(Press-News.org) The imposition of various local and national restrictions in England during the summer and autumn of 2020 gradually reduced contacts between people, but these changes were smaller and more varied than during the lockdown in March, according to a study published in the open access journal BMC Medicine.
A team of researchers at London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM), UK combined data from the English participants of the UK CoMix survey and information on local and national restrictions from Gov.uk collected between August 31st and December 7th 2020. CoMix is an online survey asking individuals to record details of their direct contacts in the day prior to the survey.
The authors used the data to compare the number of contacts in different settings, such as work, school or home, reported by individuals before and after the introduction of individual restrictions in England. Restrictions investigated included the Rule of Six (announced 14th September), 10pm closures of pubs and restaurants and encouraging people to work from home (24th of September), entering into tiers 1, 2 or 3 (14th October), as well as entering into national lockdown from any of the tiers in November 2020.
The authors found that the impact of these restrictions on the number of contacts that people reported was mixed, with local restrictions and the Rule of Six associated with modest reductions in contacts, and instructions to work from home associated with larger reductions, but little evidence that the 10pm closing time for bars and restaurants had any appreciable effect.
Specifically, following the introduction of the Rule of Six, 1,314 (33.8%) out of a total of 3,884 participants included in the analysis for this restriction, reported reductions in their non-work and non-educational contacts, while 1,573 (40.5%) participants reported the same number of contacts and 997 (25.7%) reported a higher number of contacts. The average number of contacts was two before and after the introduction of the Rule of Six.
For the 10pm rule, 990 (25.5%) out of 3,887 participants included in the analysis recorded a smaller number of contacts, while 2,054 (52.8%) recorded the same number of contacts and 843 (21.7%) recorded a higher number of contacts. The average number of contacts was zero to one before and after the rule came into effect.
Under local restrictions, participants on average reduced their contacts, reporting an average of 0.69 fewer non-work and non-school contacts compared to before the restrictions. The impact of the tier system was found to be mixed, with Tier 1 and 2 having little impact on the average number of contacts, but Tier 3 reducing contacts.
The subsequent November lockdown appeared to have the largest difference for those entering lockdown form Tier 1, with 750 (35.8%) out of 2,095 participants in Tier 1 reporting that they reduced their contacts by about 1.40 contacts per day, on average. The effect of moving from Tier 2 or Tier 3 to lockdown was less pronounced, with 428 (29.4%) out of 1212 adults in Tier 2 and 85 (26.3%) of 236 adults in Tier 3 reporting that they reduced their contacts.
Dr Christopher Jarvis, Assistant Professor at LSHTM and the corresponding author said: "To put these changes in context, the full national lockdown in March reduced average daily contacts from an estimated 10.8 to 2.8 - a 74% reduction. While, in absolute terms, the changes following more recent restrictions were relatively small, this may indicate that restrictions were applied at a point when individuals had already lowered their contacts, and not that the restrictions did not have an effect."
The authors caution that local restrictions included a combination of several measures and therefore their effect on numbers of contacts is a combination of a range of interventions. Also, the relatively rapid change in policies over the autumn means that some of the effect attributed to one intervention may in fact be associated with one of the others.
Dr Jarvis said: "We have attempted to provide insight into the highly relevant issue of whether different restrictions in response to COVID-19 work and if so, how effective they are. While we only focused on contacts, the impact of the different restrictions will have broader societal implications that need to be considered for policy change."
Further exploration of the effect of restrictions on different age groups, and the potential of regional adherence to the national restrictions could help disentangle specific factors that may influence the relatively small reduction in contacts observed in this study.
INFORMATION:
Media Contact
Anne Korn
Senior Communications Manager
BMC
T: +44 (0)20 3192 2744
E: anne.korn@biomedcentral.com
Notes to editor:
1. Research article:
The impact of local and national restrictions in response to COVID-19 on social contacts in England: a longitudinal natural experiment
Jarvis et al. BMC Medicine 2021
DOI: 10.1186/s12916-021-01924-7
For an embargoed copy of the research article please contact Anne Korn at BMC.
After the embargo lifts, the article will be available here:
https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-021-01924-7
Please name the journal in any story you write. If you are writing for the web, please link to the article. All articles are available free of charge, according to BMC's open access policy.
2. BMC Medicine is the flagship medical journal of the BMC series. An open access, open peer-reviewed general medical journal, BMC Medicine publishes outstanding and influential research in all areas of clinical practice, translational medicine, medical and health advances, public health, global health, policy, and general topics of interest to the biomedical and sociomedical professional communities. We also publish stimulating debates and reviews as well as unique forum articles and concise tutorials.
3. A pioneer of open access publishing, BMC has an evolving portfolio of high quality peer-reviewed journals including broad interest titles such as BMC Biology and BMC Medicine, specialist journals such as Malaria Journal and Microbiome, and the BMC series. At BMC, research is always in progress. We are committed to continual innovation to better support the needs of our communities, ensuring the integrity of the research we publish, and championing the benefits of open research. BMC is part of Springer Nature, giving us greater opportunities to help authors connect and advance discoveries across the world.
Boys who regularly play video games at age 11 are less likely to develop depressive symptoms three years later, finds a new study led by a UCL researcher.
The study, published in Psychological Medicine, also found that girls who spend more time on social media appear to develop more depressive symptoms.
Taken together, the findings demonstrate how different types of screen time can positively or negatively influence young people's mental health, and may also impact boys and girls differently.
Lead author, PhD student Aaron Kandola (UCL Psychiatry) said: "Screens allow us to engage in a wide range of activities. Guidelines and recommendations about screen time should be based on our understanding of how these different ...
Peer-reviewed | Observational | People
Study based on 26.5 million Medicare records finds significant racial and ethnic disparities in uptake of seasonal flu vaccine in people living in the USA aged 65 years and older during the 2015-2016 flu season.
Inequities persist among those who were vaccinated, with racial and ethnic minority groups 26-32% less likely to receive the High Dose Vaccine, which is more effective in older people, compared with white older adults.
Authors note that while these results are from the 2015-2016 flu season, the findings ...
UPTON, NY--Scientists have demonstrated that modifying the topmost layer of atoms on the surface of electrodes can have a remarkable impact on the activity of solar water splitting. As they reported in Nature Energy on Feb. 18, bismuth vanadate electrodes with more bismuth on the surface (relative to vanadium) generate higher amounts of electrical current when they absorb energy from sunlight. This photocurrent drives the chemical reactions that split water into oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen can be stored for later use as a clean fuel. Producing only water when it recombines with oxygen to generate electricity in fuel cells, hydrogen could help us achieve a clean ...
Several treatments for cancer have been devised by science, but unfortunately none of them are completely efficient or foolproof. Novel treatments with minimum side effects are one of the main aims of the ongoing cancer research. All research so far points to several therapy modes, of which immunotherapy, which prepares the body's own immune system to fight cancer, is a promising option. Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are synthetically made proteins that emerged as a promising second-generation immunotherapy. They engage with immune cells and enable them to target cancer in a specific manner.
Conventional use of T cells for this therapy has caused adverse effects in some cases. Moreover, they are ineffective against cold tumors, which are invisible to T cells of the immune system. ...
Mount Sinai researchers have discovered that Polycomb complexes, groups of proteins that maintain gene expression patterns, are essential for proper skin development, according to a paper published in Genes & Development on February 18. This latest discovery could improve development of future stem cell therapies to generate "skin on a dish" to transplant into burn victims and patients with skin-blistering disorders.
Polycomb complexes are groups of proteins that maintain the gene-expression patterns during early development by regulating the structure of DNA and proteins in cells. They play a critical role in the repression of gene expression, or the switching-off of individual genes to help control responses ...
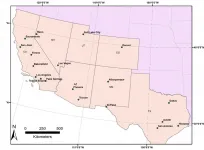
Acres of asphalt parking lots, unshaded roads, dense apartment complexes and neighborhoods with few parks have taken their toll on the poor. As climate change accelerates, low-income districts in the Southwestern United States are 4 to 7 degrees hotter in Fahrenheit -- on average -- than wealthy neighborhoods in the same metro regions, University of California, Davis, researchers have found in a new analysis.
This study provides the most detailed mapping yet of how summer temperatures in 20 urban centers in California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico and Texas affected different neighborhoods between 2018 and 2020. The researchers found even greater heat disparities in California than in other states. The largest disparities showed up in the Riverside and San Bernardino ...
KANSAS CITY, MO--Researchers at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research, in collaboration with colleagues at Stanford University and Technical University of Munich have developed advanced explainable artificial intelligence (AI) in a technical tour de force to decipher regulatory instructions encoded in DNA. In a report published online February 18, 2021, in Nature Genetics, the team found that a neural network trained on high-resolution maps of protein-DNA interactions can uncover subtle DNA sequence patterns throughout the genome and provide a deeper understanding of how these sequences are organized to regulate genes.
Neural networks are powerful AI models that can learn complex patterns from diverse types of data such ...
The media has been rife with stories about democracy in decline: the recent coup in Myanmar, the ascent of strongman Narendra Modi in India, and of course ex-President Trump's attempts to overturn the U.S. presidential election--all of which raise alarms about the current status of democracies worldwide. Such threats to the voices of the people are often attributed to the excesses of individual leaders. But while leadership is certainly important, over the past decade, as established democracies like Venezuela and Turkey fell and others slid toward greater authoritarianism, political scientists and pundits have largely overlooked a key factor: ...
When falling in love, humans often pay attention to looks. Many non-human animals also choose a sexual partner based on appearance. Male birds may sport flashy feathers to attract females, lionesses prefer lions with thicker manes and colorful male guppies with large spots attract the most females. But bats are active in the dark. How do they attract mates? Mariana Muñoz-Romo, a senior Latin American postdoctoral fellow at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) and National Geographic explorer, pioneers research to understand the role of odors in bat mating behavior.
"Aside from their genitalia, most male and female bat species look identical at first glance. However, a detailed examination during mating season reveals odor-producing glands or structures that are only present ...
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are a subytpe of cancers known as sarcomas. GIST is the most common type of sarcoma with approximately 5,000 to 6,000 new patient cases annually in the United States. GIST cannot be cured by drugs alone, and targeted therapies are only modestly effective, with a high rate of drug resistance. In a recent study, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine identified new therapeutic targets that could lead to new treatment options for patients.
The study, published in the February 18, 2021 online edition of Oncogene, found that specific cell-to-cell communication influences GIST biology and is strongly associated with cancer ...