New study evaluates the advancement of ecology from a 2D to 3D science
2021-02-17
(Press-News.org) A new study, published in Bioscience, considers the future of ecology, where technological advancement towards a multidimensional science will continue to fundamentally shift the way we view, explore, and conceptualize the natural world.
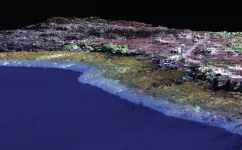
The study, co-led by Greg Asner, Director of the Arizona State University Center for Global Discovery and Conservation Science, in collaboration with Auburn University, the Oxford Seascape Ecology Lab, and other partners, demonstrates how the integration of remotely sensed 3D information holds great potential to provide new ecological insights on land and in the oceans.
Scientific research into 3D digital applications in ecology has grown in the last decade. Landscape and seascape ecologists can now critically frame 3D ecological questions that have been challenging to answer across broad study areas--until recently. Advances in high-resolution remote sensing systems and data processing are allowing us to model the complex surface of the Earth, both above and below water, with greater detail and accuracy than ever before.
Future research applications in the marine environment should focus on addressing the challenges associated with integrating dynamic oceanographic information into maps capable of capturing 3D variability in the environment over time.
"3D-capable data sources have wide-ranging ecological applications and help in estimating carbon sequestration, quantifying habitat structure, mapping ecosystem services, and measuring and modeling consequences of climate change," said Asner.
As landscape and seascape ecology looks toward the future, the study notes a need for a continued progression toward a 3D science that will shift the way ecological patterns and processes are conceptualized. The paper provides key examples of 3D data application in terrestrial and marine environments to illustrate how state-of-the-art advances in ecology have been achieved through novel data fusion, spatial analysis, and visualization.
"This article highlights the unprecedented opportunity for understanding 3D ecological dynamics and human impacts on land and in the oceans, with a view to better inform management decisions," said Lisa Wedding, co-author and Associate Professor at the University of Oxford.
As a result of this 3D approach, natural resource management may support the development of conservation and management plans and shift the way that policymakers evaluate current and future regulations in a dynamic environment.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-17
With every passing day, human technology becomes more refined and we become slightly better equipped to look deeper into biological processes and molecular and cellular structures, thereby gaining greater understanding of mechanisms underlying diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's, and others.
Today, nanoimaging, one such cutting-edge technology, is widely used to structurally characterize subcellular components and cellular molecules such as cholesterol and fatty acids. But it is not without its limitations, as Professor Dae Won Moon of Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Technology (DGIST), Korea, lead scientist in a recent groundbreaking study advancing the field, explains: "Most advanced nanoimaging techniques use accelerated electron or ion beams ...
2021-02-17
Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines to prevent COVID-19 have made headlines around the world recently, but scientists have also been working on mRNA vaccines to treat or prevent other diseases, including some forms of cancer. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have developed a hydrogel that, when injected into mice with melanoma, slowly released RNA nanovaccines that shrank tumors and kept them from metastasizing.
Cancer immunotherapy vaccines work similarly to mRNA vaccines for COVID-19, except they activate the immune system to attack tumors instead of a virus. These vaccines contain mRNA that encodes proteins made specifically by tumor cells. When the mRNA enters antigen-presenting cells, they begin making the tumor protein and displaying it on their surfaces, ...
2021-02-17
Swimming in indoor or outdoor pools is a healthy form of exercise and recreation for many people. However, studies have linked compounds that arise from chlorine disinfection of the pools to respiratory problems, including asthma, in avid swimmers. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have found that using a complementary form of disinfection, known as copper-silver ionization (CSI), can decrease disinfection byproducts and cell toxicity of chlorinated swimming pool water.
Disinfecting swimming pool water is necessary to inactivate harmful pathogens. Although an effective ...
2021-02-17
Washington, February 17, 2021--As higher education institutions worldwide transition to new methods of instruction, including the use of more pre-recorded videos, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, many observers are concerned that student learning is suffering as a result. However, a new comprehensive review of research offers some positive news for college students. The authors found that, in many cases, replacing teaching methods with pre-recorded videos leads to small improvements in learning and that supplementing existing content with videos results in strong learning benefits. The study ...
2021-02-17
Geologists have developed a new theory about the state of Earth billions of years ago after examining the very old rocks formed in the Earth's mantle below the continents.
Assistant Professor Emma Tomlinson from Trinity College Dublin and Queensland University of Technology's Professor Balz Kamber have just published their research in leading international journal, Nature Communications.
The seven continents on Earth today are each built around a stable interior called a craton, and geologists believe that craton stabilisation some 2.5 - 3 billion years ago was critical to the emergence of land masses on Earth.
Little is known about how cratons and their supporting ...
2021-02-17
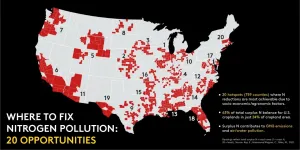
A pioneering study of U.S nitrogen use in agriculture has identified 20 places across the country where farmers, government, and citizens should target nitrogen reduction efforts.
Nitrogen from fertilizer and manure is essential for crop growth, but in high levels can cause a host of problems, including coastal "dead zones", freshwater pollution, poor air quality, biodiversity loss, and greenhouse gas emissions.
The 20 nitrogen "hotspots of opportunity" represent a whopping 63% of the total surplus nitrogen balance in U.S. croplands, but only 24% of U.S. cropland area. In total, ...
2021-02-17
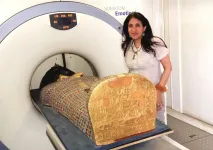
Modern medical technology is helping scholars tell a more nuanced story about the fate of an ancient king whose violent death indirectly led to the reunification of Egypt in the 16th century BC. The research was published in Frontiers in Medicine.
Pharaoh Seqenenre-Taa-II, the Brave, briefly ruled over Southern Egypt during the country's occupation by the Hyksos, a foriegn dynasty that held power across the kingdom for about a century (c. 1650-1550 BCE). In his attempt to oust the Hyskos, Seqenenre-Taa-II was killed. Scholars have debated the exact nature of the pharaoh's death since his mummy was first discovered and studied in the 1880s.
These and subsequent examinations -- including an X-ray study in the 1960s -- noted the dead king had suffered several severe head injuries but no ...
2021-02-17
Although interest in studying prosocial behaviors among U.S. Latinx individuals has increased recently, there is still limited existing research with this population. Evidence shows that prosocial behaviors (actions intended to benefit others) are a marker of healthy social functioning and can both support positive development (such as academic achievement) and mitigate problematic outcomes (such as anxiety and depression). An important question is whether prosocial behavior is fostered by parents in ways that are specific to their cultural groups or through more universal aspects of parenting. A new longitudinal study in the United States examined relations among parenting, culture, and prosocial behaviors in U.S. Mexican youth.
The findings were published in a Child ...
2021-02-17
Children raised in neighborhoods with low socio-economic status are at risk for low academic achievement. A new longitudinal study followed young children from such neighborhoods from birth until age seven to explore whether children's capacity to act kindly or generously towards others (prosocial behavior) - including peers, teachers, and family - is linked to their ability to perform well in school. The study showed that prosocial behavior may mitigate academic risk across early childhood.
The findings were published in a Child Development article written by researchers at Stanford University and the University of Leeds, and the Bradford Institute for Health Research.
"Identifying factors that can help children achieve academic ...
2021-02-17
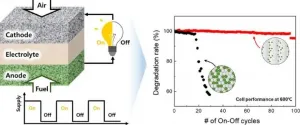
A research team in Korea has developed a ceramic fuel cell that offers both stability and high performance while reducing the required amount of catalyst by a factor of 20. The application range for ceramic fuel cells, which have so far only been used for large-scale power generation due to the difficulties associated with frequent start-ups, can be expected to expand to new fields, such as electric vehicles, robots, and drones.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that a team led by Dr. Ji-Won Son at the Center for Energy Materials Research, through joint research with Professor Seung Min Han at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a new technology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study evaluates the advancement of ecology from a 2D to 3D science