists lead by the German Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) suggests that viruses can use restricted freshwater sources as a vector to be spread among animals. The key prediction of this idea is that animal viruses remain stable and infectious in water. The team ...
The effects of microplastics on our health and the environment are being rigorously studied all across the world. Researchers are identifying microplastic sources and their potential routes to the environment by examining rainwater, wastewater, and soil.
Microplastics have been found in nearly all organisms and habitats everywhere in the world. However, factors contributing to the influx and accumulation of microplastics in water ecosystems aren't fully understood yet. The focus of microplastics research has, for a long time, been on the age of microplastics found in sediments, and on the ...
The researchers analysed cells, mouse models, and human patient samples using biochemical, mathematical, and biophysical methods. They identified a protein present in the mesh-like membrane structure (the basement membrane) associated with tumour and vessel softness, and good survival of cancer patients. The researchers tested if removing this protein from the basement membrane would enhance the spread of cancer, which it did, and if supply of this protein would reduce cancer spread, which it did. They proceeded to show that the levels of this protein (netrin-4) already present in basement membrane of organs may determine cancer spread even before cancer develops, ...