(Press-News.org) Even in the world of the smallest particles with their own special rules, things cannot proceed infinitely fast. Physicists at the University of Bonn have now shown what the speed limit is for complex quantum operations. The study also involved scientists from MIT, the universities of Hamburg, Cologne and Padua, and the Jülich Research Center. The results are important for the realization of quantum computers, among other things. They are published in the prestigious journal Physical Review X, and covered by the Physics Magazine of the American Physical Society.
Suppose you observe a waiter (the lockdown is already history) who on New Year's Eve has to serve an entire tray of champagne glasses just a few minutes before midnight. He rushes from guest to guest at top speed. Thanks to his technique, perfected over many years of work, he nevertheless manages not to spill even a single drop of the precious liquid.
A little trick helps him to do this: While the waiter accelerates his steps, he tilts the tray a bit so that the champagne does not spill out of the glasses. Halfway to the table, he tilts it in the opposite direction and slows down. Only when he has come to a complete stop does he hold it upright again.
Atoms are in some ways similar to champagne. They can be described as waves of matter, which behave not like a billiard ball but more like a liquid. Anyone who wants to transport atoms from one place to another as quickly as possible must therefore be as skillful as the waiter on New Year's Eve. "And even then, there is a speed limit that this transport cannot exceed," explains Dr. Andrea Alberti, who led this study at the Institute of Applied Physics of the University of Bonn.
Cesium atom as a champagne substitute
In their study, the researchers experimentally investigated exactly where this limit lies. They used a cesium atom as a champagne substitute and two laser beams perfectly superimposed but directed against each other as a tray. This superposition, called interference by physicists, creates a standing wave of light: a sequence of mountains and valleys that initially do not move. "We loaded the atom into one of these valleys, and then set the standing wave in motion - this displaced the position of the valley itself," says Alberti. "Our goal was to get the atom to the target location in the shortest possible time without it spilling out of the valley, so to speak."
The fact that there is a speed limit in the microcosm was already theoretically demonstrated by two Soviet physicists, Leonid Mandelstam and Igor Tamm more than 60 years ago. They showed that the maximum speed of a quantum process depends on the energy uncertainty, i.e., how "free" the manipulated particle is with respect to its possible energy states: the more energetic freedom it has, the faster it is. In the case of the transport of an atom, for example, the deeper the valley into which the cesium atom is trapped, the more spread the energies of the quantum states in the valley are, and ultimately the faster the atom can be transported. Something similar can be seen in the example of the waiter: If he only fills the glasses half full (to the chagrin of the guests), he runs less risk that the champagne spills over as he accelerates and decelerates. However, the energetic freedom of a particle cannot be increased arbitrarily. "We can't make our valley infinitely deep - it would cost us too much energy," stresses Alberti.
Beam me up, Scotty!
The speed limit of Mandelstam and Tamm is a fundamental limit. However, one can only reach it under certain circumstances, namely in systems with only two quantum states. "In our case, for example, this happens when the point of origin and destination are very close to each other," the physicist explains. "Then the matter waves of the atom at both locations overlap, and the atom could be transported directly to its destination in one go, that is, without any stops in between - almost like the teleportation in the Starship Enterprise of Star Trek."
However, the situation is different when the distance grows to several dozens of matter wave widths as in the Bonn experiment. For these distances, direct teleportation is impossible. Instead, the particle must go through several intermediate states to reach its final destination: The two-level system becomes a multi-level system. The study shows that a lower speed limit applies to such processes than that predicted by the two Soviet physicists: It is determined not only by the energy uncertainty, but also by the number of intermediate states. In this way, the work improves the theoretical understanding of complex quantum processes and their constraints.
The physicists' findings are important not least for quantum computing. The computations that are possible with quantum computers are mostly based on the manipulation of multi-level systems. Quantum states are very fragile, though. They last only a short lapse of time, which physicists call coherence time. It is therefore important to pack as many computational operations as possible into this time. "Our study reveals the maximum number of operations we can perform in the coherence time," Alberti explains. "This makes it possible to make optimal use of it."
INFORMATION:
Funding:
The study was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the Collaborative Research Center SFB/TR 185 OSCAR. Funding was also provided by the Reinhard Frank Foundation in collaboration with the German Technion Society, and by the German Academic Exchange Service.
Publication: Manolo R. Lam, Natalie Peter, Thorsten Groh, Wolfgang Alt, Carsten Robens, Dieter Meschede, Antonio Negretti, Simone Montangero, Tommaso Calarco und Andrea Alberti: Demonstration of Quantum Brachistochrones between Distant States of an Atom; Physical Review X;
https://journals.aps.org/prx/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevX.11.011035
Contact:
Dr. Andrea Alberti
Institut für Angewandte Physik der Universität Bonn
Tel. +49 228 73-3471
E-mail: alberti@iap.uni-bonn.de
Exploratory analyses including 17,178 participants find that higher vaccine efficacy is obtained with a longer interval between the first and second standard dose (81% for 3-month interval vs 55% for up to 6-week interval). In addition, a single dose of vaccine is highly efficacious in the first 3 months (76% efficacy from 22 days after vaccination onwards).
The study also includes updated estimates of overall vaccine efficacy against symptomatic disease for two standard doses, which confirm that the vaccine is effective. There were no hospitalisations or deaths among those receiving ...
The battle against late-stage prostate cancer might have found a potential new strategy to combat this deadly disease. Research led by Baylor College of Medicine reveals in the Journal of Clinical Investigation that the enzyme MAPK4 concertedly activates androgen receptor (AR) and AKT, molecules at the core of two cellular signaling pathways known to promote prostate cancer growth and resistance to standard therapy. Importantly, inhibiting MAPK4 simultaneously inactivated both AR and AKT and stopped cancer growth in animal models. The findings open the possibility that targeting MAPK4 in human prostate cancer might provide a novel therapeutic strategy for this ...
The results, recently published in the journal Communications Biology, have important applications in the field of coevolutionary biology
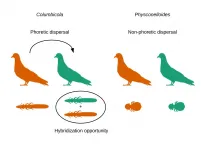
The physical movement of species determines their potential scope to leave their primary ecosystem behind in the quest for new niches in which to survive or reproduce--a decisive factor for the processes that determine their genomic characteristics.
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) and the University of Illinois (UI) have, for the first time, analysed the relationship between this potential for movement in different species of parasites--their dispersal capacity--and their levels of genetic introgression. Introgression--the gradual movement of genes from one species into the gene pool of another--affects the proportion of regions of ...
A new study, in which the Andalusian Earth Sciences Institute (IACT) (CSIC-UGR) participated, has described for the first time a key stage in the beginning of the great glaciations and indicates that it can happen to our planet in the future. The findings were recently published in the scientific journal Nature
The study claims to have found a new connection that could explain the beginning of the ice ages on Earth
Antarctic iceberg melt could hold the key to the activation of a series of mechanisms that cause the Earth to suffer prolonged periods of global ...
The mating process is one of the most important mechanisms for maintaining genetic variation in natural populations. The emergence of sexual reproduction turned out to be the most important evolutionary innovation that facilitated the evolution of eukaryotes. Paramecium is a well-known genus of ciliated protists with a complex system of 'sexes', or mating types. Paramecium reproduces asexually, by binary fission, which is not related to the mating process. During conjugation, Paramecium of compatible mating types exchange haploid nuclei, equivalent to gametes. The nuclei of each organism ...
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has caused tremendous upheaval, leading to more than 2.3 million deaths worldwide and 465,000 in the United States. Understanding the impact of seasonal temperature changes on transmission of the virus is an important factor in reducing the virus's spread in the years to come.
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to a large family of human coronaviruses, most of which are characterized by increased transmission in cooler, less humid months and decreased transmission in warmer, more humid months. With this understanding, researchers at the University of Louisville's Christina ...
HSE University researchers Yuri Markov and Natalia Tyurina discovered that when people visually estimate the size of objects, they are also able to consider their distance from the observer, even if there are many such objects. The observers rely not only on the objects' retinal representation, but also on the surrounding context. The paper was published in the journal Acta Psychologica.
Multiple studies in visual 'ensemble statistics' have proven that humans are able to visually estimate the statistical characteristics of multiple objects in a fast and rather ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. ? Researchers at Mayo Clinic have combined results from a functional test measuring the effect of inherited variants in the BRCA2 breast and ovarian cancer gene with clinical information from women who received genetic testing to determine the clinical importance of many BRCA2 variants of uncertain significance (VUS). The findings were published today in a study in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
"There are 4,565 different VUS in the BRCA2 gene listed in the National Institutes for Health (NIH) Clinical Variant Database," says Fergus Couch, Ph.D., a breast cancer researcher at ...
A gene linked to unusually long lifespans in humans protects brain stem cells from the harmful effects of stress, according to a new study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
Studies of humans who live longer than 100 years have shown that many share an unusual version of a gene called Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3). That discovery led Dr. Jihye Paik, associate professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, and her colleagues to investigate how this gene contributes to brain health during aging.
In 2018, Dr. Paik and her team showed that mice who lack the FOXO3 gene ...
How much personal information can our phone apps gather through location tracking? To answer this question, two researchers - Mirco Musolesi (University of Bologna, Italy) and Benjamin Baron (University College London, UK) - carried out a field study using an app specifically developed for this research. Through the app employed in the study - published in Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies - researchers were able to identify which kind of personal information the app extracted and its privacy sensitivity according to users.
"Users are largely unaware of the privacy implications ...