(Press-News.org) Metabolic diseases, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, have risen to epidemic proportions in the U.S. and occur in about 30 percent of the population. Skeletal muscle plays a prominent role in controlling the body's glucose levels, which is important for the development of metabolic diseases like diabetes.
In a recent study, published in END
Researchers identify muscle factor that controls fat metabolism
New discovery from team at University Hospitals and Case Western Reserve University could lead to metabolic disease therapies
2021-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds gender disparities on National Institutes of Health study sections
2021-02-16
Investigators at the University of Chicago Medicine have found that women are less likely to be represented as chairs and reviewers on study sections for the National Institutes of Health (NIH), based on data from one review cycle in 2019. The results, published on Feb. 15 in JAMA Network Open, have implications for the distribution of federal scientific funding.
The NIH is the top source of federal funding for biomedical research in the U.S., providing critical support and guidance on the nation's research programs. The study sought to understand the gender distribution ...
Campylobacter strains exchange genes, can become more virulent and antibiotic resistant
2021-02-16
New research from North Carolina State University has found that Campylobacter bacteria persist throughout poultry production - from farm to grocery shelves - and that two of the most common strains are exchanging genetic material, which could result in more antibiotic-resistant and infectious Campylobacter strains.
Campylobacter is a well-known group of foodborne bacteria, spread primarily through consumption of contaminated food products. In humans it causes symptoms commonly associated with food poisoning, such as diarrhea, fever and cramps. However, Campylobacter infections also constitute one of the leading precursors ...
A groundbreaking solution? Polymers can protect buildings from large fault ruptures
2021-02-16
Surface rupturing during earthquakes is a significant risk to any structure that is built across a fault zone that may be active, in addition to any risk from ground shaking. Surface rupture can affect large areas of land, and it can damage all structures in the vicinity of the fracture. Although current seismic codes restrict the construction in the vicinity of active tectonic faults, finding the exact location of fault outcrop is often difficult.
In many regions around the world, engineering structures such as earth dams, buildings, pipelines, landfills, bridges, roads and railroads have been built in areas very close to active fault segments. Strike-slip fault rupture occurs when the rock masses slip past each other ...
To improve immunotherapy, researchers look to shift immune cells' access to sugar
2021-02-16
Cancer cells and immune cells share something in common: They both love sugar.
Sugar is an important nutrient. All cells use sugar as a vital source of energy and building blocks. For immune cells, gobbling up sugar is a good thing, since it means getting enough nutrients to grow and divide for stronger immune responses. But cancer cells use sugar for more nefarious ends.
So, what happens when tumor cells and immune cells battle for access to the same supply of sugar? That's the central question that Memorial Sloan Kettering researchers Taha Merghoub, Jedd Wolchok, and Roberta Zappasodi explore in a new study published February 15 in the journal Nature.
Using mouse models and data ...
Regional variation in the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on data collection
2021-02-16
Ithaca, NY--The COVID-19 pandemic has changed life as we know it all around the world. It's changed human behavior, and that has major consequences for data-gathering citizen-science projects such as eBird, run by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. This worldwide database now contains more than a billion observations and is a mainstay of many scientific studies of bird populations. Newly published research in the journal Biological Conservation finds that when human behaviors change, so do the data.
"We examined eBird data submitted during April 2020 and compared them to data from April of prior years," explains lead ...
Unlocking the mystery behind skeletal aging
2021-02-16
Researchers from the UCLA School of Dentistry have identified the role a critical enzyme plays in skeletal aging and bone loss, putting them one step closer to understanding the complex biological mechanisms that lead to osteoporosis, the bone disease that afflicts some 200 million people worldwide.
The findings from their study in mice, END ...
Exercise now proven to have mental health benefits for prostate cancer
2021-02-16
New Edith Cowan University (ECU) research has found that exercise not only has physical benefits for men with prostate cancer, it also helps reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Up to one in four men experience anxiety either before or after prostate cancer treatment and up to one in five report depression, although few men access the support they need.
The study, published in the Nature journal Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases, is the first randomised controlled trial to examine the long-term effects of different exercise on psychological distress in men with prostate cancer undergoing androgen deprivation therapy (ADT).
Researchers randomly selected 135 prostate cancer patients aged ...
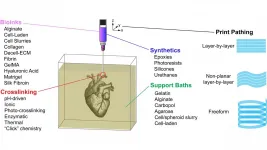
FRESH 3D-printing platform paves way for tissues, organs
2021-02-16
WASHINGTON, February 16, 2021 -- Research into 3D bioprinting has grown rapidly in recent years as scientists seek to re-create the structure and function of complex biological systems from human tissues to entire organs.
The most popular 3D printing approach uses a solution of biological material or bioink that is loaded into a syringe pump extruder and deposited in a layer-by-layer fashion to build the 3D object. Gravity, however, can distort the soft and liquid bioinks used in this method.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Carnegie Mellon University provide perspective on the Freefrom Reversible Embedding of Suspended Hydrogels ...
Association of maternal cardiovascular health during pregnancy with later health of offspring in adolescence
2021-02-16
What The Study Did: The observational study examined associations between maternal cardiovascular health during pregnancy (as measured by body mass index, blood pressure, total cholesterol level, glucose level and smoking) with the later cardiovascular health of their offspring at ages 10 to 14 years old (as measured by body mass index, blood pressure, total cholesterol level and glucose level).
Authors: Amanda M. Perak, M.D., M.S., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0247)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support ...
Low-value health care drops only marginally despite effort to curb practices
2021-02-16
Spending on low-value health care among fee-for-service Medicare recipients dropped only marginally from 2014 to 2018, despite both a national campaign to better educate clinicians and increasing use of payment revisions that discourage wasteful care, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Three items accounted for two-thirds of the low-value care. Among these, prescribing opioids for acute back pain increased despite a growing national awareness of the harms caused by the drugs and the role of such prescribing in fueling the nation's opioid ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Researchers identify muscle factor that controls fat metabolismNew discovery from team at University Hospitals and Case Western Reserve University could lead to metabolic disease therapies