(Press-News.org) Although interest in studying prosocial behaviors among U.S. Latinx individuals has increased recently, there is still limited existing research with this population. Evidence shows that prosocial behaviors (actions intended to benefit others) are a marker of healthy social functioning and can both support positive development (such as academic achievement) and mitigate problematic outcomes (such as anxiety and depression). An important question is whether prosocial behavior is fostered by parents in ways that are specific to their cultural groups or through more universal aspects of parenting. A new longitudinal study in the United States examined relations among parenting, culture, and prosocial behaviors in U.S. Mexican youth.
The findings were published in a Child Development article written by researchers at the University of New Mexico, University of California at Irvine, Arizona State University, and University of Missouri.
The results point to the importance of both cultural practices and aspects of parenting seen across cultural groups, such as acceptance and harshness. They also underscore the importance of both fathers and mothers in supporting prosocial behavior.
Results showed that fathers' but not mothers' acceptance predicted youth's prosocial behaviors (helping others when asked, helping in emergency situations, and comforting others when upset).
Similarly, paternal but not maternal harshness predicted less helping in situations where there was no expectation of benefit from others, but also predicted more helping in front of others (perhaps when acknowledgement or rewards might be anticipated).
In addition, ethnic socialization practices by both mothers and fathers predicted more prosocial behaviors by fostering youth's ethnic identity and familism values (supporting the family emotionally, physically, and financially; having a sense of obligation; and incorporating the family as part of the self).
Both parents' ethnic socialization practices were important to youth sense of ethnic identity in 10th grade, but with maternal behavior showing a greater influence earlier in development (at 5th but not 7th grade) and paternal behavior later (in 7th but not 5th grade).
"Researchers have often emphasized the role of parenting in fostering youth's prosocial development," said Cara Streit assistant professor in the Department of Individual, Family, and Community Education at the University of New Mexico. "Our findings suggest the need for integrative, culturally-sensitive theories that focus on the relations between culture-related mechanisms (such as ethnic socialization and familism), and parenting practices that are more universal (such as acceptance and harshness) to successfully promote positive youth development among U.S. Latinx youth."
Participants were recruited from diverse communities in a metropolitan area of the U.S. Southwest and included 462 Mexican adolescents (48 percent female) and their mothers and fathers. The families participated in four waves of data collection at the 5th, 7th, 10th, and 12th grades and were assessed through the following measures:
Acceptance and harsh parenting (5th and 7th grade): parents were asked to review statements such as "You made [child] feel better after talking over his/her worries with him/her" or "You lost your temper with [child] when s/he didn't help around the house" using a scale ranging from "almost never" or to "almost always or always."
Parental ethnic cultural socialization (5th and 7th grade): using a scale ranging from "almost never" to "a lot of the time (frequently)," parents were asked to review statements such as "How often do you: tell your child to be proud of his/her Mexican background."
Ethnic identity (7th grade): adolescents were asked to review statements such as "You have attended events that have helped you learn more about your Mexican/Mexican American background" using a scale ranging from "not at all true" to "
very true."
Familism values (10th grade): adolescents were asked to review statements such as "A person should share their home with relatives if they need a place to stay" using a scale ranging from "not at all" to "strongly agree."
Prosocial behaviors (12th grade): using a scale ranging from "does not describe me well at all" to "describes me greatly," adolescents reported their prosocial behaviors by reviewing statements such as "You never wait to help others when they ask for it." The study separated out different types of prosocial behavior, such as helping in emergency situations, comforting others when upset, and helping others when there is no expectation of benefit to self.
"Family support programs can best promote positive youth development among U.S. Latinx youth if they include both fathers and mothers and incorporate a focus on ethnic heritage, ethnic identity, and traditional cultural values," said Gustavo Carlo, professor in the School of Education at the University of California, Irvine.
The authors recognize that the study relies entirely on participant self-reports. They also recommend that future studies should consider bidirectional and fully reciprocal study designs to allow for more stringent tests of direction of effects as well as a sample that includes more recent emigrants.
INFORMATION:
Funding was provided by the National Institute of Mental Health and The William T. Grant Foundation Scholars Program
Summarized from Child Development, Relations among Parenting, Culture, and Prosocial Behaviors in U.S. Mexican youth: An Integrative Socialization Approach by Streit, C. (University of New Mexico), Carlo, G. (University of California, Irvine), Knight, G.P. (Arizona State University), White, R.M.B. (Arizona State University), Maiya, S. (University of Missouri). Copyright 2021 The Society for Research in Child Development, Inc. All rights reserved.
Children raised in neighborhoods with low socio-economic status are at risk for low academic achievement. A new longitudinal study followed young children from such neighborhoods from birth until age seven to explore whether children's capacity to act kindly or generously towards others (prosocial behavior) - including peers, teachers, and family - is linked to their ability to perform well in school. The study showed that prosocial behavior may mitigate academic risk across early childhood.
The findings were published in a Child Development article written by researchers at Stanford University and the University of Leeds, and the Bradford Institute for Health Research.
"Identifying factors that can help children achieve academic ...
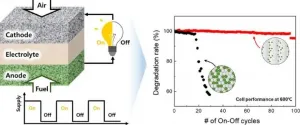
A research team in Korea has developed a ceramic fuel cell that offers both stability and high performance while reducing the required amount of catalyst by a factor of 20. The application range for ceramic fuel cells, which have so far only been used for large-scale power generation due to the difficulties associated with frequent start-ups, can be expected to expand to new fields, such as electric vehicles, robots, and drones.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that a team led by Dr. Ji-Won Son at the Center for Energy Materials Research, through joint research with Professor Seung Min Han at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a new technology ...
Your morning cereal or oatmeal. The bread on your sandwich. The corn chips for your snack, and the cookies for dessert. Not one would be possible with the humblest of ingredients: the seed.
Seeds such as wheat, rice and corn directly provide about 70% of the calories eaten by people every day. And they ultimately provide nearly every morsel of food, either by providing feed for livestock or by being grown into fruits and vegetables. It's no overstatement to say that without seeds, civilization would be impossible.
But seeds need our help. They are under stress from climate change, and under pressure to feed a growing population.
Scores ...
Researchers from University of Calgary, University of Montana, HEC Paris, and University of Cincinnati published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that explores the linguistic aspects of a name that can influence brand perceptions without people even realizing it.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Is Nestlé a Lady? The Feminine Brand Name Advantage" and is authored by Ruth Pogacar, Justin Angle, Tina Lowrey, L. J. Shrum, and Frank Kardes.
What do iconic brands Nike, Coca-Cola, and Disney have in common? They all have linguistically feminine names. In fact, the highest-ranking companies on Interbrand's Global Top Brands list for the past twenty years have, on average, more feminine names than lower-ranked companies. ...
A study recently completed in Europe and North America indicates that the composition of wintering and breeding bird communities changes in line with global warming. However, wintering bird communities are considerably faster at tracking the changing climate compared to breeding communities.
Climate change is driving species' distribution towards the poles and mountaintops, resulting in changes to bird communities. As a considerable share of birds are migratory species, with the distance they travel varying by species, the rate of change in bird communities is different in the breeding season and in the winter. ...
Some of the planet's rarest metals - used in the manufacture of smartphones and other electrical equipment - are increasingly being found in everyday consumer plastics, according to new research.
Scientists from the University of Plymouth and University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign tested a range of new and used products including children's toys, office equipment and cosmetic containers.
Through a number of detailed assessments, they examined levels of rare earth elements (REEs) but also quantities of bromine and antimony, used as flame retardants in electrical equipment and a sign of the presence of recycled electronic plastic.
The results showed one or more REEs were found ...
Lesbian, gay and bisexual (LGB*) people are significantly more likely to have mental health conditions and report alcohol and drug misuse than heterosexual people - according to a new study led by UCL researchers in collaboration with the University of East Anglia and City, University of London.
The findings, published today in Psychological Medicine, come despite apparently more tolerant societal attitudes towards same-sex relationships.
Given this continued disparity, the report's authors are now calling for Government action to ensure equity in health and social care services. They highlight the need for improved awareness among health professionals ...
Each year an estimated 1.2 million Chinese citizens die prematurely due to poor air quality. And public health consequences are particularly dire during extreme air quality events, such as infamous "Airpocalypse" winter haze episodes.
A team of Northwestern University researchers wondered if widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) could help China avoid these deadly events. The answer? It depends.
In a new study, the researchers concluded air quality and public health benefits of EVs -- as well as their ability to reduce carbon emissions -- in China are dependent on the type of transport electrified and the composition of the electric grid.
The study was published today (Feb. 16) in the February 2021 issue of the journal Earth's Future.
"A ...
As most of us learned in school, plants use sunlight to synthesize carbon dioxide (CO2) and water into carbohydrates in a process called photosynthesis. But nature's "factories" don't just provide us with food -- they also generate insights into how ecosystems will react to a changing climate and carbon-filled atmosphere.
Because of their ability to make valuable products from organic compounds like CO2, plants are known as "primary producers." Gross primary production (GPP), which quantifies the rate of CO2 fixation in plants through photosynthesis, is a key metric to track the health and performance of any plant-based ecosystem.
A research team with the U.S. Department of Energy's Center for ...
DAVIS, Calif., Feb 16, 2021 - Researchers publishing in the peer-review journal Frontiers in Pediatrics report that pre-term infants fed Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis (activated B. infantis EVC001) experienced significantly lower level of intestinal inflammation, 62% less diaper rash, and required 62% fewer antibiotics- all of which are critical health indicators in neonatal care.
The study, END ...