An eco-route for heavy-duty vehicles could reduce fuel consumption
2021-02-19
(Press-News.org) Semi-trucks and other heavy-duty vehicles are responsible for nearly half of road transportation carbon dioxide emissions in Europe, according to the International Council on Clean Transportation. A team of researchers in Italy has proposed a plan to reduce the emissions without compromising priorities such as delivery times. They published their approach in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, a joint publication of the IEEE and the Chinese Association of Automation.
"Driving style, traffic and weather conditions have a significant impact on vehicle fuel consumption. Road freight traffic, in particular, contributes to significant increases in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere," said the author Maria Pia Fanti, professor of system and control engineering and chair of the Laboratory of Automation and Control at the University Polytechnic of Bari in Italy. "Our cloud platform can help the truck driver choose the eco-route that guarantees the minimum fuel consumption."
Dubbed the "Cloud Computing System," the platform is composed of two main components: a data management system that collects, fuses and integrates external data, such as road slope, speed limits and weather conditions; and a cloud optimizer that uses the collected data to determine the best eco-route. Importantly, Fanti noted, the shortest, fastest route is not always the most eco-friendly. A road with more curves requires more gear shifting, while a highway with a higher speed limit may have a significant slope--both of which necessitate more fuel use to compensate.
In simulations, the researchers saw fuel consumption reduced by anywhere from 3.3% to 9.3%, depending on the scenario. The researchers also completed a case study, in which two identical heavy-duty trucks with similarly experienced drivers transported goods from Turkey to Italy. The truck guided by the eco-route used 11% less fuel than the other truck while still delivering the payload within the expected time constraints.
"The next step is to create a collaboration between the vehicle on-board system and the cloud platform to increase the fuel consumption reduction," Fanti said, explaining that the platform is not restricted by special hardware. "The cloud platform can be used not only on innovative trucks equipped with communication devices, but also by 'normal' trucks with drivers equipped with smartphones."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors include Agostino Marcello Mangini, Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, University Polytechnic of Bari; Alfredo Favenza, Links Foundation; and Gianvito Difilippo, AutoLogS.
Fulltext of the paper is available:
http://www.ieee-jas.net/en/article/doi/10.1109/JAS.2020.1003456
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9272699
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica aims to publish high-quality, high-interest, far-reaching research achievements globally, and provide an international forum for the presentation of original ideas and recent results related to all aspects of automation.
The first Impact Factor of IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica is 5.129, ranking among Top 17% (11/63, SCI Q1) in the category of Automation & Control Systems, according to the latest Journal Citation Reports released by Clarivate Analytics in 2020. In addition, its latest CiteScore is 8.3, and has entered Q1 in all three categories it belongs to (Information System, Control and Systems Engineering, Artificial Intelligence) since 2018.
Why publish with us:
Fast and high quality peer review;
Simple and effective online submission system;
Widest possible global dissemination of your research; Indexed in SCIE, EI, IEEE, Scopus, Inspec.
JAS papers can be found at http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/mostRecentIssue.jsp?punumber=6570654 or http://www.ieee-jas.net
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-19
A major pathway for carbon sequestration in the ocean is the growth, aggregation and sinking of phytoplankton - unicellular microalgae like diatoms. Just like plants on land, phytoplankton sequester carbon from atmospheric carbon dioxide. When algae cells aggregate, they sink and take the sequestered carbon with them to the ocean floor. This so called biological carbon pump accounts for about 70 per cent of the annual global carbon export to the deep ocean. Estimated 25 to 40 per cent of carbon dioxide from fossil fuel burning emitted by humans may have been transported by this process from the atmosphere to depths below 1000 meter, where carbon can be stored for millennia. ...
2021-02-19
Early Mars is considered as an environment where life could possibly have existed. There was a time in the geological history of Mars when it could have been very similar to Earth and harbored life as we know it. In opposite to the current Mars conditions, bodies of liquid water, warmer temperature, and higher atmospheric pressure could have existed in Mars' early history. Potential early forms of life on Mars should have been able to use accessible inventories of the red planet: derive energy from inorganic mineral sources and transform CO2 into biomass. Such living entities are rock-eating microorganisms, called "chemolithotrophs", which ...
2021-02-19
The ability to speak is one of the essential characteristics that distinguishes humans from other animals. Many people would probably intuitively equate speech and language. However, cognitive science research on sign languages since the 1960s paints a different picture: Today it is clear, sign languages are fully autonomous languages and have a complex organization on several linguistic levels such as grammar and meaning. Previous studies on the processing of sign language in the human brain had already found some similarities and also differences between sign ...
2021-02-19
The last complete reversal of the Earth's magnetic field, the so-called Laschamps event, took place 42,000 years ago. Radiocarbon analyses of the remains of kauri trees from New Zealand now make it possible for the first time to precisely time and analyse this event and its associated effects, as well as to calibrate geological archives such as sediment and ice cores from this period. Simulations based on this show that the strong reduction of the magnetic field had considerable effects in the Earth's atmosphere. This is shown by an international team led by Chris Turney from the Australian University of New South Wales, with the participation of Norbert Nowaczyk from the German Research Centre for ...
2021-02-19
Researchers at Tampere University have successfully used artificial intelligence to predict nonlinear dynamics that take place when ultrashort light pulses interact with matter. This novel solution can be used for efficient and fast numerical modelling, for example, in imaging, manufacturing and surgery. The findings were published in the prestigious Nature Machine Intelligence journal.
Artificial intelligence can distinguish different types of laser pulse propagation, just as it recognizes subtle differences of expression in facial recognition. The newly found solution can make it simpler to design experiments in fundamental research and will allow algorithms ...
2021-02-19
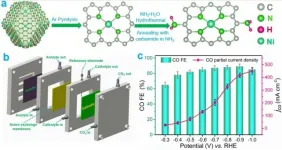
Carbon dioxide (CO2) electrocatalytic reduction driven by renewable electricity can solve the problem of excessive CO2 emissions. Since CO2 is thermodynamically stable, efficient catalysts are needed to reduce the energy consumption in the process.
The single-atom catalysts immobilized on nitrogen-doped carbon supports (M-N/C) have been widely used for CO2 electrocatalytic reduction reaction due to their high atom utilization efficiency.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. LIU Licheng from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed a two-step amination strategy to regulate the electronic structure of M-N/C catalysts (M=Ni, Fe, Zn) and enhance the intrinsic activity of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction.
In ...
2021-02-19
EUGENE, Ore. -- Feb. 19, 2021 -- Friction caused by dry Martian dust particles making contact with each other may produce electrical discharge at the surface and in the planet's atmosphere, according University of Oregon researchers.
However, such sparks are likely to be small and pose little danger to future robotic or human missions to the red planet, they report in a paper published online and scheduled to appear in the March 15 print issue of the journal Icarus.
Viking landers in the 1970s and orbiters since then detected silts, clays, wind-blown bedforms and dust devils on Mars, raising questions about potential electrical activity.
Scientists ...
2021-02-19
China is just one of many countries in the Northern Hemisphere having what researchers are calling an "extremely cold winter," due in part to both the tropical Pacific and the Arctic, according to an analysis of temperatures from Dec. 1, 2020, to mid-January of 2021. A country-specific case study, the investigation potentially has far-reaching implications for predictions and early warnings to protect against harmful impacts, researchers said.
The results were published online, ahead of print, on Feb. 12 in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences.
"We are trying to explain why the countries in the Northern Hemisphere ...
2021-02-19
Nanoparticles used in drug delivery systems, bioimaging, and regenerative medicine migrate from tissues to lymphatic vessels after entering the body, so it is necessary to clarify the interaction between nanoparticles and lymphatic vessels. Although technology to observe the flow of nanoparticles through lymphatic vessels in vivo has been developed, there has been no method to evaluate the flow of nanoparticles in a more detailed and quantitative manner ex vivo. Thus, research was conducted to develop an ex vivo lymphatic vessel lumen perfusion system to determine how nanoparticles move in lymphatic vessels and how they affect the physiological movement of lymphatic vessels.
Nanoparticles introduced into the ...
2021-02-19
A research team led by Prof. QIAN Peiyuan, Head and Chair Professor from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)'s Department of Ocean Science and David von Hansemann Professor of Science, has published their cutting-edge findings of symbiotic mechanisms of a deep-sea vent snail (Gigantopelta aegis) in the scientific journal Nature Communications. They discovered that Gigantopelta snail houses both sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and methane-oxidizing bacteria inside its esophageal gland cells (part of digestive system) as endosymbionts. By decoding the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] An eco-route for heavy-duty vehicles could reduce fuel consumption