(Press-News.org) A combination of robust vaccination programmes and strict physical distancing rules could avoid recurring peaks of COVID-19 without the need to rely on stay-at-home restrictions, according to a new study by epidemiologists and demographers from WorldPop at the University of Southampton, in collaboration with The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
This research used anonymised mobile phone geolocation data with epidemiological and coronavirus case data from China to model the potential impact of vaccination and physical distancing on virus transmission. They predicted the effect of different combinations of interventions on low, medium and high density cities in the country.
The impact of physical distancing in containing future resurgences of COVID-19 depends greatly on the intensity of measures, population density, and the availability of vaccines across geographical areas and time. The researchers set out to gain a greater understanding of the relationship between these factors.
The findings are published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour.
The team predicts that in most cities, vaccination programmes and physical distancing combined will be enough to contain virus resurgence without the need to greatly restrict population mobility. Containment in this study was defined as maintaining a low transmission rate, or 'R' below one.
The researchers report cities with medium and high density populations will need both vaccination and distancing to prevent future intense waves of COVID-19, until herd immunity is reached. However, they suggest cities with low populations and effective vaccination could fully interrupt transmission without the need for physical distancing. In all cities, full 'stay-at-home' lockdowns would no longer be necessary.
The team's results also suggest strong physical distancing interventions implemented for short periods of time may be more effective than mild, longer term ones.
The author and spatial epidemiologist, Dr Shengjie Lai, Senior Research Fellow in Geography and Environmental Sciences at the University of Southampton comments: "Our research provides a framework and set of outputs that can be used by policy-makers and public health authorities to identify appropriate levels of intervention to keep COVID-19 outbreaks in check over time. Although our study was based on data from China, our methods and findings are applicable to cities worldwide with similar levels of population density and social contact patterns."
Director of WorldPop, Professor Andy Tatem, added: "Previous studies have assumed that when people reduce mobility, they proportionately reduce their social contacts, but this isn't necessarily the case and as more SARS-CoV-2 vaccines come online, there is an urgent need to understand the relationship between these factors, so we can adjust and tailor interventions and open up sections of society in a safer way."
The researchers recognise some limitations to their study, for example, the absence of data on the contribution of handwashing and face masks and challenges of vaccine supply, but emphasise that their approach can be quickly adapted to provide near real-time data to address emerging, time critical needs.
INFORMATION:
Notes to Editors
1) The paper 'Integrated vaccination and physical distancing interventions to prevent future COVID?19 waves in Chinese cities,' is published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01063-2).
2) Mobility and social contact index data used in the study were aggregated and provided by Tencent, the largest social media company in China - covering 70 percent of the population in the mainland of the country. Epidemiological and coronavirus case data was sourced from records covering the Chinese city of Wuhan.
3) The University of Southampton drives original thinking, turns knowledge into action and impact, and creates solutions to the world's challenges. We are among the top 100 institutions globally (QS World University Rankings 2021). Our academics are leaders in their fields, forging links with high-profile international businesses and organisations, and inspiring a 22,000-strong community of exceptional students, from over 135 countries worldwide. Through our high-quality education, the University helps students on a journey of discovery to realise their potential and join our global network of over 200,000 alumni.
http://www.southampton.ac.uk
4) For more information on COVID-19 work being undertaken by WorldPop at the University of Southampton visit:
https://www.worldpop.org/covid19
5) For more about the The Chinese University of Hong Kong visit:
https://www.cuhk.edu.hk/english/index.html
For further information and interviews contact:
Charles Elder,
Media Relations, University of Southampton.
Tel: 07879 431666
Email: c.elder@southampton.ac.uk
http://www.southampton.ac.uk/news/contact-press-team.page
Follow us on twitter: http://twitter.com/unisouthampton
Like us on Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/unisouthampton
A new study published in The British Medical Journal by researchers including SFU health sciences professor Scott Lear found consuming a high number of refined grains, such as croissants and white bread, is associated with a higher risk of major cardiovascular disease, stroke and death.
The Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study has been examining diets from diverse populations in low-, middle- and high-income countries around the world. Over 16 years of analysis of 137,130 participants in 21 countries, including Canada, the researchers found the intake of refined grains and added sugars have greatly increased over the years.
Grains were categorized into three groups: refined grains, whole ...
Scientists have discovered the first evidence of protein folding driven by liquid-liquid phase separation, a phenomenon in which fluids form into microscopic droplets and separate inside cells -- like drops of oil in water.
In a study published in the journal Chemical Science, researchers at the University of Notre Dame found that elevated concentrations of proteins within the droplets triggered a folding event, increasing the potential for protein aggregation -- or misfolding -- which has been linked to neurological diseases including Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
"These particular proteins are intrinsically disordered -- they have no well-defined ...
In African Americans, the genetic risk landscape for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is very different from that of people with European ancestry, according to results of the first whole-genome study of IBD in African Americans. The authors say that future clinical research on IBD needs to take ancestry into account.
Findings of the multi-center study, which analyzed the whole genomes of more than 1,700 affected individuals with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis and more than 1,600 controls, were published on February 17 in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
As ...
In a new Review, P.J. Klasse and colleagues present an extensive overview of the immunogenicity profiles of several leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates, including several developed under the auspices of the U.S. Government's "Operation Warp Speed" program, as well as leading candidates from China and Russia. Since the paper was submitted, two of these vaccines - from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna - have been authorized for use by the FDA. The authors review data from evaluations in non-human primates as well as human clinical trials, summarizing what is known about antibody and T cell immunogenicity for roughly a dozen leading candidates. Noting the variability in ...
Even in the world of the smallest particles with their own special rules, things cannot proceed infinitely fast. Physicists at the University of Bonn have now shown what the speed limit is for complex quantum operations. The study also involved scientists from MIT, the universities of Hamburg, Cologne and Padua, and the Jülich Research Center. The results are important for the realization of quantum computers, among other things. They are published in the prestigious journal Physical Review X, and covered by the Physics Magazine of the American Physical Society.
Suppose ...
Exploratory analyses including 17,178 participants find that higher vaccine efficacy is obtained with a longer interval between the first and second standard dose (81% for 3-month interval vs 55% for up to 6-week interval). In addition, a single dose of vaccine is highly efficacious in the first 3 months (76% efficacy from 22 days after vaccination onwards).
The study also includes updated estimates of overall vaccine efficacy against symptomatic disease for two standard doses, which confirm that the vaccine is effective. There were no hospitalisations or deaths among those receiving ...
The battle against late-stage prostate cancer might have found a potential new strategy to combat this deadly disease. Research led by Baylor College of Medicine reveals in the Journal of Clinical Investigation that the enzyme MAPK4 concertedly activates androgen receptor (AR) and AKT, molecules at the core of two cellular signaling pathways known to promote prostate cancer growth and resistance to standard therapy. Importantly, inhibiting MAPK4 simultaneously inactivated both AR and AKT and stopped cancer growth in animal models. The findings open the possibility that targeting MAPK4 in human prostate cancer might provide a novel therapeutic strategy for this ...
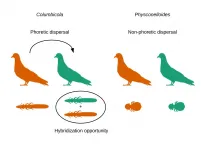
The results, recently published in the journal Communications Biology, have important applications in the field of coevolutionary biology
The physical movement of species determines their potential scope to leave their primary ecosystem behind in the quest for new niches in which to survive or reproduce--a decisive factor for the processes that determine their genomic characteristics.
Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) and the University of Illinois (UI) have, for the first time, analysed the relationship between this potential for movement in different species of parasites--their dispersal capacity--and their levels of genetic introgression. Introgression--the gradual movement of genes from one species into the gene pool of another--affects the proportion of regions of ...
A new study, in which the Andalusian Earth Sciences Institute (IACT) (CSIC-UGR) participated, has described for the first time a key stage in the beginning of the great glaciations and indicates that it can happen to our planet in the future. The findings were recently published in the scientific journal Nature
The study claims to have found a new connection that could explain the beginning of the ice ages on Earth
Antarctic iceberg melt could hold the key to the activation of a series of mechanisms that cause the Earth to suffer prolonged periods of global ...
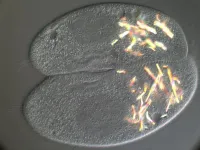
The mating process is one of the most important mechanisms for maintaining genetic variation in natural populations. The emergence of sexual reproduction turned out to be the most important evolutionary innovation that facilitated the evolution of eukaryotes. Paramecium is a well-known genus of ciliated protists with a complex system of 'sexes', or mating types. Paramecium reproduces asexually, by binary fission, which is not related to the mating process. During conjugation, Paramecium of compatible mating types exchange haploid nuclei, equivalent to gametes. The nuclei of each organism ...