Electron cryo-microscopy sheds light on how bioenergy makers are made in our body
2021-02-19
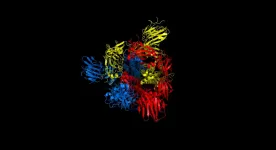
(Press-News.org) Mitochondria are organelles that act as the powerhouses in our body. They use oxygen which we inhale and food we eat to produce energy that supports our life. This molecular activity is performed by bioenergetic nano-factories incorporated in specialized mitochondrial membranes. The nano-factories consist of proteins cooperatively transporting ions and electrons to generate chemical energy. Those have to be constantly maintained, replaced and duplicated during cell division. To address this, mitochondria have their own bioenergy protein-making machine called the mitoribosome. Given its key role, a deregulation of the mitoribosome can lead to medical disorders such as deafness and diseases including cancer development. The first fundamental understanding of how mitoribosomes look was achieved in 2014.
"Seven years ago, our work on the structure of mitoribosome from yeast was termed the Resolution Revolution. The current study represents an additional advance on the original breakthrough. Not only does it reveal how the human mitoribosome is designed at an unprecedented level of detail, but it also explains the molecular mechanism that drives the process of bioenergetics to fuel life" says lead author, Alexey Amunts.
The term Resolution Revolution was coined at Science magazine in relation to the first successful structure determination of the mitoribosome. This represented a methodological innovation in applying electron cryo-microscopy to understand molecular structures. However, that first glimpse into the architecture revealed only a partial picture of a static model. Yet the mitoribosome is a flexible molecular machine that requires the motion of its parts relative to each other to perform work. Therefore, in the current study the team used an advanced infrastructure to collect and process 30 times more data that enabled them to obtain enough information to describe conformational changes during the process of protein synthesis and association with the membrane adaptor.
"Our study reveals that the mitoribosome is much more flexible and active than previously thought. The discovery of intrinsic conformational changes represents a gating mechanism of the mitoribosome without similarity in bacterial and cytosolic systems. Together, the data offer a molecular insight into how bioenergetic proteins are synthesized in human mitochondria," adds Alexey Amunts.
The sequencing of the human mitochondrial genome 40 years ago was a turning point in mitochondrial research, postulating a putative specialized mechanism for the synthesis of the mitochondrial transmembrane proteins. The discovered gating mechanism of the human mitoribosome represents a unique occurrence. Therefore, the structural data offer a crucial long-waited understanding into how bioenergetic proteins are synthesized by the mitoribosome in our body. This knowledge will help to better understand human diseases and be used for development of new therapeutics.
INFORMATION:
More information about Alexey Amunts' research group https://amuntslab.org/
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-19
A POSTECH-KAIST joint research team has successfully developed a technique to reach near-unity efficiency of SHEL by using an artificially-designed metasurface.
Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH's departments of mechanical engineering and chemical engineering, and Ph.D. candidate Minkyung Kim and Dr. Dasol Lee of Department of Mechanical Engineering in collaboration with Professor Bumki Min and Hyukjoon Cho of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have together proposed a technique to enhance the SHEL with near 100% efficiency using an anisotropic metasurface. For this, the joint research team designed a metasurface that transmits most ...
2021-02-19
Photo and map
Robotic laboratories on the bottom of Lake Erie have revealed that the muddy sediments there release nearly as much of the nutrient phosphorus into the surrounding waters as enters the lake's central basin each year from rivers and their tributaries.
Excessive phosphorus, largely from agricultural sources, contributes to the annual summer cyanobacteria bloom that plagues Lake Erie's western basin and the central basin's annual "dead zone," an oxygen-starved region that blankets several thousand square miles of lake bottom and that reduces habitat for fish and other organisms.
The release of phosphorus from Lake Erie sediments during periods of low oxygen--a phenomenon known as self-fertilization or internal loading--has been acknowledged since the 1970s. ...
2021-02-19
We are most familiar with the four conventional phases of matter: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Changes between two phases, known as phase transitions, are marked by abrupt changes in material properties such as density. In recent decades a wide body of physics research has been devoted to discovering new unconventional phases of matter, which typically emerge at ultra-low temperatures or in specially-structured materials. Exotic "topological" phases exhibit properties that can only change in a quantized (step-wise) manner, making them intrinsically robust against impurities and defects.
In addition to topological ...
2021-02-19
Despite our great progress in understanding various cellular mechanisms over the last decades, many of them remain unclear. Such is the case for exosomes, small vesicles released by cells that contain genetic materials called "RNA" and various proteins. The roles of exosomes are believed to be very varied and important, both for normal bodily functions and also in the spreading of diseases like cancer. However, exosomes are so small that studying them is challenging and calls for costly and time-consuming techniques, such as electron microscopy (EM).
To tackle this issue, a team of undergraduate students from ...
2021-02-19
Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in predicting the behaviour of neurons in large networks operating at the mysterious edge of chaos.
New research from the University of Sussex and Kyoto University outlines a new method capable of analysing the masses of data generated by thousands of individual neurons.
The new framework outperforms previous models in predicting and assessing network properties by more accurately estimating a system's fluctuations with greater sensitivity to parameter changes.
As new technologies allow recording of thousands of neurons from living animals, there is a pressing demand for mathematical tools to study the non-equilibrium, complex dynamics of the high-dimensional ...
2021-02-19
Cancer researcher Rita Fior uses zebrafish to study human cancer. Though this may seem like an unlikely match, her work shows great promise with forthcoming applications in personalised medicine.
The basic principle of Fior's approach relies on transplanting human cancer cells into dozens of zebrafish larvae. The fish then serve as "living test tubes" where various treatments, such as different chemotherapy drugs, can be tested to reveal which works best. The assay is rapid, producing an answer within four short days.
Some years ago, when Fior was developing this assay, she noticed something curious. "The majority of human ...
2021-02-19
University of Warwick scientists model movements of nearly 300 protein structures in Covid-19
Scientists can use the simulations to identify potential targets to test with existing drugs, and even check effectiveness with future Covid variants
Simulation of virus spike protein, part of the virus's 'corona', shows promising mechanism that could potentially be blocked
Researchers have publicly released data on all protein structures to aid efforts to find potential drug targets: https://warwick.ac.uk/flex-covid19-data
Researchers have detailed a mechanism in the ...
2021-02-19
Genetic mutations which occur naturally during the earliest stages of an embryo's development can cause the severe birth defect spina bifida, finds a new experimental study in mice led by UCL scientists.
The research, published in Nature Communications, explains for the first time how a 'mosaic mutation' - a mutation which is not inherited from either parent (either via sperm or egg cell) but occurs randomly during cell divisions in the developing embryo - causes spina bifida.
Specifically the scientists, based at UCL Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, found that when a mutation in the gene Vangl2 (which contains information needed to create spinal cord tissue) was present in 16% of developing spinal cord cells of mouse embryos, this ...
2021-02-19
The Biden administration is revising the social cost of carbon (SCC), a decade-old cost-benefit metric used to inform climate policy by placing a monetary value on the impact of climate change. In a newly published analysis in the journal Nature, a team of researchers lists a series of measures the administration should consider in recalculating the SCC.
"President Biden signed a Day One executive order to create an interim SCC within a month and setting up a process to produce a final, updated SCC within a year," explains Gernot Wagner, a climate economist at New York University's Department of Environmental Studies and NYU's Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service and the paper's lead author. "Our work outlines how the ...
2021-02-19
Scientific strides in HIV treatment and prevention have reduced transmissions and HIV-related deaths significantly in the United States in the past two decades. However, despite coordinated national efforts to implement HIV services, the epidemic persists, especially in the South. It also disproportionately impacts marginalized groups, such as Black/African-American and Latinx communities, women, people who use drugs, men who have sex with men, and other sexual and gender minorities. Following the release of the HIV National Strategic Plan and marking two years since the launch of the Ending the HIV Epidemic: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Electron cryo-microscopy sheds light on how bioenergy makers are made in our body