Direct cloning method CAPTUREs novel microbial natural products
2021-02-19
(Press-News.org) Microorganisms possess natural product biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) that may harbor unique bioactivities for use in drug development and agricultural applications. However, many uncharacterized microbial BGCs remain inaccessible. Researchers at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign previously demonstrated a technique using transcription factor decoys to activate large, silent BGCs in bacteria to aid in natural product discovery.
Now, they have developed a direct cloning method that aims to accelerate large-scale discovery of novel natural products. Their findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications.
Named Cas12a assisted precise targeted cloning using in vivo Cre-lox recombination (CAPTURE), the method allows for direct cloning of large genomic fragments, including those with high-GC content or sequence repeats. Where existing direct cloning methods fail to effectively clone natural product BGCs of this nature, CAPTURE excels.
"Using CAPTURE, microbial natural product BGCs can be directly cloned and heterologously expressed at an unprecedented rate," said study leader and Steven L. Miller Chair professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering Huimin Zhao, also a member of the Carl R. Woese Institute for Genomic Biology at Illinois. "As a result, CAPTURE allows large-scale cloning of natural product BGCs from various organisms, which can lead to discovery of numerous novel natural products."
Researchers first characterized the efficiency and robustness of CAPTURE by cloning 47 natural product BGCs from both Actinomycetes and Bacilli. After demonstrating nearly 100% efficiency of CAPTURE, 43 uncharacterized natural product BGCs from 14 Streptomyces and three Bacillus species were cloned and heterologously expressed by researchers. The produced compounds were purified and determined as 15 novel natural products, including six unprecedented compounds designated as bipentaromycins. Four of the bipentaromycins exhibited antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, and Bacillus anthracis.
"Addressing the current antimicrobial resistance crisis requires discovery of novel molecules capable of treating drug-resistant infections," said Zhao. "Discovery of bipentaromycins not only demonstrates the possibility of discovering novel antimicrobials, but it also provides an example on how this strategy can be applied for discovery of unique bioactive compounds for use in drug development and agricultural applications."
The researchers plan next to characterize these compounds for other bioactivities such as anticancer, antiparasitic and anticancer properties. Preliminary results are already showing anticancer properties for some of the compounds.
"Due to its exceptional robustness and efficiency, CAPTURE will likely become the method of choice for direct cloning of large DNA molecules such as natural product BGCs from genomic or metagenomic DNA for various basic and applied biological applications," said Zhao.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-19
DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke researchers have been studying something that happens too slowly for our eyes to see. A team in biologist Philip Benfey's lab wanted to see how plant roots burrow into the soil. So they set up a camera on rice seeds sprouting in clear gel, taking a new picture every 15 minutes for several days after germination.
When they played their footage back at 15 frames per second, compressing 100 hours of growth into less than a minute, they saw that rice roots use a trick to gain their first foothold in the soil: their growing tips make ...
2021-02-19
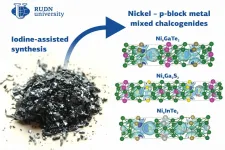
A chemist from RUDN University, working with a group of colleagues, synthesized three new chalcogenides (compounds that contain metals and elements from group 16 of the periodic table). The team suggested an unusual approach to synthesis that was based on iodine. An article about the work was published in the Dalton Transactions journal.
Chalcogens are elements of group 16 of the periodic table that include oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium, polonium, and livermorium--an artificial radioactive element. Chalcogenides are compounds of chalcogens with metals that are used as photosensitive ...
2021-02-19
Several University of Illinois Chicago faculty members have addressed the issue of how to ethically conduct research with Black populations.
In their paper "Ethics of Research at the Intersection of COVID-19 and Black Lives Matter: A Call to Action," authors Natasha Crooks, an assistant professor, Phoenix Matthews, a professor, both of the UIC College of Nursing, and Geri Donenberg, director of the Center for Dissemination and Implementation Science at the UIC College of Medicine, highlight the historical issues that impact research involving Black populations. They also provide recommendations for researchers to ethically engage Black populations in research. ...
2021-02-19
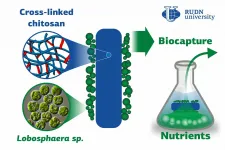
Biotechnologists from RUDN University in collaboration with Lomonosov MSU and Kurchatov institute made an important contribution to the technology of phosphate and nitrate biocapture from wastewater using Lobosphaera algae fixed on the filters.The biomass obtained in the course of this process can be used as a fertilizer. The results of the study were published in the Journal of Water Process Engineering.
Phosphates and nitrates get to the wastewater together with industrial and household waste, especially detergents. Both substances are parts of phosphorus and nitrogen chemical cycles. However, these cycles are disturbed by human activity, as the growing amounts of phosphates and nitrates cannot be processed by water ecosystems. As a result, these substances turn from useful nutrients ...
2021-02-19
New Orleans, LA - A retrospective study conducted by LSU Health New Orleans reports that contrary to previous research, most patients who drop out of peritoneal dialysis may do so for psychosocial reasons. The findings are published in The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, available here. The paper inspired a companion editorial, available here.
The research team evaluated the reasons that 27 of the 83 patients enrolled in the peritoneal dialysis program withdrew between 2016 and 2018. Twenty-four or 86% were African American. They found that psychosocial factors, including mental health illness such as anxiety and depression, loss of support networks, or inability to tolerate ...
2021-02-19
Since Charles Darwin's day, the abundance of life on coral reefs has been puzzling, given that most oceanic surface waters in the tropics are low in nutrients and unproductive.
But now research, led by Newcastle University and published in in the journal Science Advances, has confirmed that the food web of a coral reef in the Maldives relies heavily on what comes in from the open ocean.
The team found that these offshore resources contribute to more than 70% of reef predator diets, the rest being derived from reef associated sources.
Led by Dr Christina Skinner, now based at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, the researchers included collaborators from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (USA), Banyan Tree Marine ...
2021-02-19
Cooperative operations between a solar observation satellite and a sounding-rocket telescope have measured the magnetic field strength in the photosphere and chromosphere above an active solar plage region. This is the first time that the magnetic field in the chromosphere has been charted all the way up to its top. This finding brings us closer to understanding how energy is transferred between layers of the Sun.
Despite being the brightest object in the sky, the Sun still holds many mysteries for astronomers. It is generally believed that magnetic fields play an important role in heating the solar corona, but the details of the process are still unclear. To solve this mystery it is important to understand the magnetic field in the chromosphere, which is sandwiched ...
2021-02-19
Northwestern University synthetic biologist Joshua Leonard used to build devices when he was a child using electronic kits. Now he and his team have developed a design-driven process that uses parts from a very different kind of toolkit to build complex genetic circuits for cellular engineering.
One of the most exciting frontiers in medicine is the use of living cells as therapies. Using this approach to treat cancer, for example, many patients have been cured of previously untreatable disease. These advances employ the approaches of synthetic biology, a growing ...
2021-02-19
Every day space telescopes provide spectacular images of the solar activity. However, their instruments are blind to its main driver: the magnetic field in the outer layers of the solar atmosphere, where the explosive events that occasionally affect the Earth occur. The extraordinary observations of the polarization of the Sun's ultraviolet light achieved by the CLASP2 mission have made it possible to map the magnetic field throughout the entire solar atmosphere, from the photosphere until the base of the extremely hot corona. This investigation, published today in the journal Science Advances, has been carried out by the international team responsible for this suborbital experiment, which includes several scientists of the POLMAG group of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias ...
2021-02-19
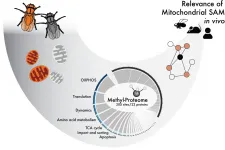
Disorders of the cells' energy supply can cause a number of serious diseases, but also seem to be connected to ageing. More research is needed on mitochondrial function to find future treatments. A new study involving researchers at Karolinska Institutet shows how an important molecule inside the mitochondria affects their function in mice and fruit flies. The study, which is published in Science Advances, adds valuable knowledge on formerly relatively unexplored protein modifications.
In each cell of the body is an organ called the mitochondrion, which converts nutrients in our food to energy. Mitochondria are an essential part of the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Direct cloning method CAPTUREs novel microbial natural products