(Press-News.org) Northwestern University synthetic biologist Joshua Leonard used to build devices when he was a child using electronic kits. Now he and his team have developed a design-driven process that uses parts from a very different kind of toolkit to build complex genetic circuits for cellular engineering.
One of the most exciting frontiers in medicine is the use of living cells as therapies. Using this approach to treat cancer, for example, many patients have been cured of previously untreatable disease. These advances employ the approaches of synthetic biology, a growing field that blends tools and concepts from biology and engineering.
The new Northwestern technology uses computational modeling to more efficiently identify useful genetic designs before building them in the lab. Faced with myriad possibilities, modeling points researchers to designs that offer real opportunity.
"To engineer a cell, we first encode a desired biological function in a piece of DNA, and that DNA program is then delivered to a human cell to guide its execution of the desired function, such as activating a gene only in response to certain signals in the cell's environment," Leonard said. He led a team of researchers from Northwestern in collaboration with Neda Bagheri from the University of Washington for this study.
Leonard is an associate professor of chemical and biological engineering in the McCormick School of Engineering and a leading faculty member within Northwestern's Center for Synthetic Biology. His lab is focused on using this kind of programming capability to build therapies such as engineered cells that activate the immune system, to treat cancer.
Bagheri is an associate professor of biology and chemical engineering and a Washington Research Foundation Investigator at the University of Washington Seattle. Her lab uses computational models to better understand -- and subsequently control -- cell decisions. Leonard and Bagheri co-advised Joseph Muldoon, a recent doctoral student and the paper's first author.
"Model-guided design has been explored in cell types such as bacteria and yeast, but this approach is relatively new in mammalian cells," Muldoon said.
The study, in which dozens of genetic circuits were designed and tested, will be published Feb. 19 in the journal Science Advances. Like other synthetic biology technologies, a key feature of this approach is that it is intended to be readily adopted by other bioengineering groups.
To date, it remains difficult and time-consuming to develop genetic programs when relying upon trial and error. It is also challenging to implement biological functions beyond relatively simple ones. The research team used a "toolkit" of genetic parts invented in Leonard's lab and paired these parts with computational tools for simulating many potential genetic programs before conducting experiments. They found that a wide variety of genetic programs, each of which carries out a desired and useful function in a human cell, can be constructed such that each program works as predicted. Not only that, but the designs worked the first time.
"In my experience, nothing works like that in science; nothing works the first time. We usually spend a lot of time debugging and refining any new genetic design before it works as desired," Leonard said. "If each design works as expected, we are no longer limited to building by trial and error. Instead, we can spend our time evaluating ideas that might be useful in order to hone in on the really great ideas."
"Robust representative models can have disruptive scientific and translational impact," Bagheri added. "This development is just the tip of the iceberg."
The genetic circuits developed and implemented in this study are also more complex than the previous state of the art. This advance creates the opportunity to engineer cells to perform more sophisticated functions and to make therapies safer and more effective.
"With this new capability, we have taken a big step in being able to truly engineer biology," Leonard said.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (award number 1R01EB026510), the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (award number T32GM008152) and the National Cancer Institute (award number F30CA203325).
The title of the paper is "Model-guided design of mammalian genetic programs."
Every day space telescopes provide spectacular images of the solar activity. However, their instruments are blind to its main driver: the magnetic field in the outer layers of the solar atmosphere, where the explosive events that occasionally affect the Earth occur. The extraordinary observations of the polarization of the Sun's ultraviolet light achieved by the CLASP2 mission have made it possible to map the magnetic field throughout the entire solar atmosphere, from the photosphere until the base of the extremely hot corona. This investigation, published today in the journal Science Advances, has been carried out by the international team responsible for this suborbital experiment, which includes several scientists of the POLMAG group of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias ...
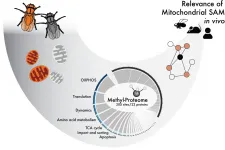
Disorders of the cells' energy supply can cause a number of serious diseases, but also seem to be connected to ageing. More research is needed on mitochondrial function to find future treatments. A new study involving researchers at Karolinska Institutet shows how an important molecule inside the mitochondria affects their function in mice and fruit flies. The study, which is published in Science Advances, adds valuable knowledge on formerly relatively unexplored protein modifications.
In each cell of the body is an organ called the mitochondrion, which converts nutrients in our food to energy. Mitochondria are an essential part of the ...
A combination of robust vaccination programmes and strict physical distancing rules could avoid recurring peaks of COVID-19 without the need to rely on stay-at-home restrictions, according to a new study by epidemiologists and demographers from WorldPop at the University of Southampton, in collaboration with The Chinese University of Hong Kong.
This research used anonymised mobile phone geolocation data with epidemiological and coronavirus case data from China to model the potential impact of vaccination and physical distancing on virus transmission. They predicted the effect of different combinations of interventions on low, medium and high density cities in the country.
The ...
A new study published in The British Medical Journal by researchers including SFU health sciences professor Scott Lear found consuming a high number of refined grains, such as croissants and white bread, is associated with a higher risk of major cardiovascular disease, stroke and death.
The Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study has been examining diets from diverse populations in low-, middle- and high-income countries around the world. Over 16 years of analysis of 137,130 participants in 21 countries, including Canada, the researchers found the intake of refined grains and added sugars have greatly increased over the years.
Grains were categorized into three groups: refined grains, whole ...
Scientists have discovered the first evidence of protein folding driven by liquid-liquid phase separation, a phenomenon in which fluids form into microscopic droplets and separate inside cells -- like drops of oil in water.
In a study published in the journal Chemical Science, researchers at the University of Notre Dame found that elevated concentrations of proteins within the droplets triggered a folding event, increasing the potential for protein aggregation -- or misfolding -- which has been linked to neurological diseases including Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
"These particular proteins are intrinsically disordered -- they have no well-defined ...
In African Americans, the genetic risk landscape for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is very different from that of people with European ancestry, according to results of the first whole-genome study of IBD in African Americans. The authors say that future clinical research on IBD needs to take ancestry into account.
Findings of the multi-center study, which analyzed the whole genomes of more than 1,700 affected individuals with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis and more than 1,600 controls, were published on February 17 in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
As ...
In a new Review, P.J. Klasse and colleagues present an extensive overview of the immunogenicity profiles of several leading SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates, including several developed under the auspices of the U.S. Government's "Operation Warp Speed" program, as well as leading candidates from China and Russia. Since the paper was submitted, two of these vaccines - from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna - have been authorized for use by the FDA. The authors review data from evaluations in non-human primates as well as human clinical trials, summarizing what is known about antibody and T cell immunogenicity for roughly a dozen leading candidates. Noting the variability in ...
Even in the world of the smallest particles with their own special rules, things cannot proceed infinitely fast. Physicists at the University of Bonn have now shown what the speed limit is for complex quantum operations. The study also involved scientists from MIT, the universities of Hamburg, Cologne and Padua, and the Jülich Research Center. The results are important for the realization of quantum computers, among other things. They are published in the prestigious journal Physical Review X, and covered by the Physics Magazine of the American Physical Society.
Suppose ...
Exploratory analyses including 17,178 participants find that higher vaccine efficacy is obtained with a longer interval between the first and second standard dose (81% for 3-month interval vs 55% for up to 6-week interval). In addition, a single dose of vaccine is highly efficacious in the first 3 months (76% efficacy from 22 days after vaccination onwards).
The study also includes updated estimates of overall vaccine efficacy against symptomatic disease for two standard doses, which confirm that the vaccine is effective. There were no hospitalisations or deaths among those receiving ...
The battle against late-stage prostate cancer might have found a potential new strategy to combat this deadly disease. Research led by Baylor College of Medicine reveals in the Journal of Clinical Investigation that the enzyme MAPK4 concertedly activates androgen receptor (AR) and AKT, molecules at the core of two cellular signaling pathways known to promote prostate cancer growth and resistance to standard therapy. Importantly, inhibiting MAPK4 simultaneously inactivated both AR and AKT and stopped cancer growth in animal models. The findings open the possibility that targeting MAPK4 in human prostate cancer might provide a novel therapeutic strategy for this ...