3-dimensionally printed nasopharyngeal swab for SARS-CoV-2 testing
2021-02-18
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did:
This is a diagnostic study that examines the accuracy and acceptability of a 3-dimensionally printed swab for identifying SARS-CoV-2.
Authors:
David M. Allen, M.D., of the National University of Singapore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study:
Visit our For The Media website at this link
https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5680)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory:
The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article
This link will be live at the embargo time
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5680?guestAccessKey=dec45c9f-5439-46e3-b477-ea07dd94a834&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=021821
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-18
Over 20.5 million years of life may have been lost due to COVID-19 globally, with an average of 16 years lost per death, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. Years of life lost (YLL) - the difference between an individual's age at death and their life expectancy - due to COVID-19 in heavily affected countries may be two to nine times higher than YLL due to average seasonal influenza.
Héctor Pifarré i Arolas, Mikko Mÿrskyla and colleagues estimated YLL due to COVID-19 using data on over 1,279,866 deaths in 81 countries, as well as life ...
2021-02-18
Viruses are the most numerous biological entities on the planet. Now researchers at the Wellcome Sanger Institute and EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have identified over 140,000 viral species living in the human gut, more than half of which have never been seen before.
The paper, published today (18 February 2021) in Cell, contains an analysis of over 28,000 gut microbiome samples collected in different parts of the world. The number and diversity of the viruses the researchers found was surprisingly high, and the data opens up new research avenues for understanding how viruses living in the gut affect human health.
The human gut is an incredibly biodiverse environment. In addition to bacteria, hundreds of thousands of viruses ...
2021-02-18
The incidence of surgical site infections after an operation is an important quality indicator for hospitals. An overview from six European countries published in 2017 documented increased costs and, in some cases, significantly poorer surgical outcomes due to SSIs. The European Center for Disease Control (ECDC) and authorities in the U.S. have therefore defined criteria for recording and documenting the rate of surgical site infections per procedure. Swissnoso has issued binding guidelines for Switzerland based on these criteria. The study investigated to what extent surgical site ...
2021-02-18
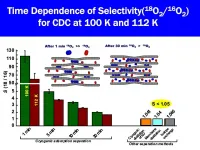
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) plays a major role in the early detection of various types of cancer. A research group led by Specially Appointed Professor Katsumi Kaneko of the Research Initiative for Supra-Materials (RISM), Shinshu University have discovered a method to separate oxygen-18 from oxygen-16, an essential isotope for PET diagnosis, at high speed and high efficiency. The results of this research were recently published online in the journal Nature Communications.
The novel method for the rapid and efficient separation of O-18 from O2-16, which ...
2021-02-18
Covid-19 has not made people any less concerned about climate change - despite the pandemic disrupting and dominating many aspects of their lives, a study suggests.
Over a period of 14 months - including the first three months of the Covid-19 lockdown - neither concern about climate change nor belief in the severity of the problem declined in the UK, the research found.
Researchers compared responses to the pandemic with the financial crisis of 2008 to better understand how worries and priorities can change in a crisis.
In contrast to the economic collapse of 2008, which led to reduced concern with environmental issues, the pandemic has not decreased people's belief in the severity of climate change.
The findings shed light on how a concept called the finite pool ...
2021-02-18
A team of researchers has devised a method using smartphones in order to measure food consumption--an approach that also offers new ways to predict physical well-being.
"We've harnessed the expanding presence of mobile and smartphones around the globe to measure food consumption over time with precision and with the potential to capture seasonal shifts in diet and food consumption patterns," explains Andrew Reid Bell, an assistant professor in New York University's Department of Environmental Studies and an author of the paper, which appears in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Food consumption ...
2021-02-18
Menopause is associated with several physiological changes, including loss of skeletal muscle mass. However, the mechanisms underlying muscle wasting are not clear. A new study conducted in collaboration between the universities of Minnesota (USA) and Jyväskylä (Finland) reveals that estrogen deficiency alters the microRNA signalling in skeletal muscle, which may activate signalling cascades leading to loss of muscle mass.
Menopause leads to an estrogen deficiency that is associated with decreases in skeletal muscle mass and strength. This is likely due to changes in both muscle function and the size of muscle cells commonly referred to as fibers.
"The mechanistic role of estrogen in the loss of muscle mass had not been established. In our study, we focused on signaling cascades ...
2021-02-18
PHILADELPHIA--A significant number of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients in a Penn Medicine-initiated clinical trial continue to be in remission five years after receiving the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy Kymriah™, researchers in Penn's Abramson Cancer Center reported today in the END ...
2021-02-18
Tsukuba, Japan - Scientists at the University of Tsukuba demonstrated the possibility of electrons moving as if they were massless when certain materials called "topological insulators" are irradiated with laser beams. This work may lead to a new class of highly efficient electronic devices and photonic crystals.
Conventional electronic devices rely primarily on silicon crystals. From the point of view of electrons that make up the electrical signals coursing through these materials, the systems are so big as to be practically endless. This causes most of the electronic structures ...
2021-02-18
A unique brain protein measured in the blood could be used to diagnose Alzheimer's disease decades before symptoms develop, according to new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research.
Published in Nature journal Translational Psychiatry, the study is the first to find that people with elevated glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the blood also have increased amyloid beta in the brain, a known indicator of Alzheimer's disease.
GFAP is a protein normally found in the brain, but it is released into the blood when the brain is damaged by early Alzheimer's disease.
Alzheimer's disease affects more than 340,000 Australians and more than 35 million people in the world. Current ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 3-dimensionally printed nasopharyngeal swab for SARS-CoV-2 testing