(Press-News.org) Acres of asphalt parking lots, unshaded roads, dense apartment complexes and neighborhoods with few parks have taken their toll on the poor. As climate change accelerates, low-income districts in the Southwestern United States are 4 to 7 degrees hotter in Fahrenheit -- on average -- than wealthy neighborhoods in the same metro regions, University of California, Davis, researchers have found in a new analysis.
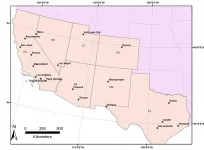
This study provides the most detailed mapping yet of how summer temperatures in 20 urban centers in California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico and Texas affected different neighborhoods between 2018 and 2020. The researchers found even greater heat disparities in California than in other states. The largest disparities showed up in the Riverside and San Bernardino County urban areas.
The unequal impact on Latino communities was especially apparent, the authors said. In Los Angeles on a hot summer day, for example, the most heavily Latino neighborhoods were 6.7 degrees hotter than the least Latino neighborhoods.
"This study provides strong new evidence of climate impact disparities affecting disadvantaged communities, and of the need for proactive steps to reduce those risks," said the study's lead author, John Dialesandro, a doctoral student in geography in the Department of Human Ecology.
The authors said that lower socio-economic groups often have less access to cooled housing, transportation, workplaces and schools. Excess heat can cause heat stroke, exhaustion, and ampli?ed respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
It has long been known that paved surfaces of urban areas absorb and retain solar radiation, increasing urban temperatures. The surrounding suburbs -- with more plant life, parks or proximity to bodies of water -- will be cooler, creating heat islands in the denser areas.
"There is a strong need for state and local governments to take action to mitigate heat disparities by reducing paved surfaces, adding drought-tolerant vegetation, and encouraging building forms that increase shade and reduce temperatures," Dialesandro said.
The study was published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. Co-authors include Noli Brazi, assistant professor, and Stephen Wheeler, professor, each in the Department of Human Ecology, and Yaser Abunnasr, Department of Landscape Design and Ecosystem Management, American University of Beirut.
Researchers looked at U.S. Census data for each area studied, focusing on median household income and percentage of Latinx, Black and Asian populations in each. They also looked at education levels attained. They then assessed radiant and atmospheric temperatures recorded by satellite on the warmest summer days and nights in those cities over a two-year period.
On average, the poorest 10 percent of neighborhoods in an urban region were 4 degrees hotter than the wealthiest 10 percent on both extreme heat days and average summer days, the study said.
California's urban regions had much larger temperature differences between the wealthiest and poorest neighborhoods compared with regions in the rest of the Southwest. The greatest differences were seen in Palm Springs, Bakersfield and Fresno. The smallest differences were seen in Sacramento.
On extreme heat days, the poorest California neighborhoods in each region were nearly 5 degrees hotter, on average, than the wealthiest neighborhoods. This compares to about 3 degrees difference in average temperatures for other Southwestern cities when comparing wealthier and poorer neighborhoods.
The largest differences occurred in the Inland Empire and Palm Springs areas in Riverside and San Bernardino County, where disparities in average temperatures between wealthier and poorer differed by more than 6 degrees.
"Programs to increase vegetation within disadvantaged neighborhoods and reduce or lighten pavements and rooftops could help reduce thermal disparities between neighborhoods of different socioeconomic characteristics," the authors said.
While neighborhoods populated by Blacks in Southern California showed some disparities in temperature -- about 1 to 2 degrees, when compared with white neighborhoods -- this difference was not statistically significant. Black populations throughout Southwestern metropolitan areas are relatively small, authors said, meaning that findings on this demographic dimension were less pronounced.
INFORMATION:
PHILADELPHIA (February 18, 2021) - With stressors mounting daily on the health care system due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a de-prioritization of the childbearing family has been noted. Their care has changed, resulting in mothers forced to go through labor and birth without their partners, parents barred from NICU visitation, and discharge of mothers and newborns early without enough expert lactation care. There is great concern that these changes in childbearing families' care may become permanent - to the detriment of the health of both mother and ...
American values, attitudes and activities have changed dramatically during COVID-19, according to a new study of online behavior.
Researchers from UCLA and Harvard University analyzed how two types of internet activity changed in the U.S. for 10 weeks before and 10 weeks after March 13, 2020 -- the date then-President Donald Trump declared COVID-19 a national emergency. One was Google searches; the other was the phrasing of more than a half-billion words and phrases posted on Twitter, blogs and internet forums.
The study is the lead research article in a special issue of the journal Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies ...
ORLANDO, Feb. 18, 2021 - University of Central Florida researchers are homing in on the cause of a major disease of sea turtles, with some of their latest findings implicating saltwater leeches as a possible factor.
The disease, known as fibropapillomatosis, or FP, causes sea turtles to develop tumors on their bodies, which can limit their mobility and also their health by interfering with their ability to catch and eat prey.
While the cause of FP isn't known, saltwater leeches have been suspected to play a role due to their frequent presence on areas of sea turtles where FP tumors often develop, such as on their eyes, mouths and ...
MALVERN, Pa. -- Doctors and healthcare workers may one day use a machine learning model, called deep learning, to guide their treatment decisions for lung cancer patients, according to a team of Penn State Great Valley researchers.
In a study, the researchers report that they developed a deep learning model that, in certain conditions, was more than 71 percent accurate in predicting survival expectancy of lung cancer patients, significantly better than traditional machine learning models that the team tested. The other machine learning models the team ...
HOUSTON -- The first randomized Phase II clinical trial to report on single and combined neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in stage I-III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) found combination therapy produced a significant clinical benefit, as assessed by major pathologic response (MPR) rate, as well as enhanced tumor immune cell infiltration and immunological memory. Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center published the study results today in Nature Medicine.
The NEOSTAR trial tested combined neoadjuvant therapy of nivolumab plus ipilimumab, as well as neoadjuvant nivolumab monotherapy in patients with operable NSCLC. The trial met its prespecified primary endpoint efficacy threshold in ...
Throughout nature, there are instances of animals aiding one another and living together in mutually beneficial relationships that have helped shape the world's landscapes and biodiversity.
These domesticator-domesticate relationships form when one species provides multigenerational support to another species in exchange for a resource or service that benefits both species. An example of this type of relationship is how early humans domesticated gray wolves. The wolves were attracted to the human encampments, which provided them with protection and resources, and the wolves, in turn, helped the humans increase their hunting proficiency.
One area ...
Richer countries were more likely to see rates of COVID-19 fall faster during the first wave of the pandemic, according to new research published in the journal Frontiers in Public Health.
The study by Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) professors Shahina Pardhan and Nick Drydakis examined economic indicators in 38 European countries, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita, life expectancy, and public spending, and the number of new coronavirus cases per million of the population between 1 April and 31 May 2020, using data from Our World in Data based on the seven-day rolling average of new cases for each country.
A significant negative correlation ...
UCLA RESEARCH ALERT
FINDINGS
UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers have uncovered a potential new way to target pancreatic tumors that express high intratumoral interferon signaling (IFN). The team found that high type I IFN signaling is present in a subset of pancreatic tumors and it triggers a decrease in the level of NAD and NADH in pancreatic cancer cells, which are vital cofactors in critical metabolic processes.
After the researchers delineated the mechanism by which the NAD depletion occurs, they demonstrated that cells with high IFN signaling were more sensitive to NAMPT inhibitors, which inhibit a major pathway ...
NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 18, 2021)--A research team at the Center of Prevention and Evaluation (COPE) at Columbia University Irving Medical Center and the New York State Psychiatric Institute, led by Drs. Gary Brucato and Ragy R. Girgis, found that, contrary to popular belief, serious mental illness was present in only 11% of all mass murderers and in only 8% of mass shooters.
The study--the first published report on mass shootings from the Columbia Mass Murder Database--appeared online Feb. 17th in Psychological Medicine.
The investigators sought to gain much-needed insight into the relationship between serious mental ...
As climate change takes hold across the Americas, some areas will get wetter, and others will get hotter and drier. A new study of the yellow warbler, a widespread migratory songbird, shows that individuals have the same climatic preferences across their migratory range. The work is published Feb. 17 in Ecology Letters.
"What's amazing is that the birds track similar climates despite the fact that they have migrated thousands of miles," said Rachael Bay, assistant professor in the Department of Evolution and Ecology, College of Biological Sciences at the University of California, Davis. "It seems that individual birds may be adapted to particular ...