Molecular imaging determines effectiveness of novel metastatic breast cancer treatment
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) Reston, VA--Molecular imaging can successfully predict response to a novel treatment for ER-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients who are resistant to hormonal therapy. According to research published in the February issue of the Journal of Nuclear Medicine, positron emission tomography (PET) imaging using an imaging agent called 18F-fluoroestradiol can help to determine which patients could benefit from treatments that could spare them from unnecessary chemotherapy.
Nearly two-thirds of invasive breast cancers are ER-positive, and endocrine therapy is the mainstay of treatment for these tumors because of its favorable toxicity profile and efficacy. Should cancer progress in these patients, however, salvage endocrine therapy with molecularly targeted agents or chemotherapy can help.
"In some ER-positive breast cancer patients, cancer progression can be a result of a gradual resistance to endocrine therapy," noted Hannah M Linden, MD, FACP, Athena Distinguished Professor and breast medical oncologist at the University of Washington Fred Hutchison Cancer Research Center and Seattle Cancer Care Alliance in Seattle, Washington. "Histone daecetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) have been proposed as a mechanism to reverse endocrine resistance, and clinical studies have shown promising results when combining endocrine therapy with HDACIs to restore endocrine sensitivity."
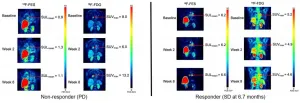
To further explore the efficacy of this combination therapy, researchers designed a study in which 18F-FDG PET imaging with 18F-fluoroestradiol was conducted on patients receiving vorinostat, a potent HDACI, along with an aromatase inhibitor, a type of endocrine therapy. Scans were performed at baseline, week two and week eight of the study. Subjects included ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer patients who had previously responded well to endocrine therapy while on an aromatase inhibitor. Eight of the study participants were treated with vorinostat followed by an aromatase inhibitor, while 15 were treated with both at the same time.
After eight weeks, eight patients had stable disease, and six of the eight patients were stable for more than six months. Higher baseline 18F-fluoroestradiol uptake was associated with longer progression-free survival. 18F-fluoroestradiol uptake did not systematically increase with vorinostat exposure, indicating no change in regional ER estradiol binding, and 18F-FDG uptake did not show a significant decrease, which is expected with tumor regression.
"We test ER expression in a metastatic biopsy once at the beginning of the patient's journey," explained Linden, "and we make decisions all along--when to give chemotherapy, when to use endocrine therapy, whether or not to use targeted agents--based o
INFORMATION:
n that one measurement. Since we know that ER expression can fluctuate, imaging with 18F-fluoroestradiol at various time points could help clinicians predict response to endocrine therapy and select optimal treatment in the future."
18F-fluoroestradiol was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in May 2020.
This study was made available online in June 2020 ahead of final publication in print in February 2021.
The authors of "18F-Fluoroestradiol PET Imaging in a Phase II Trial of Vorinostat to Restore Endocrine Sensitivity in ER+/HER2? Metastatic Breast Cancer" include Lanell M. Peterson, Fengting Yan, Jennifer M. Specht, Julie R. Gralow and Hannah M. Linden, Division of Medical Oncology, University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Seattle, Washington; Brenda F. Kurland, Department of Biostatistics, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; Alena Novakova-Jiresova, Department of Oncology, First Faculty of Medicine, Charles University and Thomayer Hospital, Prague, Czech Republic; Vijayakrishna K. Gadi, Division of Medical Oncology, University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Seattle, Washington, and Clinical Research and Public Health Sciences Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, Washington; Erin K. Schubert and David A. Mankoff, Department of Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Jeanne M. Link and Kenneth A. Krohn, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon; and Janet F. Eary, Cancer Imaging Program, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Maryland.
Funding Organizations: This study was sponsored by NIH P01- CA042045, NCI T32CA009515, NCRR/NIH (REDCap) UL1 RR025014, and P30CA047904 (UPMC Hillman Cancer Center Biostatistics Shared Resource Facility). It was also supported in part by a research grant from Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp (Merck proposal 35637). The opinions expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center for more information about molecular imaging and precision imaging. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Rebecca Maxey at (703) 652-6772 or rmaxey@snmmi.org.
About the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (JNM) is the world's leading nuclear medicine, molecular imaging and theranostics journal, accessed close to 10 million times each year by practitioners around the globe, providing them with the information they need to advance this rapidly expanding field. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.snmjournals.org.
JNM is published by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI), an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging--precision medicine that allows diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes. For more information, visit http://www.snmmi.org. END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-16
Of the nine treatments and preventives for COVID-19 authorized for emergency use by the Food and Drug Administration, three are drugs made from so-called monoclonal antibodies. Such drugs provide patients with ready-made antibodies that neutralize the virus, bypassing the body's slower and sometimes less effective process of making its own antibodies.
But such therapies were developed without detailed information about how antibodies interact with the rest of the immune system during COVID-19. Faced with a new, deadly and fast-spreading disease, drug designers started work ...
2021-02-16
Irvine, Calif., Feb. 16, 2021 -- A radioactive bone cement that's injected into bone to provide support and local irradiation is proving to be a safer alternative to conventional radiation therapy for bone tumors, according to a study led by University of California, Irvine researchers.
The study shows that this brachytherapy cement can be placed into spinal bones to directly irradiate tumors without harming the spinal cord, and the radioactive material will stay localized in the bones, which promises to virtually eliminate side effects.
Lead researcher Joyce Keyak, UCI professor of radiological sciences, presented the results at the 2021 annual meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society, which was held virtually Feb. 12-16.
Cancers ...
2021-02-16
ITHACA, N.Y. - Working with a "star" employee - someone who demonstrates exceptional performance and enjoys broad visibility relative to industry peers - offers both risks and rewards, according to new research from the Cornell University's ILR School.
In collaborations, stars tend to get more than their share of the credit when things go well - and more of the blame when projects don't succeed, according to "Shadows and Shields: Stars Limit Their Collaborators' Exposure to Attributions of Both Credit and Blame," published Dec. 10, 2020, by Personnel Psychology.
"We look at ...
2021-02-16
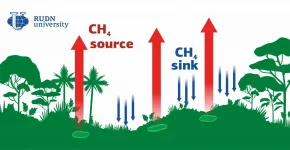
Biologists from RUDN University described the role of tropical rainforests in the production of methane, the second most harmful greenhouse gas after CO2. It turned out that some areas of rainforests not only consumed methane but also emitted it. The results of the study were published in the Forests journal.
Although the share of methane in the atmosphere is relatively small (less than 1%), its contribution to the greenhouse effect is 20 to 30 times bigger than that of the same amount of carbon dioxide. The tropics are one of the main sources of methane. Previously, soil scientists used to focus only on swampy tropical areas, because methane-producing microorganisms live and multiply in the anaerobic conditions of swamps. As for ...
2021-02-16
UCLA RESEARCH ALERT
FINDINGS
A new study led by researchers at the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center helps identify which patients with prostate cancer will benefit most from the use of prostate-specific membrane antigen PET imaging, PSMA PET, a novel imaging technique that recently was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
By studying different variables and risk factors, researchers created a model that can be used in the clinic to identify patients who may have more extensive disease than anticipated and identify patients who are at higher risk of prostate cancer spreading to lymph nodes in the pelvis and beyond. The team found the percent ...
2021-02-16
In today's digital age, the use of "Internet-of-things" (devices embedded with softwares and sensors) has become widespread. These devices include wireless equipment, autonomous machinery, wearable sensors, and security systems. With their intricate structures and properties stems the need to scrutinize them closely to assess their safety and utility and rule out any potential defects. But, at the same time, damage to the device during inspection must be avoided.
Terahertz (THz) imaging, based on radiation with frequencies between 0.1 and 10 THz, is one such non-destructive method that is rapidly gaining popularity owing ...
2021-02-16
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [February 16, 2021] -- New research in the February 2021 issue of JNCCN--Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network examined body mass index (BMI) data for people with HER2-positive early breast cancer, and found a 5% weight loss in patients over two years in was associated with worse outcomes. Weight gain over the same time period did not affect survival rates.
"The finding that weight loss, and not weight gain, was associated with worse outcomes is unexpected," said lead researcher Samuel Martel, MD, Universitè de Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada, who worked with researchers in Belgium, Brazil, Germany, Italy, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom, as well as the ...
2021-02-16
Images provide information - what we can observe with our own eyes enables us to understand. Constantly expanding the field of perception into dimensions that are initially hidden from the naked eye, drives science forward. Today, increasingly powerful microscopes let us see into the cells and tissues of living organisms, into the world of microorganisms as well as into inanimate nature. But even the best microscopes have their limits. "To be able to observe structures and processes down to the nanoscale level and below, we need new methods and technologies," says Dr Silvio Fuchs from the Institute of Optics and Quantum Electronics at the University of Jena. This applies in particular to technological ...
2021-02-16
A recent qualitative study sheds light on how people cope with health and financial challenges, highlighting the important role that communication plays in these coping strategies.
"This is one of the first studies to look at how people respond to the combination of financial uncertainties and health uncertainties," says Lynsey Romo, first author of the study and an associate professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "And it drives home that uncertainty about money and uncertainty about health go hand in hand. Financial limitations created significant health challenges - such as an inability to afford prescription medications. And health problems created significant expenses leading to serious financial challenges.
"The study also highlights that these ...
2021-02-16
A comprehensive database of Estonian soils and a map application has been completed in cooperation with researchers of the University of Tartu and the Estonian University of Life Sciences. The database makes Estonian soil information easily accessible and can be used from local farm-scale to national-level big data statistical analysis and machine-learning models.
"Soil data is possibly the most undervalued and yet complicated type of environmental data there is. The diversity of organic, chemical, living and dead materials that make up a handful of dirt is astounding," said Alexander Kmoch, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Molecular imaging determines effectiveness of novel metastatic breast cancer treatment