Breakthrough in the fight against spruce bark beetles
2021-02-16
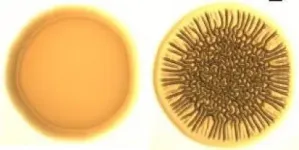
(Press-News.org) For the first time, a research team led by Lund University in Sweden has mapped out exactly what happens when spruce bark beetles use their sense of smell to find trees and partners to reproduce with. The hope is that the results will lead to better pest control and protection of the forest in the future.
The Eurasian spruce bark beetle uses its sense of smell to locate trees and partners. The odours are captured via odorant receptors (proteins) in their antennae. Researchers have long understood the connection, but so far they have not known exactly which receptors bind to what pheromones. This is key knowledge for the long-term development of more effective and environmentally friendly pesticides and bark beetle traps used to protect the forest.
The research team were able to characterize the response of odorant receptors in bark beetles for the first time. They identified 73 different receptors in the antennae of the Eurasian spruce bark beetle (Ips typographus), and succeeded in characterizing the odour response in two of the receptors. One responds to the pheromone ipsenol, the other to ipsdienol.
"A large number of different bark beetle species use these pheromones when communicating with scents, so the fact that we have been able to to characterize them is a breakthrough", says Martin N Andersson who led the research group consisting of researchers in Lund, Germany and the Czech Republic.
The two receptors are thus the first ever to be characterized in bark beetles. To put the result into context, Martin N Andersson says that within the entire insect order Coleoptera beetles, with more than 300,000 species on Earth, only three odour receptors had been characterized previously.
"Our results indicate that the pheromone receptors of different beetle species are evolutionarily unrelated, at least in the few species that have been studied. We also show that the odour response in these receptors is very specific, and we are the first in the world to be able to show exactly where in the receptors the pheromones are likely to bind", he says.
The results could make it possible to develop better and more environmentally friendly pest control methods. One approach is to try to find other odours that bind even better to the two receptors than ipsenol and ipsdienol. If such odours can be found, they can hopefully be used to disrupt the pheromone communication of spruce bark beetles - either by a stronger activation of the receptor compared with the natural pheromone, or by blocking the receptor.
Another way could be to use the two characterized receptors in a biosensor that is under development. This would quickly locate spruce bark beetles and thus be able to identify infested trees before the bark beetles spread.
According to Martin N Andersson, the practical applications are a few years away.
"Screening for better substances can begin in 2021. If we find something, the results must be confirmed in the lab and then evaluated in the field, and that would take two or three years. Using it in biosensors for monitoring and detection will probably take longer than that. However, our discovery means that the process can now begin", he concludes.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
Scientists have discovered an essential protein in cholera-causing bacteria that allows them to adapt to changes in temperature, according to a study published today in eLife.
The protein, BipA, is conserved across bacterial species, which suggests it could hold the key to how other types of bacteria change their biology and growth to survive at suboptimal temperatures.
Vibrio cholerae (V. cholerae) is the bacteria responsible for the severe diarrhoeal disease cholera. As with other species, V. cholerae forms biofilms - communities of bacteria enclosed in a structure made up of sugars and proteins - to protect against predators and stress conditions. V. cholerae forms these biofilms both in their aquatic environment and in the human intestine. There is evidence to suggest that biofilm ...
2021-02-16
An international team of researchers has solved a puzzling phenomenon whereby strangely beautiful, vortex-like structures appear between materials deposited onto engineering components used in multiple settings - from space shuttles to household items and everyday transport vehicles.
The discovery may ultimately improve the efficiency of the "Cold Spray" (CS) deposition process from which these structures are formed - a not-insignificant consideration from a financial perspective, or from a functional one given that some of the materials created by CS are pushed to the limit in outer space.
The discovery is featured on the front cover of international journal, Materials & Design.
Cold Spray (CS) and deposition efficiency (DE)
CS enables the formation of coatings, ...
2021-02-16
Why do genes need to be silenced? The "genes" in question are in fact transposons, selfish genetic elements that seek to self-multiply at the host's expense and that need to be controlled. Julius Brennecke's group at IMBA focuses on lifting the mysteries of a specific type of transposon silencing, namely the piRNA pathway in animal gonads. Understanding this ancient silencing system promises to reveal general mechanistic principles of gene expression and chromatin biology.
Gene silencing: either before they "speak", or right as they attempt to
Heterochromatin, a tightly packed form of DNA, plays an essential role in transposon ...
2021-02-16
Many steep valleys in the European Alps show the relicts of large rockslides, during which several hundreds of million cubic metres of rocks get instable, collapse and impact everything on their path. "For most of these, we still do not know how they are caused, because these rockslides occurred long before the start of written history in the region about 1000 years ago," says Patrick Oswald, PhD student at the Department of Geology of the University of Innsbruck and lead author of the study. "Curiously, many of these ancient rockslides occurred together in clusters, meaning they are found in small regions and have a rather comparable age". This enigmatic pattern has puzzled researchers over the last decades and fuelled some intense debates. Some experts ...
2021-02-16
"Thin films are solid state substances that can be only several atomic layers thick. Usually, their properties are considerably different from the properties of the original substances on the macroscale. The areas of their application keep expanding and include nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, spintronics, electro-, and photocatalysis, as well as such important fields of economics as space technologies and instrument building. Micromodule devices for space crafts and medical technologies are also promising areas in which thin films can be used," said Vyacheslav Fominski, a project supervisor representing MEPhI.
To reduce friction and solve many ...
2021-02-16
Cataracts are the most common eye ailment in humans. However, the exact processes leading to this condition are not fully understood. A team of researchers headed by the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now discovered that the composition of the protein solution plays a decisive role. Their conclusions are contrary to prevailing opinion in the field.
The cells in the lens consist of a highly concentrated protein solution that is normally clear. "When the balance of the proteins in the lens is destroyed, they clump together and the lens becomes cloudy," says Prof. Johannes Buchner of the Chair of Biotechnology at TUM. This results in the condition known as cataracts.
The clouding can have different causes. Because the proteins in the lens are formed ...
2021-02-16
The 'sloshing' of a quantum fluid comprised of light and matter reveals superfluid properties.
An Australian-led team of physicists have successfully created sloshing quantum liquids in a 'bucket' formed by containment lasers.
"These quantum fluids are expected to be as wavy as the oceans, but catching clear pictures of the waves is an experimental challenge," says lead author Dr Eliezer Estrecho.
Led by the Australian National University (ANU), the team serendipitously observed the wavy motion of the quantum fluid in an optically-controlled bucket, gaining new insights of the intriguing superfluid properties of this peculiar, hybrid light-matter system.
Superfluidity ...
2021-02-16
The processes in living beings follow a finely orchestrated choreography down to the molecular level. Rhythmic processes are found everywhere in biology, for example, the 24-hour circadian cycle, a kind of "internal clock", plays an important role in regulating many processes in living cells, including metabolism and cell division mechanisms.
Scientists from Saarbrücken and Kaiserslautern have now taken a closer look at a similar cycle, the somewhat shorter ultradian cycle of baker's yeast. Under the leadership of Bruce Morgan, Professor of Biochemistry at ...
2021-02-16
Combining healthy lifestyle interventions reduces heart disease through beneficial effects on different lipoproteins and associated cholesterols, according to a study published February 9 in eLife.
Having a healthy lifestyle has long been associated with a lower risk of developing heart disease. The new study provides more detailed information on how healthy lifestyles improve cholesterol, and suggests that combining cholesterol-lowering medications and lifestyle interventions may yield the greatest benefits to heart health.
Cholesterol-lowering ...
2021-02-16
The fact that cells are motile and come into contact with each other is one of biology's fundamental principles. During embryonic development, cells must communicate with their neighbors in order to find their proper place in the differentiating organism. Wound healing is another process in which direct intercellular interactions are essential. In this context, motility enables cells to migrate to the location of the lesion and regenerate lost structures. Cancer cells also make use of this property to leave their site of origin in the primary tumor, which allows them to initiate the formation of metastatic tumors in other tissues.
"In recent years, biologists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Breakthrough in the fight against spruce bark beetles