Cytoglobin: key player in preventing liver disease
Osaka City University paves way for liver health by discovering the use of cytoglobin in anti-fibrotic therapy
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) Researchers have discovered that the use of Cytoglobin (CYGB) as an intravenous drug could delay liver fibrosis progression in mice.
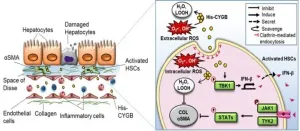
CYGB, discovered in 2001 by Professor Norifumi Kawada, is present in hepatic stellate cells, the cells that produce fibrotic molecules such as collagens when the liver has acute or chronic inflammation induced by different etiologies. The enhancement of CYGB on these cells or the injection of recombinant CYGB has the effect of suppressing liver damage and cirrhosis. These findings published in the February 2021 issue of the journal Hepatology.
Anti-fibrotic therapy remains an unmet medical need in human chronic liver diseases. A research team led by Professor Norifumi Kawada, Osaka City University (OCU), reported the novel anti-fibrotic properties of CYGB, a respiratory protein expressed in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the main cell type involved in liver fibrosis. In mice with advanced liver fibrosis, both enhancement of CYGB or recombinant CYGB injection can suppress hepatocyte damage and liver fibrosis. In chimera mice with a human liver, the injected CYGB did not show any adverse side effects.
"Fixing the liver after injury is a highly orchestrated, coordinated process, and inhibiting the fibrosis could return the liver to a healthy condition," said Norifumi Kawada, M.D., Ph.D., Dean of OCU Medical School and senior author of the study.
Liver injury starts with hepatocyte damage, following several conditions including inflammatory cell infiltration, activation of HSCs, and the production of harmful reactive oxygen species (ROSs). Dr. Kawada, along with Le Thi Thanh Thuy, PhD., OCU scientist, and their colleagues, observed that when they culture human HSCs under recombinant human CYGB treatment, it can enter the cellular organelles, hunt the harmful ROSs, and prevent the activation of HSCs leading to inhibit collagen production.
To identify potential treatment strategies, Dr. Kawada and his team developed several animal models of liver injury and investigated how the liver responds to CYGB regulation and treatment.
In both mouse models of bile flow obstruction induced cholestasis and high fat diet induced fatty liver disease, the absence of CYGB made the liver injury more severe, however, when CYGB was enhanced, the liver injury subsided.
In the next set of experiments, Dr. Kawada and his group tried to generate two other mouse models of advanced liver fibrosis using different chemical agents and applied recombinant human CYGB protein by intravenous injection. Interestingly, the therapeutic protein dramatically suppressed liver injuries, inflammation and fibrosis without any side effects.
Using the results of this research as a foothold, the research team hopes to start clinical trials using this new anti-fibrotic therapy.
INFORMATION:
Osaka City University
For more information, please visit our website: https://www.osaka-cu.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
Dry and cloudless weather was mainly responsible for the unusually high solar irradiance in western Europe during the spring of 2020, not the reduction in aerosol emissions due to the first lockdown. This was the result of an international meteorological study, in which scientists from the University of Cologne participated. The results have been published in the current issue of Nature Communications Earth & Environment.
A large part of western Europe experienced exceptionally sunny and dry weather from March 23 to the end of May 2020. New sunshine extremes were reported in the United Kingdom, Belgium, Germany, and the Netherlands, coupled with exceptionally deep blue skies. At the same time, these countries had gone into lockdown in response ...
2021-02-16
Historically, most electric transmission system operators have used heuristics (rules based on experience) to hold sufficient reserves to guard against unforeseen large outages and maintain system reliability. However, the expansion of competitive wholesale electricity markets has led to efforts to translate reserve heuristics into competitively procured services. A common approach constructs an administrative demand curve for valuing and procuring least cost reserve supply offers. The technical term for this is the operating reserve demand curve (ORDC). A new paper quantifies how better accounting for the temperature-dependent probability of large generator contingencies with time-varying dynamic ORDC construction improves reserve procurement.
The paper, "Dynamic Operating Reserve Procurement ...
2021-02-16
Between January 2012 and March 2018, there were an average of 1,000 failures each year at large North American gas power plants due to unscheduled fuel shortages and fuel conservation interruptions. This is a problem as the power grid depends on reliable natural gas delivery from these power plants in order to function. More than a third of all U.S. electricity is generated from natural gas. New research now indicates that these fuel shortages are not due to failures of pipelines and that in certain areas of the country a change in how gas is purchased ...
2021-02-16
DALLAS - Feb. 16, 2021 - A study that identifies how a coronavirus protein called Nsp1 blocks the activity of genes that promote viral replication provides hope for new COVID-19 treatments.
Since the start of the pandemic, scientists have worked endlessly to understand SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Even with the arrival of vaccines, the virus is still spreading and there is a need to develop alternative therapies. Scientists hope to achieve this by studying how SARS-CoV-2 infects cells and propagates itself while avoiding the body's natural immune system.
Now researchers at UT Southwestern have added another piece to this puzzle with their END ...
2021-02-16
TUCSON, Ariz. -- The ongoing pandemic has had a significant and alarming trend of increased alcohol use and abuse - especially among younger adults, males and those who have lost their jobs - according to a new study by University of Arizona Health Sciences researchers.
Research led by William "Scott" Killgore, PhD, professor of psychiatry in the UArizona College of Medicine - Tucson and director of the Social, Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience Lab, found that hazardous alcohol use and likely dependence increased every month for those under lockdowns compared to those not under restrictions.
"Being under lockdown during a worldwide pandemic has been hard on everyone, and many people are relying on greater quantities of alcohol to ease their distress," said Dr. ...
2021-02-16
Shoe shops sell a variety of shoe sizes to accommodate a variety of foot sizes -- but what if both the shoe and foot size depended on how it was measured? Recent developments in quantum theory suggest that the available values of a physical quantity, such as a foot size, can depend on the type of measurement used to determine them. If feet were governed by the laws of quantum mechanics, foot size would depend on the markings on a foot measure to find the best fit -- at the time of measurement -- and even if the markings were changed, the measurement could still be precise.
In quantum mechanics, the "size" of a physical ...
2021-02-16
Because cancers in children are rare, many details about their biology remain unknown. In the field of cancer genetics, there's a limited understanding of how inherited genetic changes may contribute to the formation and growth of tumors. Making connections between particular gene mutations and disease requires a lot of data, which until recently has been largely unavailable for pediatric cancers.
Now, tests like MSK-IMPACTTM can screen tumors for mutations in more than 500 genes as well as analyze patients' normal (germline) cells. In the largest study of its kind so far, researchers from Memorial Sloan Kettering's pediatric program, MSK Kids, are reporting germline genomic sequencing details for 751 pediatric patients treated for solid tumors.
The paper, ...
2021-02-16
Astronomers have tested a method for reconstructing the state of the early Universe by applying it to 4000 simulated universes using the ATERUI II supercomputer at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ). They found that together with new observations the method can set better constraints on inflation, one of the most enigmatic events in the history of the Universe. The method can shorten the observation time required to distinguish between various inflation theories.
Just after the Universe came into existence 13.8 billion years ago, it suddenly increased more than a trillion, trillion times in size, in less than a trillionth of a trillionth of a microsecond; but no one knows how or why. This sudden "inflation," is one of the ...
2021-02-16
Human health and ecosystems could be affected by microbes including cyanobacteria and algae that hitch rides in clouds and enter soil, lakes, oceans and other environments when it rains, according to a Rutgers co-authored study.
"Some of the organisms we detected in clouds and rain are known to have possible impacts on human health and could also affect microbial populations at rainfall locations," said lead author Kevin Dillon, a doctoral student in the lab of co-author Donna E. Fennell, a professor who chairs the Department of Environmental Sciences in the School of Environmental and Biological Sciences at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. "More work is needed to confirm that and to ...
2021-02-16
BETHESDA, Md. -- ASHP (American Society of Health-System Pharmacists) today announced the publication of two landmark reports that articulate a futuristic vision for pharmacy practice, including expanded roles for the pharmacy enterprise in healthcare organizations. The 2021 ASHP/ASHP Foundation Pharmacy Forecast Report and the Vizient Pharmacy Network High-Value Pharmacy Enterprise (HVPE) framework, published in AJHP, outline opportunities for pharmacy leaders to advance patient-centered care, population health, and the overall well-being of their organizations.
"During these unprecedented times, it is more important than ever for pharmacy leaders to demonstrate the value pharmacy services contribute ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cytoglobin: key player in preventing liver disease
Osaka City University paves way for liver health by discovering the use of cytoglobin in anti-fibrotic therapy